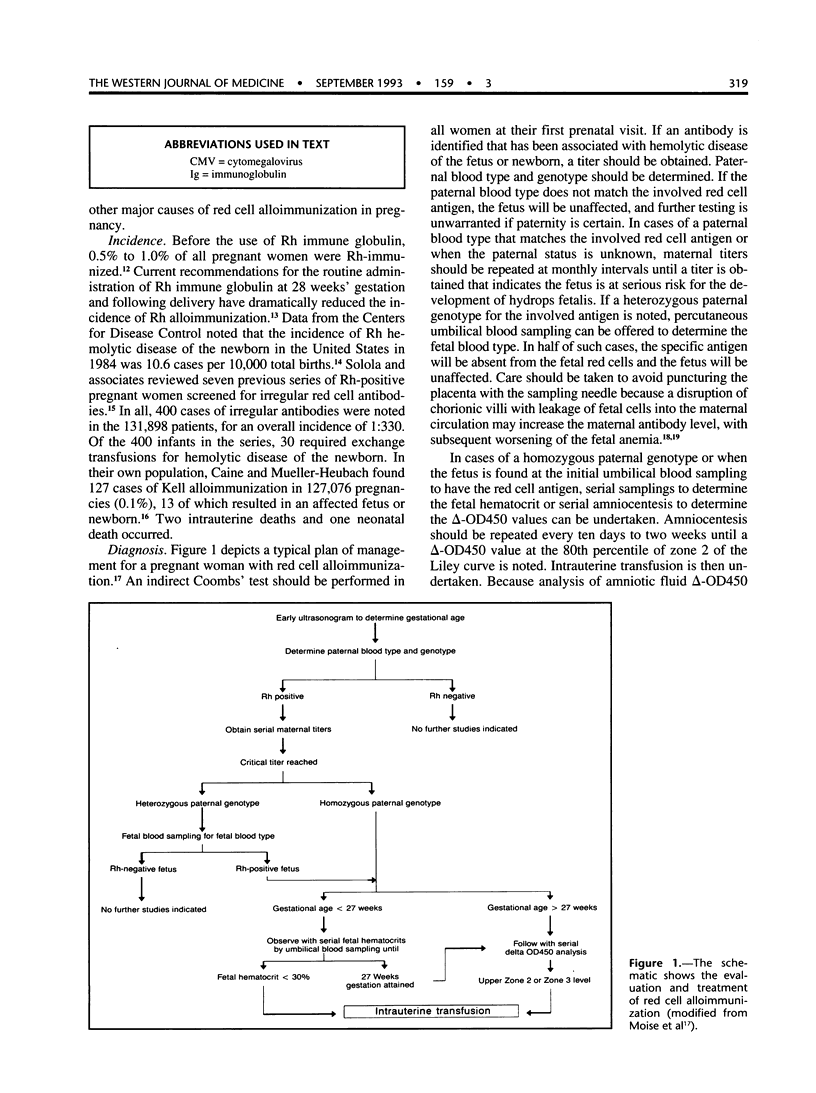
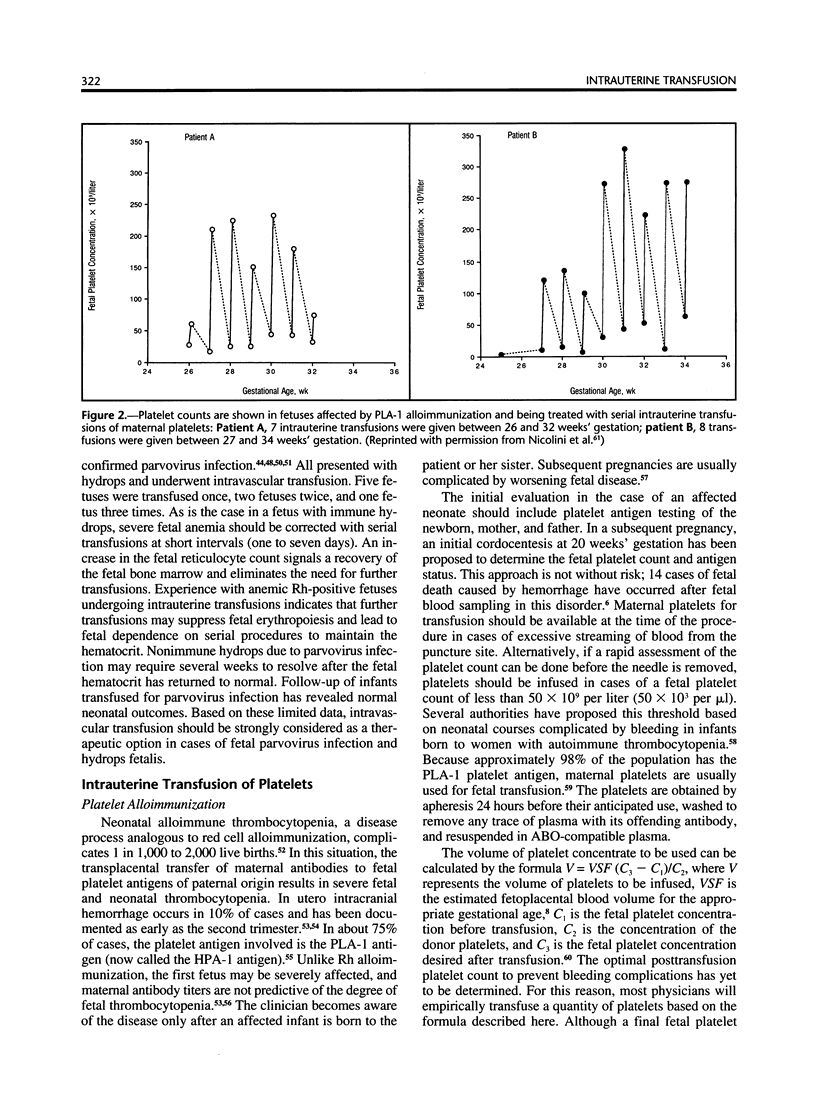
Abstract
Having direct access to the fetoplacental circulation by ultrasound-directed needle puncture has led to therapeutic interventions for fetal anemia and thrombocytopenia. Most cases of red cell alloimmunization associated with fetal anemia are caused by the antibody to the D red cell antigen. The intravascular transfusion of red cells to a hydropic fetus in such cases has notably improved survival. Nonimmune hydrops fetalis due to maternal parvovirus infection has also been treated successfully with the intravascular transfusion of red cells, whereas fetomaternal hemorrhage has not proved amenable to such therapy. Sensitization to the PLA-1 platelet antigen is the most common cause of fetal thrombocytopenia in maternal platelet alloimmunization. Fetal platelet transfusions have not proved to be a practical therapeutic modality for this disorder owing to the short half-life of the platelets. Platelets transfusions to the fetus just before delivery may avert the need for cesarean section in cases of severe thrombocytopenia.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L. J., Hurwitz E. S. Human parvovirus B19 and pregnancy. Clin Perinatol. 1988 Jun;15(2):273–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. J., Tsou C., Parker R. A., Chorba T. L., Wulff H., Tattersall P., Mortimer P. P. Detection of antibodies and antigens of human parvovirus B19 by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):522–526. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.522-526.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEVIS D. C. Blood pigments in haemolytic disease of the newborn. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1956 Feb;63(1):68–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1956.tb05435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bang J., Bock J. E., Trolle D. Ultrasound-guided fetal intravenous transfusion for severe rhesus haemolytic disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Feb 6;284(6313):373–374. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6313.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B. R., Barss V. A., Saltzman D. H., Greene M. F., Penso C. A., Frigoletto F. D., Jr Acute fetal distress associated with percutaneous umbilical blood sampling. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987 May;156(5):1218–1220. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(87)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz R. L., Chitkara U., Goldberg J. D., Wilkins I., Chervenak F. A., Lynch L. Intrauterine intravascular transfusions for severe red blood cell isoimmunization: ultrasound-guided percutaneous approach. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Sep;155(3):574–581. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(86)90282-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette V. S., Chen L., de Friedberg Z. S., Hogan V. A., Trudel E., Décary F. Alloimmunization to the PlA1 platelet antigen: results of a prospective study. Br J Haematol. 1990 Feb;74(2):209–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman J. M. The management of Rh-Isoimmunization. Obstet Gynecol. 1978 Jul;52(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussel J., Berkowitz R., McFarland J., Lynch L., Chitkara U. In-utero platelet transfusion for alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Lancet. 1988 Dec 3;2(8623):1307–1308. