Abstract
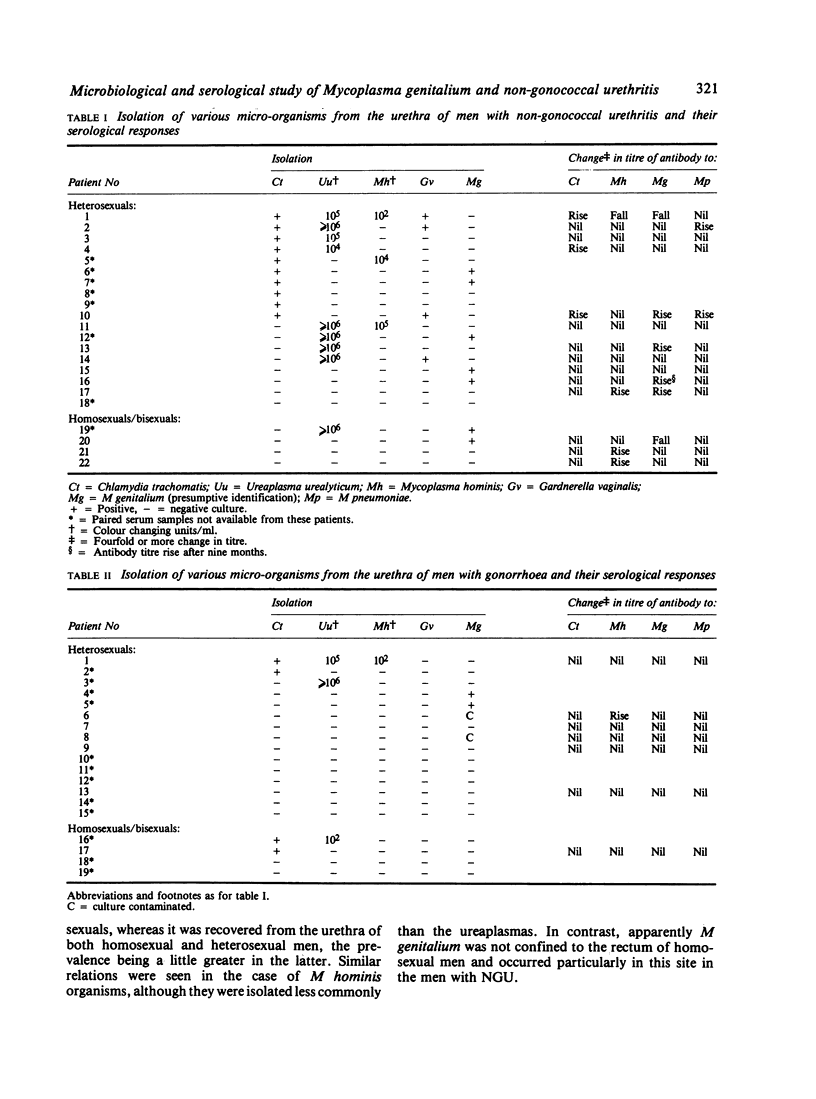
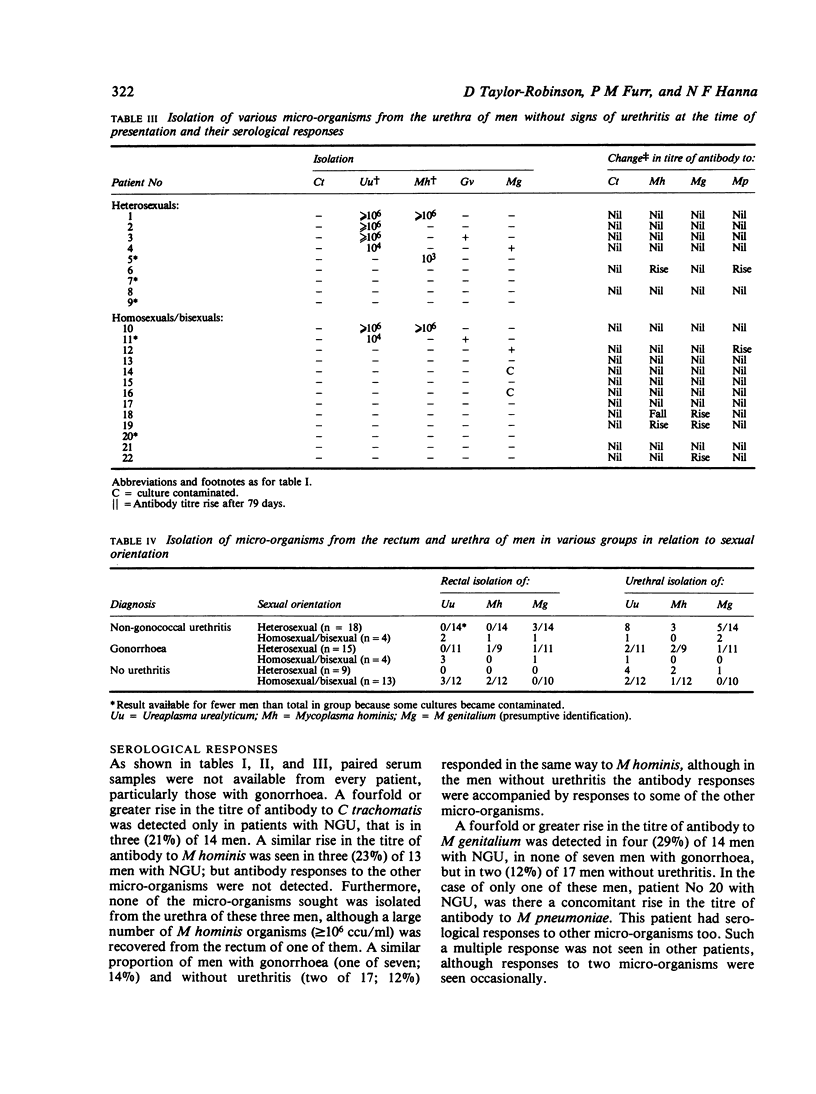
Twenty-two men with non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU), 19 with gonorrhoea, and 22 without urethritis were examined for various micro-organisms. Chlamydia trachomatis was isolated from the urethra of 45% of men with NGU, 21% of those with gonorrhoea, but from none without urethritis. Ureaplasma urealyticum but not Mycoplasma hominis was recovered from a larger proportion of men with NGU than from those in the other groups. M genitalium was isolated presumptively from 32% of men with NGU, 12% of those with gonorrhoea, from 10% of men without urethritis, and from 42% of the men with NGU from whom chlamydiae were not isolated. U urealyticum, M hominis, and M genitalium were sought also in the rectum of men in the three groups. The first two micro-organisms were confined almost exclusively to homosexual men, whereas M genitalium was apparently not restricted in this way and was found particularly in this site in men with NGU. The latter mycoplasma may be a resident primarily of the intestinal tract. A fourfold or greater rise in the titre of antibody to C trachomatis was detected in about 20% of the patients with NGU, but not in other men. A similar rise in the titre of antibody to M genitalium was seen in 29% of the patients with NGU and in 12% of those without urethritis. A concomitant antibody response to M pneumoniae, which is antigenically related to M genitalium, was seen in one patient only. The responses to M genitalium suggest infection by this mycoplasma and indicate the need for further serological studies.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Furr P. M., Taylor-Robinson D. Microimmunofluorescence technique for detection of antibody to Mycoplasma genitalium. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Sep;37(9):1072–1074. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.9.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhoff H., Rosengarten R., Lotz W., Fischer M., Lopatta D. Flask-shaped mycoplasmas: properties and pathogenicity for man and animals. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Sep;20(9):848–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K., Lindhardt B. O., Schütten H. J., Blom J., Christiansen C. Serological cross-reactions between Mycoplasma genitalium and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1036–1043. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1036-1043.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K. Serological cross-reactions between "Mycoplasma genitalium" and M. pneumoniae. Lancet. 1982 Nov 20;2(8308):1158–1159. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92809-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller B. R., Taylor-Robinson D., Furr P. M. Serological evidence implicating Mycoplasma genitalium in pelvic inflammatory disease. Lancet. 1984 May 19;1(8386):1102–1103. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92511-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Furr P. M., Hetherington C. M. The pathogenicity of a newly discovered human mycoplasma (strain G37) for the genital tract of marmosets. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Dec;89(3):449–455. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400071011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Furr P. M., Tully J. G. Serological cross-reactions between Mycoplasma genitalium and M. pneumoniae. Lancet. 1983 Mar 5;1(8323):527–527. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92212-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Martin-Bourgon C., Watanabe T., Addey J. P. Isolation of T-mycoplasmas from dogs and squirrel monkeys: biological and serological comparison with those isolated from man and cattle. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Sep;68(1):97–107. doi: 10.1099/00221287-68-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D. Mycoplasma infections of the human urogenital tract with particular reference to non-gonococcal urethritis. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1984 Jan-Feb;135A(1):129–134. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(84)80069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Tully J. G., Furr P. M., Cole R. M., Rose D. L., Hanna N. F. Urogenital mycoplasma infections of man: a review with observations on a recently discovered mycoplasma. Isr J Med Sci. 1981 Jul;17(7):524–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. E., Rosenthal R. O., Taylor-Robinson D. Serological response of patients with non-gonococcal urethritis to causative organism of contagious equine metritis 1977. Lancet. 1979 Mar 31;1(8118):700–701. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. J., Evans R. T., Hutchinson G. R., Taylor-Robinson D. Early detection of chlamydial inclusions combining the use of cycloheximide-treated McCoy cells and immunofluorescence staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):285–292. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.3.285-292.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. J., Reeve P., Oriel J. D. Simplified serological test for antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):6–10. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.6-10.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Amsel R., Hale J., Piot P., Holmes K. K. Selective differential human blood bilayer media for isolation of Gardnerella (Haemophilus) vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):141–147. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.141-147.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Rose D. L., Whitcomb R. F., Wenzel R. P. Enhanced isolation of Mycoplasma pneumoniae from throat washings with a newly-modified culture medium. J Infect Dis. 1979 Apr;139(4):478–482. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.4.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Taylor-Robinson D., Cole R. M., Rose D. L. A newly discovered mycoplasma in the human urogenital tract. Lancet. 1981 Jun 13;1(8233):1288–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92461-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


