Abstract
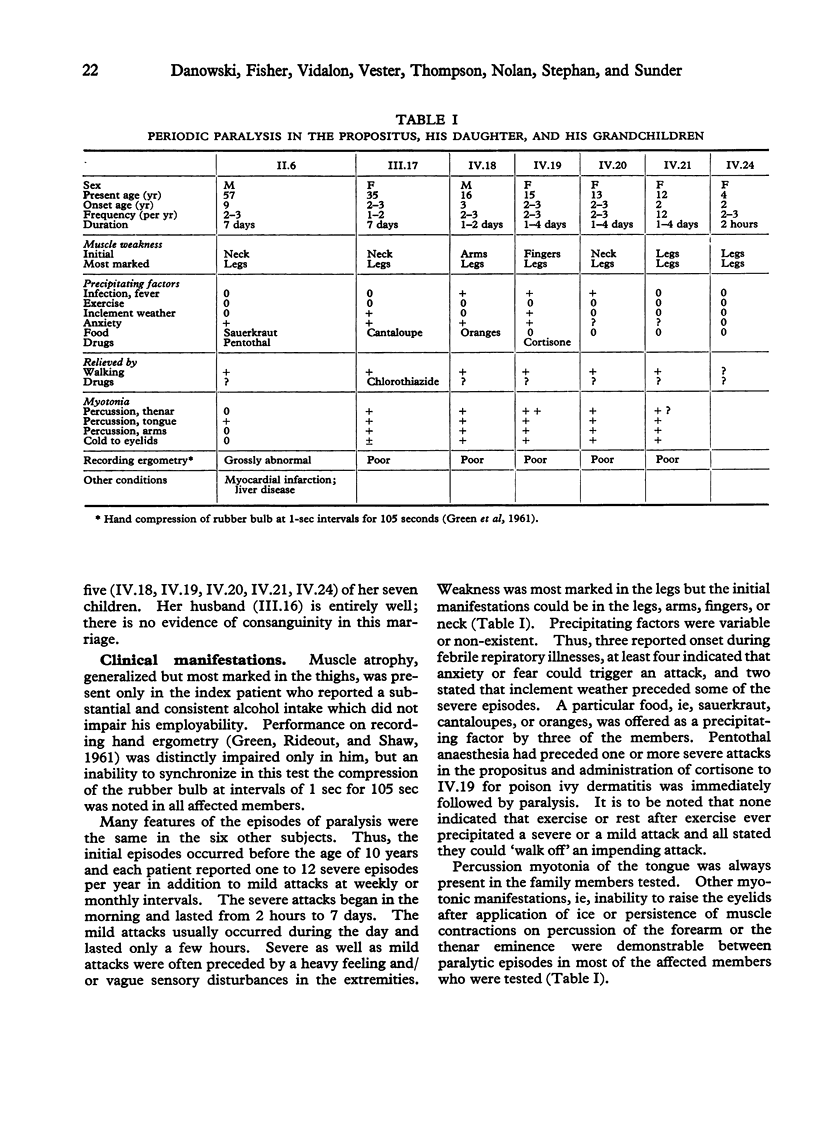
Electron microscopic studies of muscle biopsies from clinically unaffected sibs in a family with normo-hyperkalaemic periodic paralysis with variable myotonia have revealed dilatation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum similar to that observed in affected members. This supports the view that such dilatation is not only a significant and likely primary ultrastructural change but that it may precede clinical manifestations and represent an anatomical marker of the genetic trait. Identical dilatation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum was found in the clinically unaffected father of the affected and unaffected grandchildren of the propositus. This raises the possibility that this non-consanguineous member contributed to the genetic trait or its manifestations in the grandchildren of the index patient since similar dilatation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum was not observed in the muscles of healthy control subjects.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG F. S. Hyperkalemic familial periodic paralysis (adynamia episodica hereditaria). Ann Intern Med. 1962 Sep;57:455–461. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-57-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auböck L., Fladerer H. Licht- und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen von Muskeln bei Adynamia episodica hereditaria (Gamstorp-Syndrom) Wien Z Nervenheilkd Grenzgeb. 1970 Jun;28(2):104–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. A., Afifi A. K., Dunkle L. M., Johns R. J. Muscle pathology in hypokalemic periodic paralysis with hyperthyroidism. I. High resolution light microscopic study of a case. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1970 Feb;126(2):88–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. A., Afifi A. K., Dunkle L. M., Johns R. J. Muscle pathology in hypokalemic periodic paralysis with hyperthyroidism. II. A light and electron microscopic study. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1970 Feb;126(2):100–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biczyskowa W., Fidziańska A., Jedrzejowska H. Light and electron microscopic study of the muscles in hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Acta Neuropathol. 1969;12(4):329–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00809129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley W. G. Adynamia episodica hereditaria. Clinical, pathological and electrophysiological studies in an affected family. Brain. 1969;92(2):345–378. doi: 10.1093/brain/92.2.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody I. A., Dudley A. W., Jr Thyrotoxic hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Muscle morphology and functional assay of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Arch Neurol. 1969 Jul;21(1):1–6. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480130015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE GRAEFF J., LAMEIJER L. D. PERIODIC PARALYSIS. Am J Med. 1965 Jul;39:79–80. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRAGER G. A., HAMMILL J. F., SHY G. M. Paramyotonia congenita. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1958 Jul;80(1):1–9. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1958.02340070019001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danowski T. S., Peters J. H., Rathbun J. C., Quashnock J. M., Greenman L. STUDIES IN DIABETIC ACIDOSIS AND COMA, WITH PARTICULAR EMPHASIS ON THE RETENTION OF ADMINISTERED POTASSIUM. J Clin Invest. 1949 Jan;28(1):1–9. doi: 10.1172/JCI102037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danowski T. S., Sabeh G., Vester J. W., Alley R. A., Robbins T. J., Tsai C. T., Pazirandeh M., Sekaran K. Serum CPK in muscular dystrophy and myotonia dystrophica. Metabolism. 