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92914-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caine M. E., Mueller-Heubach E. Kell sensitization in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Jan;154(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(86)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardwell M. S. Successful treatment of hydrops fetalis caused by fetomaternal hemorrhage: a case report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Jan;158(1):131–132. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(88)90794-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chávez G. F., Mulinare J., Edmonds L. D. Epidemiology of Rh hemolytic disease of the newborn in the United States. JAMA. 1991 Jun 26;265(24):3270–3274. doi: 10.1001/jama.1991.03460240066029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daffos F., Capella-Pavlovsky M., Forestier F. A new procedure for fetal blood sampling in utero: preliminary results of fifty-three cases. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983 Aug 15;146(8):985–987. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(83)90982-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daffos F., Forestier F., Kaplan C., Cox W. Prenatal diagnosis and management of bleeding disorders with fetal blood sampling. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Apr;158(4):939–946. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(88)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daffos F., Forestier F., Muller J. Y., Reznikoff-Etievant M., Habibi B., Capella-Pavlovsky M., Maigret P., Kaplan C. Prenatal treatment of alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Lancet. 1984 Sep 15;2(8403):632–632. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90614-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deaver J. E., Leppert P. C., Zaroulis C. G. Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Perinatol. 1986 Apr;3(2):127–131. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-999848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dildy G. A., 3rd, Smith L. G., Jr, Moise K. J., Jr, Cano L. E., Hesketh D. E. Porencephalic cyst: a complication of fetal intravascular transfusion. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Jul;165(1):76–78. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(91)90227-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. P. Massive fetomaternal hemorrhage treated by fetal intravascular transfusion. Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Sep;78(3 Pt 2):520–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer R. L., Kuhlman K., Grover J., Montgomery O., Wapner R. J. Chronic, massive fetomaternal hemorrhage treated with repeated fetal intravascular transfusions. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Jan;162(1):203–204. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)90850-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forestier F., Daffos F., Catherine N., Renard M., Andreux J. P. Developmental hematopoiesis in normal human fetal blood. Blood. 1991 Jun 1;77(11):2360–2363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovangrandi Y., Daffos F., Kaplan C., Forestier F., Mac Aleese J., Moirot M. Very early intracranial haemorrhage in alloimmune fetal thrombocytopenia. Lancet. 1990 Aug 4;336(8710):310–310. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91842-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonsoulin W. J., Moise K. J., Jr, Milam J. D., Sala J. D., Weber V. W., Carpenter R. J., Jr Serial maternal blood donations for intrauterine transfusion. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Feb;75(2):158–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grannum P. A., Copel J. A., Plaxe S. C., Scioscia A. L., Hobbins J. C. In utero exchange transfusion by direct intravascular injection in severe erythroblastosis fetalis. N Engl J Med. 1986 May 29;314(22):1431–1434. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198605293142207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harman C. R., Bowman J. M., Manning F. A., Menticoglou S. M. Intrauterine transfusion--intraperitoneal versus intravascular approach: a case-control comparison. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Apr;162(4):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)91314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan C., Daffos F., Forestier F., Cox W. L., Lyon-Caen D., Dupuy-Montbrun M. C., Salmon C. Management of alloimmune thrombocytopenia: antenatal diagnosis and in utero transfusion of maternal platelets. Blood. 1988 Jul;72(1):340–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig J. M., Christensen R. D. Neutropenia and thrombocytopenia in infants with Rh hemolytic disease. J Pediatr. 1989 Apr;114(4 Pt 1):625–631. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80709-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. INTRAUTERINE TRANSFUSION OF FOETUS IN HAEMOLYTIC DISEASE. Br Med J. 1963 Nov 2;2(5365):1107–1109. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5365.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc L., Moise K. J., Jr, Carpenter R. J., Jr, Cano L. E. Fetoplacental blood volume estimation in pregnancies with Rh alloimmunization. Fetal Diagn Ther. 1990;5(3-4):138–146. doi: 10.1159/000263583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch L., Bussel J. B., McFarland J. G., Chitkara U., Berkowitz R. L. Antenatal treatment of alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Obstet Gynecol. 1992 Jul;80(1):67–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor S. N., Silver R. K., Sholl J. S. Enhanced sensitization after cordocentesis in a rhesus-isoimmunized pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Aug;165(2):382–383. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(91)90098-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medearis A. L., Hensleigh P. A., Parks D. R., Herzenberg L. A. Detection of fetal erythrocytes in maternal blood post partum with the fluorescence-activated cell sorter. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Feb 1;148(3):290–295. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(84)80070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moise K. J., Jr, Carpenter R. J., Jr, Huhta J. C., Deter R. L. Umbilical cord hematoma secondary to in utero intravascular transfusion for Rh isoimmunization. Fetal Ther. 1987;2(2):65–70. doi: 10.1159/000263285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moise K. J., Jr, Carpenter R. J., Jr, Kirshon B., Deter R. L., Sala J. D., Cano L. E. Comparison of four types of intrauterine transfusion: effect on fetal hematocrit. Fetal Ther. 1989;4(2-3):126–137. doi: 10.1159/000263434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moise K. J., Jr, Milam J. D., Carpenter R. J., Jr Changing trends in the diagnosis and treatment of Rh alloimmunization. Tex Med. 1987 Nov;83(11):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Eckhardt C., Kiefel V., Grubert A., Kroll H., Weisheit M., Schmidt S., Mueller-Eckhardt G., Santoso S. 348 cases of suspected neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Lancet. 