Abstract
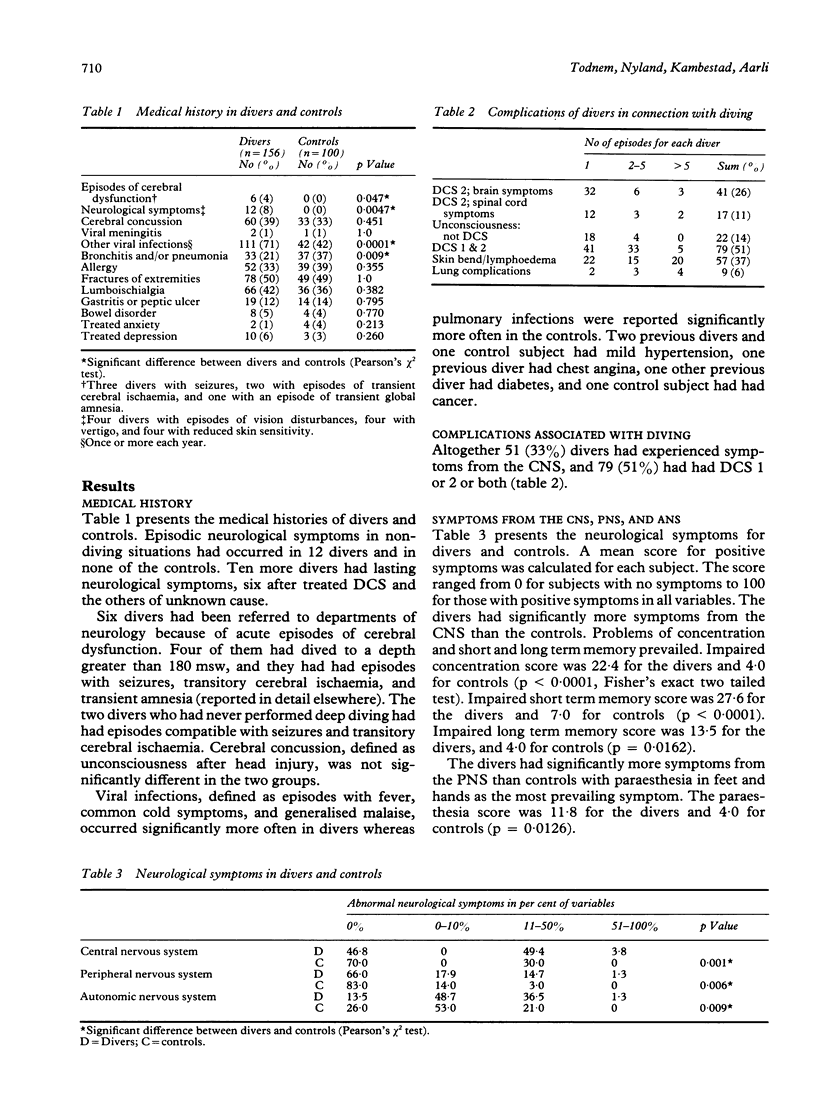
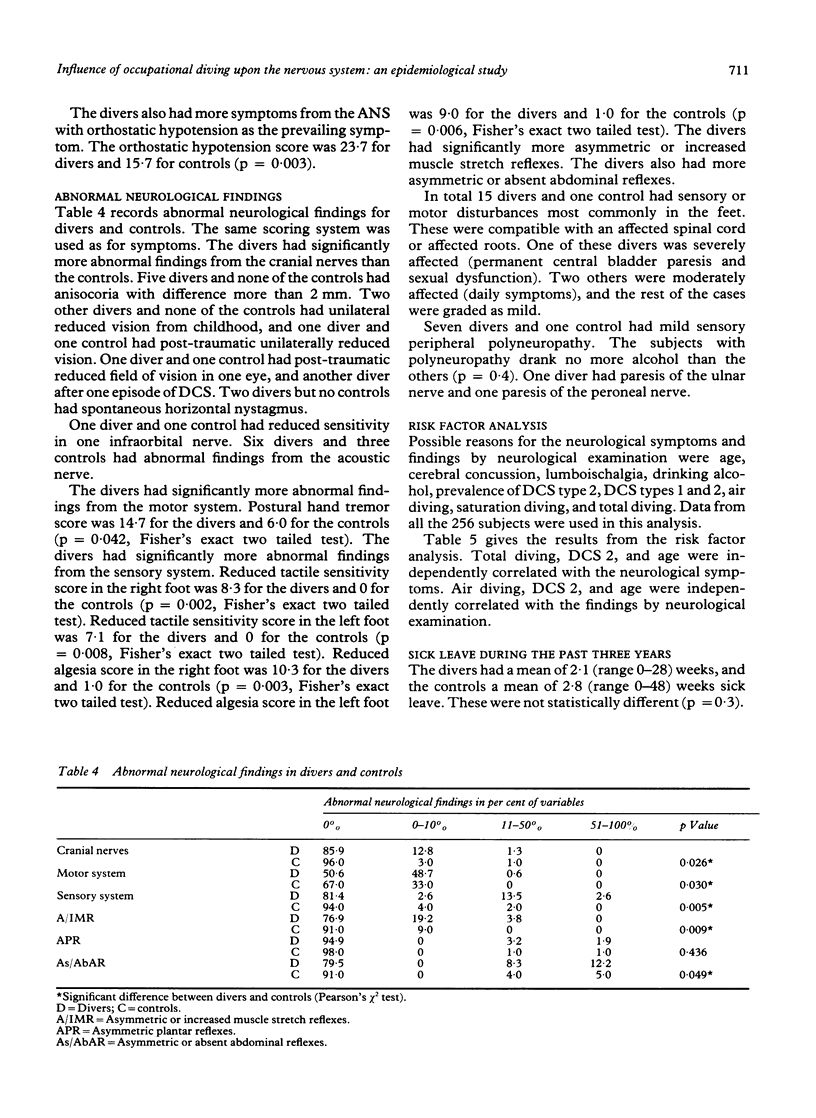
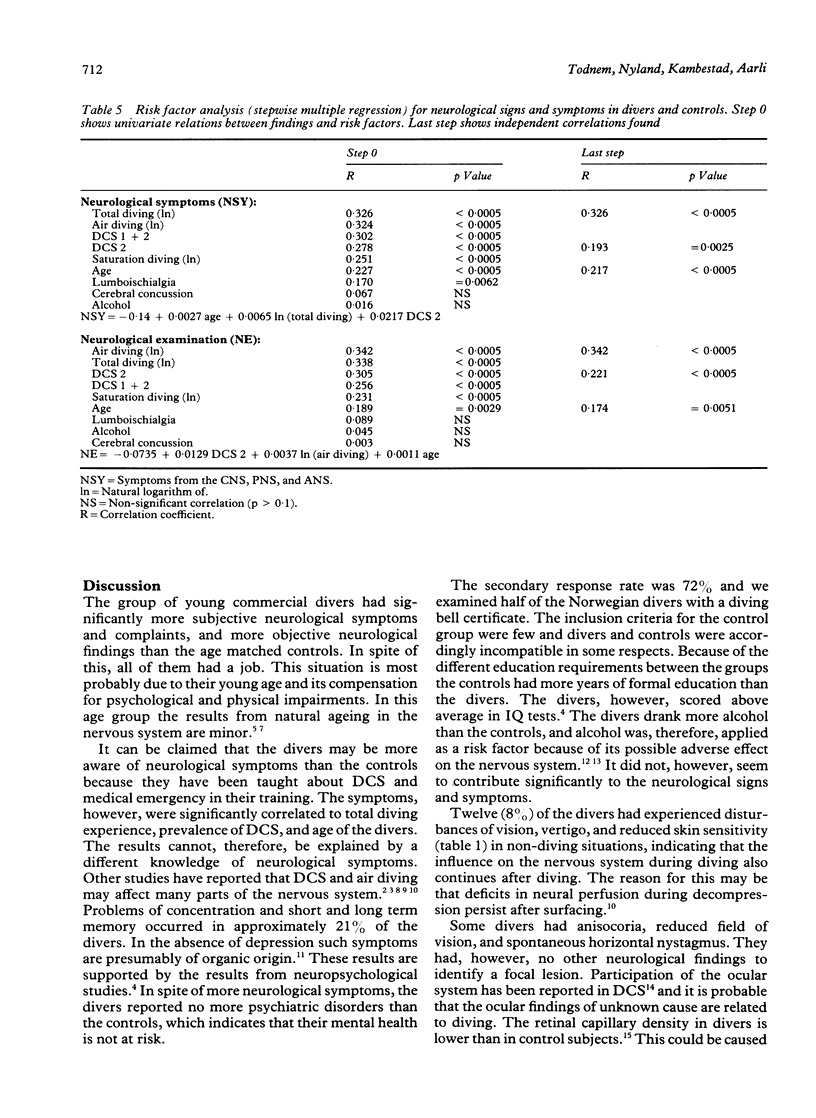
Neurological signs and symptoms were recorded from 156 air and saturation divers and 100 controls. Fifty one (33%) of the divers had had symptoms from the central nervous system during decompression. Also, 22 (14%) had been unconscious while diving. In total 79 (51%) had had decompression sickness (DCS). Twelve (8%) of the divers and no controls had had specific neurological symptoms (vision disturbances, vertigo, reduced skin sensitivity) in non-diving situations, and six (4%) of the divers (no controls) had had episodes of cerebral dysfunction (seizures, transient cerebral ischaemia, transient amnesia). The divers had significantly more general symptoms from the nervous system and more abnormal neurological findings than the controls. The most prominent symptoms were difficulties in concentration and problems with long and short term memory. The most prominent abnormal findings in the divers were compatible with dysfunction in the distal spinal cord or nerve roots, and polyneuropathy. The general neurological symptoms and findings were independently significantly correlated with diving exposure, prevalence of DCS, and age.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adkisson G. H., Macleod M. A., Hodgson M., Sykes J. J., Smith F., Strack C., Torok Z., Pearson R. R. Cerebral perfusion deficits in dysbaric illness. Lancet. 1989 Jul 15;2(8655):119–122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALD K. W. Oxygen poisoning in man. Br Med J. 1947 May 17;1(4506):667–passim. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman Y., Kendig J. J. Pressure and temperature modulation of conduction in a bifurcating axon. Undersea Biomed Res. 1986 Mar;13(1):45–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiberg A. Consequences of U.S. Navy diving mishaps: decompression sickness. Undersea Biomed Res. 1986 Sep;13(3):383–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. S., Eckenhoff R. G. Spinal cord decompression sickness after standard U.S. Navy air decompression. Mil Med. 1986 Mar;151(3):166–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkyn L. R., Reeves A. G., Warren T., Whiting R. K., Clayton R. J., Moore W. W., Rizzo A., Tuzun I. M., Bonnett J. C., Culpepper B. W. Neurologic signs in senescence. Arch Neurol. 1985 Dec;42(12):1154–1157. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060110036012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemppainen R., Juntunen J., Hillbom M. Drinking habits and peripheral alcoholic neuropathy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1982 Jan;65(1):11–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1982.tb03056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostachowicz M. Z. History of the ophthalmological investigations in decompression sickness. Bull Inst Marit Trop Med Gdynia. 1987;38(3-4):207–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer A. C., Calder I. M., Hughes J. T. Spinal cord degeneration in divers. Lancet. 1987 Dec 12;2(8572):1365–1366. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91259-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer A. C., Calder I. M., McCallum R. I., Mastaglia F. L. Spinal cord degeneration in a case of "recovered" spinal decompression sickness. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Oct 3;283(6296):888–888. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6296.