Abstract
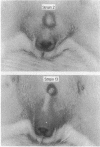
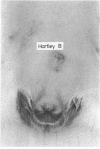
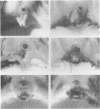
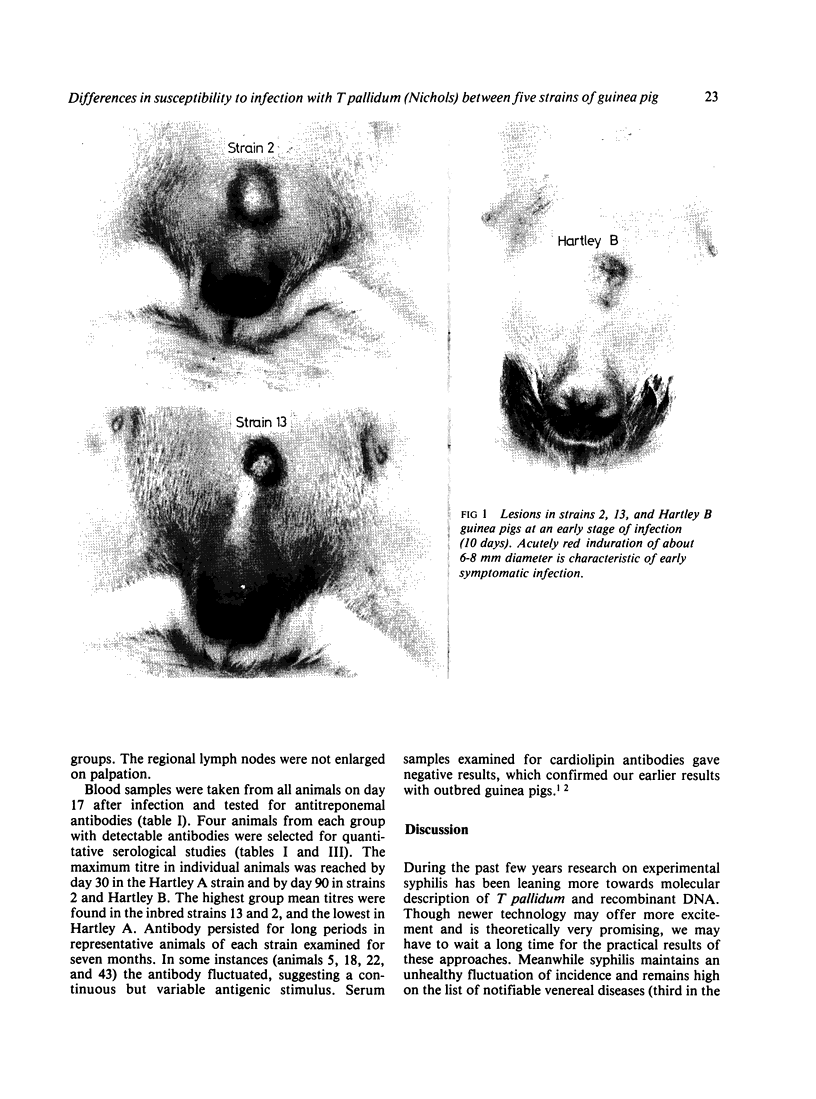
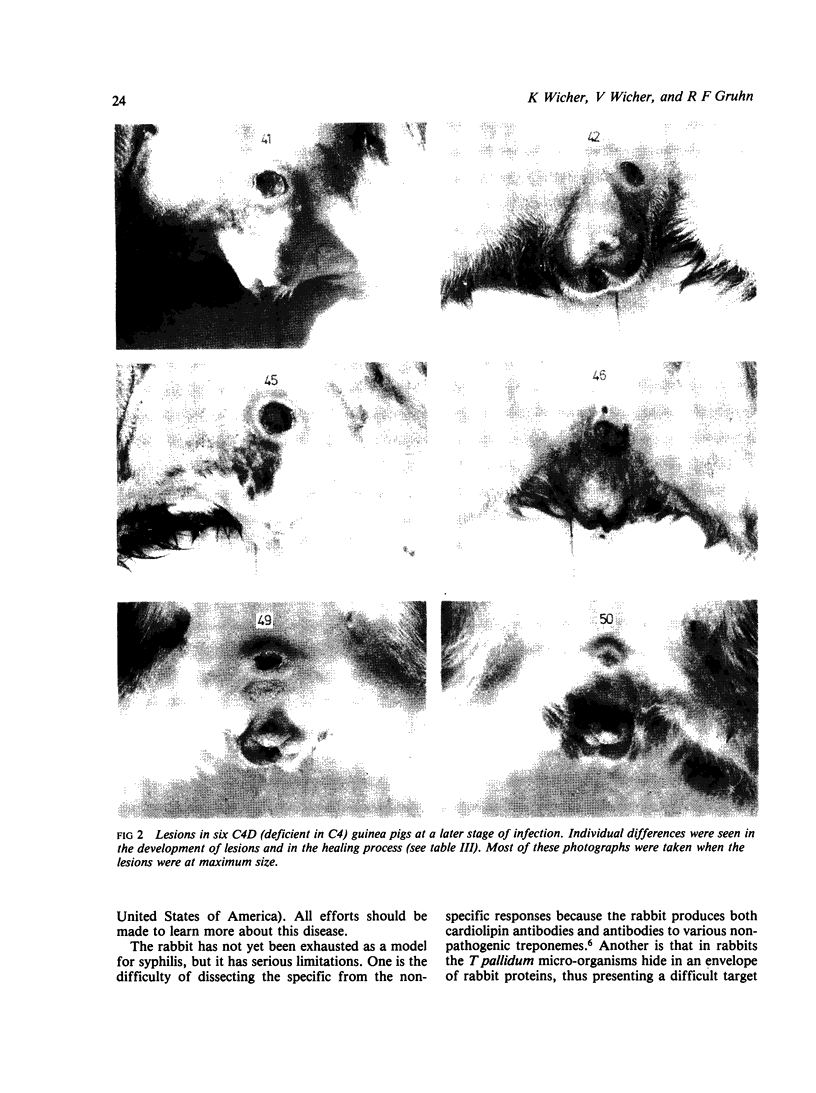
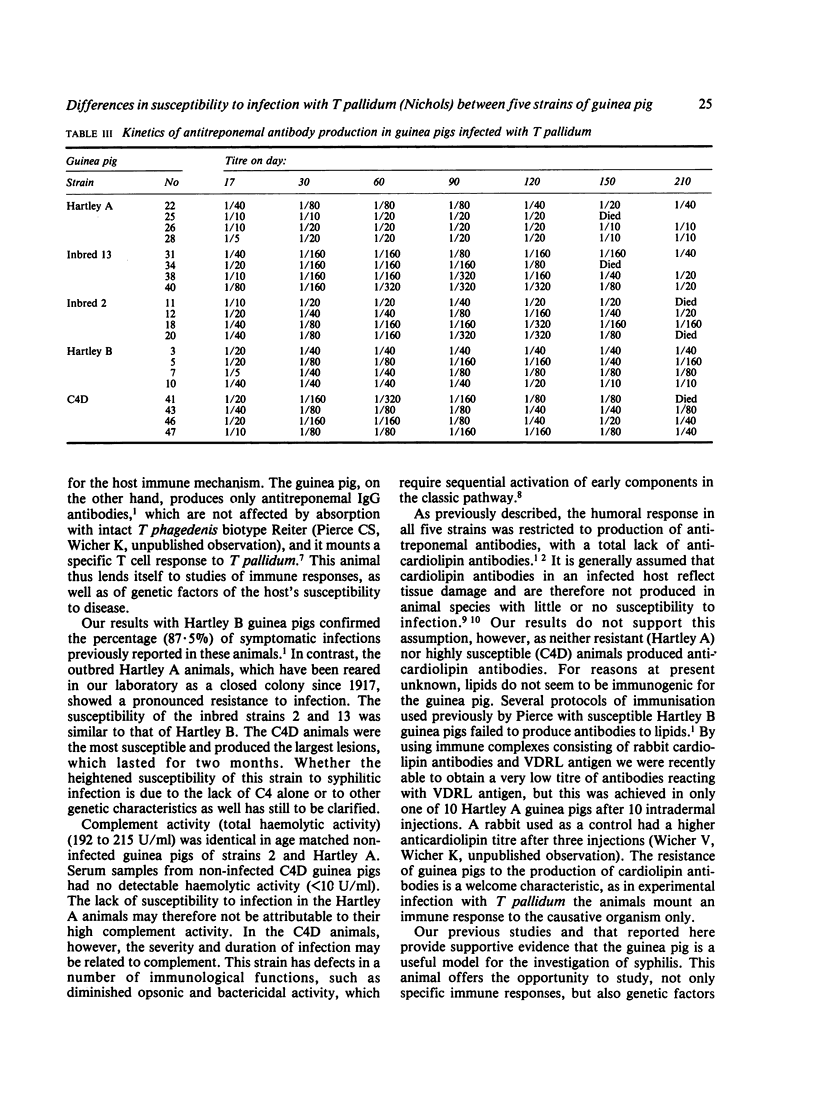
Groups of 10 young male guinea pigs of inbred strains 2 and 13 and outbred strains Hartley A, Hartley B, and one deficient in the fourth component of complement (C4D) were infected intradermally with 80 X 10(6) Treponema pallidum (Nichols). The course of infection and production of antitreponemal antibody were examined. Strain C4D guinea pigs were the most susceptible to infection (100%); inbred strains 2 and 13 and outbred strain Hartley B showed 80-90% symptomatic infection; and the Hartley A strain was the least susceptible to infection (10%). Strain 13 animals responded with the highest antitreponemal antibody activity, and the Hartley A strain with the lowest. The results suggest that genetic factors or complement, or both, may influence the degree of susceptibility to infection with T pallidum in guinea pigs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ellman L., Green I., Frank M. Genetically controlled total deficiency of the fourth component of complement in the guinea pig. Science. 1970 Oct 2;170(3953):74–75. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3953.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. S., Wicher K., Nakeeb S. Experimental syphilis: guinea pig model. Br J Vener Dis. 1983 Jun;59(3):157–168. doi: 10.1136/sti.59.3.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Ellman L., Frank M. M. Bactericidal and opsonic properties of C4-deficient guinea pig serum. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):477–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicher K., Wicher V., Wang M. C. Cellular and humoral immune response to guinea pig infected with Treponema pallidum. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;51(3):284–297. doi: 10.1159/000231603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]