1989 Feb 18;1(8634):363–366. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91733-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller J. Y., Reznikoff-Etievant M. F., Patereau C., Dangu C., Chesnel N. Thrombopénies néo-natales allo-immunes. Etude clinique et biologique de 84 cas. Presse Med. 1985 Jan 19;14(2):83–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naides S. J., Weiner C. P. Antenatal diagnosis and palliative treatment of non-immune hydrops fetalis secondary to fetal parvovirus B19 infection. Prenat Diagn. 1989 Feb;9(2):105–114. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970090205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaides K. H., Rodeck C. H., Mibashan R. S., Kemp J. R. Have Liley charts outlived their usefulness? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Jul;155(1):90–94. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(86)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaides K. H., Thilaganathan B., Mibashan R. S. Cordocentesis in the investigation of fetal erythropoiesis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Nov;161(5):1197–1200. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90664-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolini U., Kochenour N. K., Greco P., Letsky E. A., Johnson R. D., Contreras M., Rodeck C. H. Consequences of fetomaternal haemorrhage after intrauterine transfusion. BMJ. 1988 Nov 26;297(6660):1379–1381. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6660.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolini U., Tannirandorn Y., Gonzalez P., Fisk N. M., Beacham J., Letsky E. A., Rodeck C. H. Continuing controversy in alloimmune thrombocytopenia: fetal hyperimmunoglobulinemia fails to prevent thrombocytopenia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Oct;163(4 Pt 1):1144–1146. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)90674-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters M. T., Nicolaides K. H. Cordocentesis for the diagnosis and treatment of human fetal parvovirus infection. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Mar;75(3 Pt 2):501–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radunovic N., Lockwood C. J., Alvarez M., Plecas D., Chitkara U., Berkowitz R. L. The severely anemic and hydropic isoimmune fetus: changes in fetal hematocrit associated with intrauterine death. Obstet Gynecol. 1992 Mar;79(3):390–393. doi: 10.1097/00006250-199203000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaer M., Van de Putte I., Vermylen C. Massive feto-maternal hemorrhage as a cause of perinatal mortality and morbidity. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1976;6(3):125–140. doi: 10.1016/0028-2243(76)90140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeck C. H., Kemp J. R., Holman C. A., Whitmore D. N., Karnicki J., Austin M. A. Direct intravascular fetal blood transfusion by fetoscopy in severe Rhesus isoimmunisation. Lancet. 1981 Mar 21;1(8221):625–627. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91549-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeck C. H., Nicolaides K. H. Fetoscopy and fetal tissue sampling. Br Med Bull. 1983 Oct;39(4):332–337. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodis J. F., Hovick T. J., Jr, Quinn D. L., Rosengren S. S., Tattersall P. Human parvovirus infection in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Nov;72(5):733–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodis J. F., Quinn D. L., Gary G. W., Jr, Anderson L. J., Rosengren S., Cartter M. L., Campbell W. A., Vintzileos A. M. Management and outcomes of pregnancies complicated by human B19 parvovirus infection: a prospective study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Oct;163(4 Pt 1):1168–1171. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)90681-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse D., Weiner C. Ongoing fetomaternal hemorrhage treated by serial fetal intravascular transfusions. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Nov;76(5 Pt 2):974–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahakian V., Weiner C. P., Naides S. J., Williamson R. A., Scharosch L. L. Intrauterine transfusion treatment of nonimmune hydrops fetalis secondary to human parvovirus B19 infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Apr;164(4):1090–1091. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(91)90591-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz T. F., Roggendorf M., Hottenträger B., Deinhardt F., Enders G., Gloning K. P., Schramm T., Hansmann M. Human parvovirus B19 infection in pregnancy. Lancet. 1988 Sep 3;2(8610):566–567. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92684-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. R., Cruikshank D. P., Kochenour N. K., Pitkin R. M., Warenski J. C. Fetal platelet counts in the obstetric management of immunologic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Feb 15;136(4):495–499. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)90677-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sia C. G., Amigo N. C., Harper R. G., Farahani G., Kochen J. Failure of cesarean section to prevent intracranial hemorrhage in siblings with isoimmune neonatal thrombocytopenia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Sep 1;153(1):79–81. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(85)90598-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solola A., Sibai B., Mason J. M. Irregular antibodies: an assessment of routine prenatal screening. Obstet Gynecol. 1983 Jan;61(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill P. Intrauterine blood transfusion for non-immune hydrops fetalis due to parvovirus B19 infection. Lancet. 1990 Jul 14;336(8707):121–122. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91642-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soulier J. P., Patereau C., Drouet J. Platelet indirect radioactive Coombs test. Its utilization for PLA1 grouping. Vox Sang. 1975;29(4):253–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1975.tb00506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenti C. Antenatal detection of hemoglobinopathies. A preliminary report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1973 Mar 15;115(6):851–853. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(73)90532-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner C. P., Williamson R. A., Wenstrom K. D., Sipes S. L., Grant S. S., Widness J. A. Management of fetal hemolytic disease by cordocentesis. I. Prediction of fetal anemia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Sep;165(3):546–553. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(91)90281-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner C. P., Williamson R. A., Wenstrom K. D., Sipes S. L., Widness J. A., Grant S. S., Estle L. Management of fetal hemolytic disease by cordocentesis. II. Outcome of treatment. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Nov;165(5 Pt 1):1302–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]