1968 Sep;17(9):808–817. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(68)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkle L. M., Diggs C. H., Bergman R. A., Johns R. J. A light and electron microscopic study of a second case of hypokalemic periodic paralysis with hyperthyroidism. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1970 Apr;126(4):225–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGAN T. J., KLEIN R. Hyperkalemic familial periodic paralysis. Pediatrics. 1959 Nov;24:761–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGEL A. G., LAMBERT E. H., ROSEVEAR J. W., TAUXE W. N. CLINICAL AND ELECTROMYOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN A PATIENT WITH PRIMARY HYPOKALEMIC PERIODIC PARALYSIS. Am J Med. 1965 Apr;38:626–640. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G. Electron microscopic observations in primary hypokalemic and thyrotoxic periodic paralyses. Mayo Clin Proc. 1966 Nov;41(11):797–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G. Evolution and content of vacuoles in primary hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1970 Nov-Dec;45(11):774–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. R., Cohn R. E., Danowski T. S. Ultrastructural observations of skeletal muscle in myopathy and neuropathy with special reference to muscular dystrophy. Lab Invest. 1966 Apr;15(4):778–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAMSTORP I. Adynamia episodica hereditaria. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1956 May;45(Suppl 108):1–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAMSTORP I., HAUGE M., HELWEGLARSEN H. F., MJONES H., SAGILD U. Adynamia episodica hereditaria: a disease clinically resembling familial periodic paralysis but characterized by increasing serum potassium during the paralytic attacks. Am J Med. 1957 Sep;23(3):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(57)90318-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENE R., RIDEOUT D. F., SHAW M. L. Ergometry in the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis. Lancet. 1961 Aug 5;2(7197):281–284. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)90577-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. M., Green J. R., Lagunoff D. Studies on a patient with hypokalemic familial periodic paralysis. Am J Med. 1970 Feb;48(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(70)90114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs R. C., Engel W. K., Resnick J. S. Acetazolamide treatment of hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Prevention of attacks and improvement of persistent weakness. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Jul;73(1):39–48. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross E. G., Dexter J. D., Roth R. G. Hypokalemic myopathy with myoglobinuria associated with licorice ingestion. N Engl J Med. 1966 Mar 17;274(11):602–606. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196603172741104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS M. L. Serum aldolase determination as a routine laboratory procedure. Am J Med Technol. 1958 Mar-Apr;24(2):99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRY R. J., CHIAMORI N., GOLUB O. J., BERKMAN S. Revised spectrophotometric methods for the determination of glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase, glutamic-pyruvic transaminase, and lactic acid dehydrogenase. Am J Clin Pathol. 1960 Oct;34:381–398. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/34.4_ts.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochella N. J., Weinhouse S. Automated assay of lactate dehydrogenase in urine. Anal Biochem. 1965 Nov;13(2):322–335. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann W. W., Smith R. A. Hypokalemic periodic paralysis studies in vitro. Brain. 1970;93(3):445–474. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.3.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes E. L., Jr, Price H. M., Blumberg J. M., Pearson C. M. Hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Electromicroscopic changes in the sarcoplasm. Neurology. 1966 Mar;16(3):242–256. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.3.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu V., Radu H., Nicolescu P. Ultrastructural changes in hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Rev Roum Neurol. 1971;8(6):419–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeune M., David M., de Villard R. Adynamie épisodique héréditaire: étude clinique et biologique d'une famille. J Med Lyon. 1970 Jan 20;51(179):321–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIND P. R., KING E. J. Estimation of plasma phosphatase by determination of hydrolysed phenol with amino-antipyrine. J Clin Pathol. 1954 Nov;7(4):322–326. doi: 10.1136/jcp.7.4.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN R., EGAN T., USHER P. Changes in sodium, potassium and water in hyperkalemic familial periodic paralysis. Metabolism. 1960 Nov;9:1005–1024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layzer R. B., Lovelace R. E., Rowland L. P. Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Arch Neurol. 1967 May;16(5):455–472. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470230007002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTINGLY D. A simple fluorimetric method for the estimation of free 11-hydroxycorticoids in human plasma. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Jul;15:374–379. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.4.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. D., Rewcastle N. B., Humphrey J. G. Myopathy of hypokalemic periodic paralysis. An electron microscopic study. Arch Neurol. 1969 Jun;20(6):565–585. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480120011001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. D., Rewcastle N. B., Humphrey J. G. The myopathy of hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. An electron microscopic study. Arch Neurol. 1968 Sep;19(3):274–283. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00480030052005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odor D. L., Patel A. N., Pearce L. A. Familial hypokalemic periodic paralysis with permanent myopathy. A clinical and ultrastructural study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1967 Jan;26(1):98–114. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196701000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick J. S., Engel W. K., Griggs R. C., Stam A. C. Acetazolamide prophylaxis in hypokalemic periodic paralysis. N Engl J Med. 1968 Mar 14;278(11):582–586. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196803142781102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutta H. S., Armitage J. L. The sarcoplasmic reticulum in thyrotoxic hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Metabolism. 1969 Feb;18(2):81–83. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeten D. H., Dalakos T. G., Fellerman H. Studies on hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Evidence of changes in plasma Na and Cl and induction of paralysis by adrenal glucocorticoids. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):142–155. doi: 10.1172/JCI106468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller R. O., McArdle B. Calcification within muscle fibres in the periodic paralyses. Brain. 1971;94(2):263–272. doi: 10.1093/brain/94.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolsey R. M., Nelson J. S., Rossini A. A. Paramyotonia and progressive neurogenic atrophy. Neurology. 1969 Sep;19(9):909–914. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.9.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