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters B. H., Levin H. S., Kelly P. J. Neurologic and psychologic manifestations of decompression illness in divers. Neurology. 1977 Feb;27(2):125–127. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.2.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polkinghorne P. J., Sehmi K., Cross M. R., Minassian D., Bird A. C. Ocular fundus lesions in divers. Lancet. 1988 Dec 17;2(8625):1381–1383. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90583-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROZSAHEGYI I. Late consequences of the neurological forms of decompression sickness. Br J Ind Med. 1959 Oct;16:311–317. doi: 10.1136/oem.16.4.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozsahegyi I., Roth B. Participation of the central nervous system in decompression. Ind Med Surg. 1966 Feb;35(2):101–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skre H. Neurological signs in a normal population. Acta Neurol Scand. 1972;48(5):575–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1972.tb07577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todnem K., Knudsen G., Riise T., Nyland H., Aarli J. A. Nerve conduction velocity in man during deep diving to 360 msw. Undersea Biomed Res. 1989 Jan;16(1):31–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaernes R. J., Kløve H., Ellertsen B. Neuropsychologic effects of saturation diving. Undersea Biomed Res. 1989 May;16(3):233–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weathersby P. K., Hart B. L., Flynn E. T., Walker W. F. Role of oxygen in the production of human decompression sickness. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Dec;63(6):2380–2387. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.6.2380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


