Abstract
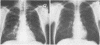
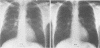
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia is a protozoal infection that, in the setting of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), is often lethal and unresponsive to conventional therapy with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or pentamidine. In the present study, we have prospectively assessed the use of α-difluoromethylornithine (DFMO), an inhibitor of polyamine biosynthesis, in the treatment of P carinii pneumonia in patients with AIDS who were intolerant or unresponsive to conventional drugs. Improvement by both clinical and objective criteria was observed in six patients who completed six to eight weeks of DFMO therapy. Expansion of these early trials of DFMO is warranted.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeloff M. D., Slavik M., Luk G. D., Griffin C. A., Hermann J., Blanc O., Sjoerdsma A., Baylin S. B. Phase I trial and pharmacokinetic studies of alpha-difluoromethylornithine--an inhibitor of polyamine biosynthesis. J Clin Oncol. 1984 Feb;2(2):124–130. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1984.2.2.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammann A. J., Abrams D., Conant M., Chudwin D., Cowan M., Volberding P., Lewis B., Casavant C. Acquired immune dysfunction in homosexual men: immunologic profiles. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Jun;27(3):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacchi C. J., Nathan H. C., Hutner S. H., McCann P. P., Sjoerdsma A. Polyamine metabolism: a potential therapeutic target in trypanosomes. Science. 1980 Oct 17;210(4467):332–334. doi: 10.1126/science.6775372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney W. P., Rubin R. H., Hoffman R. A., Hansen W. P., Healey K., Hirsch M. S. Analysis of T lymphocyte subsets in cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2114–2116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T. Opportunistic infections and Kaposi's sarcoma in homosexual men. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1465–1467. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. The syndrome of Kaposi's sarcoma and opportunistic infections: an epidemiologically restricted disorder of immunoregulation. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 1):777–779. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillet J. M., Boné G., Herman F. Inhibitory action of alpha-difluoromethylornithine on rodent malaria (Plasmodium berghei). Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(6):776–777. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Reiner D. S., McCann P. P. Inhibition of growth of Giardia lamblia by difluoromethylornithine, a specific inhibitor of polyamine biosynthesis. J Protozool. 1984 Feb;31(1):161–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb04308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson W. L., Bradford M. M., Chapman W. L., Jr, Waits V. B., McCann P. P., Sjoerdsma A. alpha-Difluoromethylornithine: a promising lead for preventive chemotherapy for coccidiosis. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Sep;43(9):1651–1653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., McNabb P. C., Makres T. D., Feldman S. Efficacy of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in the prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 22;297(25):1381–1383. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712222972505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H. S., Abrams D. I., Ammann A. J., Lewis B. J., Golden J. A. Complications of co-trimoxazole in treatment of AIDS-associated Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in homosexual men. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1109–1111. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90627-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby H. B., Kenamore B., Guckian J. C. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia treated with pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Oct;75(4):505–509. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-4-505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau W. K., Young L. S. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in adults. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 23;295(13):716–718. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609232951308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M., McLeod R., Young Q., Abrahams C., Chambliss M., Walzer P., Kabins S. A. Pneumocystis pneumonia: importance of gallium scan for early diagnosis and description of a new immunoperoxidase technique to demonstrate Pneumocystis carinii. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jul;128(1):182–185. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.1.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman R., Ryo U. Y., Bekerman C., Pinsky S. M. Ga-67 scan of a homosexual man with pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Clin Nucl Med. 1982 Oct;7(10):480–481. doi: 10.1097/00003072-198210000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann P. P., Bacchi C. J., Clarkson A. B., Jr, Seed J. R., Nathan H. C., Amole B. O., Hutner S. H., Sjoerdsma A. Further studies on difluoromethylornithine in African trypanosomes. Med Biol. 1981 Dec;59(5-6):434–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuyasu R., Groopman J., Volberding P. Cutaneous reaction to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in patients with AIDS and Kaposi's sarcoma. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 23;308(25):1535–1536. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306233082512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy K. L., Bakshi S. P., Bender M. A. Radiogallium scan in P. carinii pneumonia. Clin Nucl Med. 1982 Feb;7(2):71–74. doi: 10.1097/00003072-198202000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E., McCann P. P. Polyamine metabolism and function. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):C212–C221. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.5.C212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Stagno S., Woods D. Pneumocystis carinii infection: evidence for high prevalence in normal and immunosuppressed children. Pediatrics. 1978 Jan;61(1):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattler F. R., Remington J. S. Intravenous trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole therapy for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Am J Med. 1981 Jun;70(6):1215–1221. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90830-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkis S. J., Luk G. D., Collector M. I., McCann P. P., Baylin S. B., Sensenbrenner L. L. Regulation of hematopoiesis II: the role of polyamine inhibition on helper or suppressor influences of the thymus. Blood. 1983 Mar;61(3):604–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjoerdsma A., Schechter P. J. Chemotherapeutic implications of polyamine biosynthesis inhibition. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1984 Mar;35(3):287–300. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1984.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turbiner E. H., Yeh S. D., Rosen P. P., Bains M. S., Benua R. S. Abnormal gallium scintigraphy in Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia with a normal chest radiograph. Radiology. 1978 May;127(2):437–438. doi: 10.1148/127.2.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyms A. S., Williamson J. D. Inhibitors of polyamine biosynthesis block human cytomegalovirus replication. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):690–691. doi: 10.1038/297690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Perl D. P., Krogstad D. J., Rawson P. G., Schultz M. G. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the United States. Epidemiologic, diagnostic, and clinical features. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):83–93. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Western K. A., Perera D. R., Schultz M. G. Pentamidine isethionate in the treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Nov;73(5):695–702. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-5-695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]