Abstract
Three hundred and fifty pregnancies were monitored by transabdominal amniocentesis in the fourteenth to sixteenth week of gestation followed by karyotyping or biochemica assays of cultured amniotic fluid cells and analysis of alpha-fetoprotein in the amniotic fluid supernatant. The pregnancy was interrupted in 36 cases (10%) either becasue of a fetal abnormality or the presence of a male fetus in pregnancies at risk for an X-linked disease. Four chromosomal aberrations were found in 87 pregnancies tested because of advanced maternal age. In 101 pregnancies with a recurrence risk of Down's syndrome, 2 fetuses with an abnormal karyotype were detected. In 11 cases, in which 1 parent was a carrier of a balanced translocation, 2 unbalanced fetal karyotypes were found. Fetal chromosome studies in 43 pregancies at risk for an X-linked disease indicated the presence of a male fetus in 21 cases. Prenatal diagnosis of 11 different metabolic diseases was performed in a total of 34 cases. Microchemical techniques were used to allow completion of the diagnosis of seven different enzyme deficiencies within 9 to 22 days after amniocentesis. Alpha-fetoprotein assay in the amniotic fluid supernatant of 47 pregnancies at risk for an open neural tube defect resulted in the detection of 3 anencephalic fetuses during the second half of pregnancy. The safety and reliability of amniocentesis and the possible effects on the outcome of pregnancy are evaluated. Prenatal diagnosis offers a promising alternative for parents who are at risk of having a child with a genetic disease which can be detected in amniotic fluid or in cultured amniotic fluid cells.
Full text
PDF
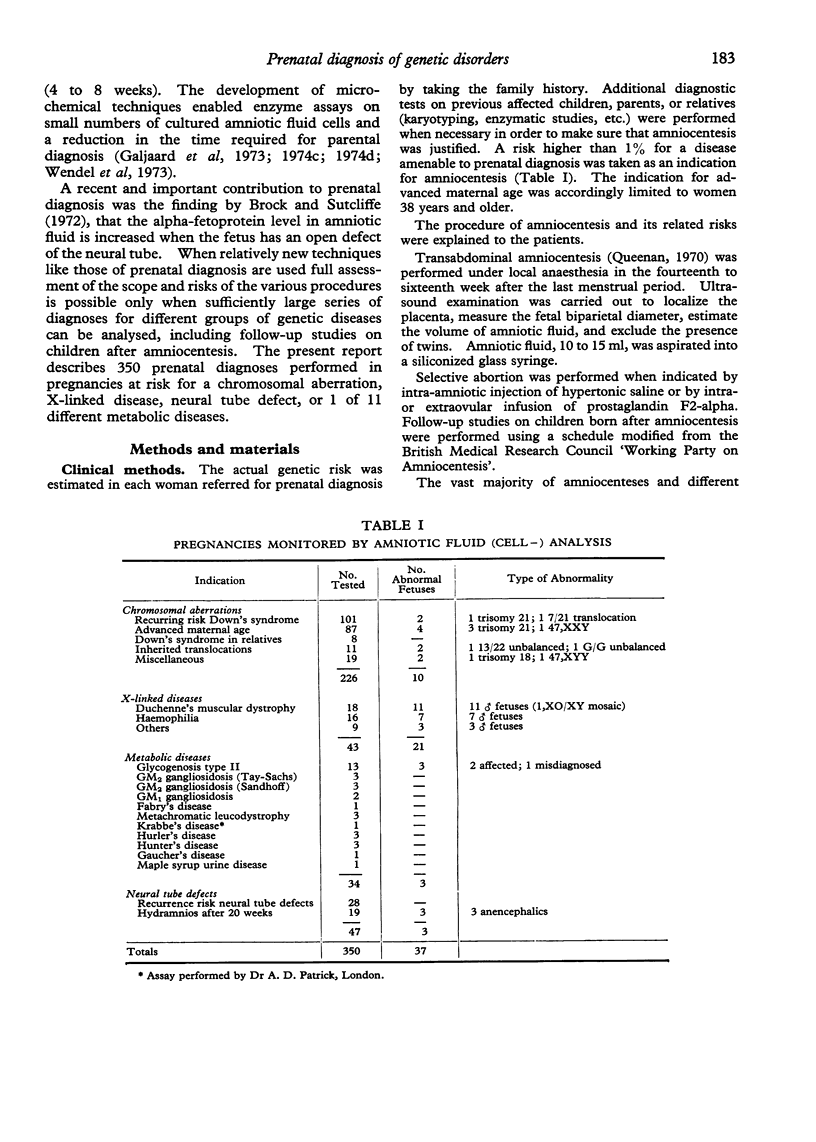


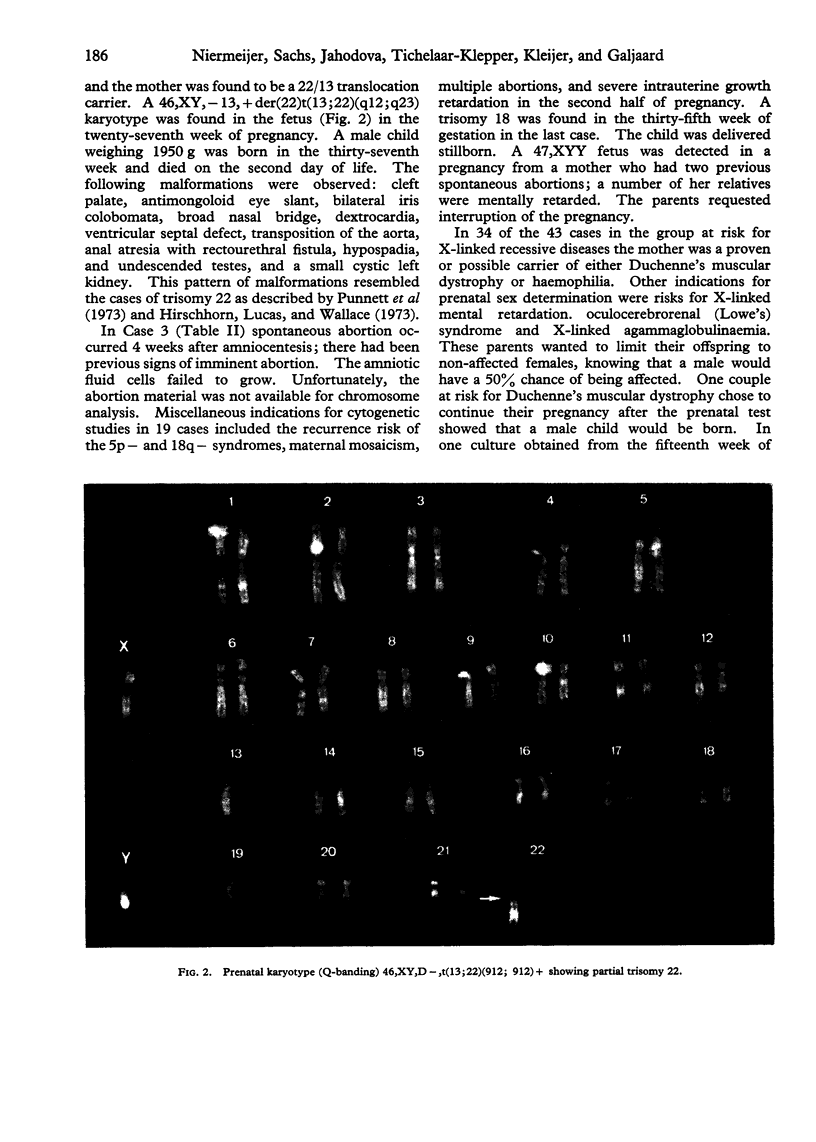








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan L. D., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Donald I., Sweet E. M., Gibson A. A. Amniotic-fluid alpha-fetoprotein in the antenatal diagnosis of spina bifida. Lancet. 1973 Sep 8;2(7828):522–525. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen H. H., Sergovich F., Stuart E. M., Pozsonyi J., Murray B. Infants undergoing antenatal genetic diagnosis: a preliminary report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Feb 1;118(3):310–313. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)33784-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Kuhl W., Trinidad F., Teplitz R., Nadler H. Beta-glucosidase activity in fibroblasts from homozygotes and heterozygotes for Gaucher's disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1971 Jan;23(1):62–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth C. W., Gerbie A. B., Nadler H. L. Intrauterine detection of GM1 gangliosidosis, type 2. Pediatrics. 1973 Oct;52(4):521–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgaonkar D. S., Shah S. A. The xyy chromosome male--or syndrome? Prog Med Genet. 1974;10:135–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boué J., Boué A. L'intérêt en diagnostic prénatal des techniques nouvelles d'identification chromosomique dans des translocations et une aneusomie de recombinaison. Nouv Presse Med. 1973 Dec;2(46):3097–3102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock D. J., Scrimgeour J. B., Nelson M. M. Amniotic fluid alphafetoprotein measurements in the early prenatal diagnosis of central nervous system disorders. Clin Genet. 1975 Feb;7(2):163–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1975.tb00313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock D. J., Sutcliffe R. G. Alpha-fetoprotein in the antenatal diagnosis of anencephaly and spina bifida. Lancet. 1972 Jul 29;2(7770):197–199. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91634-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton B. K., Gerbie A. B., Nadler H. L. Present status of intrauterine diagnosis of genetic defects. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Mar 1;118(5):718–746. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)33747-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth J., Sutherland G. R., Broadhead D. M., Bain A. D. Effect of serum concentration, type of culture medium and pH on the lysosomal enzyme activity of cultured human amniotic fluid cells. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Jun 19;53(2):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Lomakka G., Zech L. The 24 fluorescence patterns of the human metaphase chromosomes - distinguishing characters and variability. Hereditas. 1972;67(1):89–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1971.tb02363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. M., Niewczas-Late V., Riffell M. I., Hamerton J. L. Chromosomal mosaicism in diagnostic amniotic fluid cell cultures. Pediatr Res. 1974 Jun;8(6):679–683. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197406000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. A., Rudd N. L., Gardner H. A., Lowden J. A., Benzie R. J., Liedgren S. I. The antenatal diagnosis of genetic disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Feb 1;118(3):314–321. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)33785-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle H. The effect of environmental pH on the growth of normal and malignant cells. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Aug;82(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040820102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. B., Ikonne J. U., Patrick A. D., Stephens R., Willcox P. Letter: Prenatal diagnosis of Tay-Sachs disease. Lancet. 1973 Nov 17;2(7838):1144–1145. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90953-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsas L. J., Priest J. H., Wheeler F. B., Danner D. J., Pask B. A. Maple syrup urine disease: coenzyme function and prenatal monitoring. Metabolism. 1974 Jun;23(6):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Smith M. A. Prenatal diagnosis. Practitioner. 1974 Nov;213(1277):655–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Smith M. E., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Nevin N. C., Stone M. Chromosome analysis before birth and its value in genetic counselling. Br Med J. 1971 Oct 9;4(5779):69–74. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5779.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field B., Mitchell G., Garrett W., Kerr C. Prenatal diagnosis and selective abortion for anencephaly and spina bifida. Med J Aust. 1974 Apr 20;1(16):608–610. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1974.tb93200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratantoni J. C., Neufeld E. F., Uhlendorf B. W., Jacobson C. B. Intrauterine diagnosis of the hurler and hunter syndromes. N Engl J Med. 1969 Mar 27;280(13):686–688. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196903272801303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galjaard H., Hoogeveen A., Keijzer W., De Wit-Verbeek E., Vlek-Noot C. The use of quantiatative cytochemical analyses in rapid prenatal detection and somatic cell genetic studies of metabolic diseases. Histochem J. 1974 Sep;6(5):491–509. doi: 10.1007/BF01003266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galjaard H., Hoogeveen A., de Wit-Verbeek H. A., Reuser A. J., Keijzer W., Westerveld A., Bootsma D. Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff's disease: intergenic complementation after somatic cell hybridization. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Aug;87(2):444–448. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galjaard H., Mekes M., Josselin de Jong JE D. E., Niermeijer M. F. A method for rapid prenatal diagnosis of glycogenosis II (Pompe's disease). Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Dec 27;49(3):361–375. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galjaard H., Van Hoogstraten J. J., De Josselin de Jong J. E., Mulder M. P. Methodology of the quantitative cytochemical analysis of single or small numbers of cultured cells. Histochem J. 1974 Jul;6(4):409–429. doi: 10.1007/BF01012433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerbie A. B., Melancon S. B., Ryan C., Nadler H. L. Cultivated epithelial-like cells and fibroblasts from amniotic fluid: their relationship to enzymatic and cytologic analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Oct 1;114(3):314–320. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90608-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Globus M. S., Conte F. A., Schneider E. L., Epstein C. J. Intrauterine diagnosis of genetic defects: results, problems, and follow-up of one hundred cases in a prenatal genetic detection center. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Apr 1;118(7):897–905. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(74)90658-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. W., Neufeld E. F. Alpha-L-iduronidase activity in cultured skin fibroblasts and amniotic fluid cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Oct;158(2):817–821. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90577-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R., Jennison R. F., Barson A. J., Laurence K. M., Ruoslahti E., Seppälä M. Comparison of amniotic-fluid and maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein levels in the early antenatal diagnosis of spina bifida and anencephaly. Lancet. 1974 Mar 16;1(7855):428–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn K., Lucas M., Wallace I. Precise identification of various chromosomal abnormalities. Ann Hum Genet. 1973 Apr;36(4):375–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1973.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoo J. J., Latta E., Schaumlöffel E. Antenatal diagnosis of maple syrup urine disease. Z Kinderheilkd. 1974;118(3):225–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00464613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. B. Behavioral implications of the human XYY genotype. Science. 1973 Jan 12;179(4069):139–150. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4069.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. Y., Dubin E. C., Kerenyi T., Hirschhorn K. Results and pitfalls in prenatal cytogenetic diagnosis. J Med Genet. 1973 Jun;10(2):112–119. doi: 10.1136/jmg.10.2.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. Y., Hirschhorn K. Prenatal diagnosis of genetic disease. Life Sci. 1974 Jun 16;14(12):2311–2336. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A. Correlation between euploid structural chromosome rearrangements and mental subnormality in humans. Nature. 1974 May 10;249(453):164–165. doi: 10.1038/249164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Melville M., Ratcliffe S., Keay A. J., Syme J. A cytogenetic survey of 11,680 newborn infants. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 May;37(4):359–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson C. B., Barter R. H. Intrauterine diagnosis and management of genetic defects. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1967 Nov 15;99(6):796–807. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(67)90395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback M. M., Leonard C. O., Parmley T. H. Intrauterine diagnosis: comparative enzymology of cells cultivated from maternal skin, fetal skin, and amniotic fluid cells. Pediatr Res. 1971 Aug;5(8):366–371. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197108000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback M. M., Sloan H. R., Sonneborn M., Herndon R. M., Percy A. K. Gm-gangliosidosis type I: in utero detection and fetal manifestations. J Pediatr. 1973 Jun;82(6):1037–1041. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80438-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kardon N. B., Chernay P. R., Hsu L. Y., Martin J. L., Hirschhorn K. Pitfalls in prenatal diagnosis resulting from chromosomal mosaicism. J Pediatr. 1972 Feb;80(2):297–299. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80597-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurence K. M., Turnbull A. C., Harris R., Jennison R. F., Ruoslahti E., Seppälä M. Letter: Antenatal diagnosis of spina bifida. Lancet. 1973 Oct 13;2(7833):860–860. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90920-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. L., Gregson N. M., Walker S. Eliminating red blood-cells from amniotic-fluid samples. Lancet. 1970 Aug 8;2(7667):316–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy J. G., Van Elsen A. F., Martin J. J., Dumon J. E., Hulet A. E., Okada S., Navarro C. Infantile metachromatic leukodystrophy. Confirmation of a prenatal diagnosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jun 28;288(26):1365–1369. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197306282882602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lie S. O., Schofield B. H., Taylor H. A., Jr, Doty S. B. Structure and function of the lysosomes of human fibroblasts in culture: dependence on medium pH. Pediatr Res. 1973 Jan;7(1):13–19. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197301000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlefield J. W. Problems in the use of cultured amniotic fluid cells for biochemical diagnoses. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1971 Apr;7(5):15–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowden J. A., Cutz E., Conen P. E., Rudd N., Doran T. A. Prenatal diagnosis of G M1 -gangliosidosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 1;288(5):225–228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302012880502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milunsky A., Alpert E. The value of alpha-fetoprotein in the prenatal diagnosis of neural tube defects. J Pediatr. 1974 Jun;84(6):889–893. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80776-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milunsky A., Atkins L., Littlefield J. W. Amniocentesis for prenatal genetic studies. Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Jul;40(1):104–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milunsky A., Atkins L. Prenatal diagnosis of genetic disorders. An analysis of experience with 600 cases. JAMA. 1974 Oct 14;230(2):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milunsky A., Littlefield J. W. The prenatal diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism. Annu Rev Med. 1972;23:57–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.23.020172.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler H. L. Antenatal detection of hereditary disorders. Pediatrics. 1968 Dec;42(6):912–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler H. L., Gerbie A. B. Role of amniocentesis in the intrauterine detection of genetic disorders. N Engl J Med. 1970 Mar 12;282(11):596–599. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197003122821105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler H. L., Messina A. M. In-utero detection of type-II glycogenosis (pompe's disease). Lancet. 1969 Dec 13;2(7633):1277–1278. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90811-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler H. L. Prenatal detection of genetic defects. J Pediatr. 1969 Jan;74(1):132–143. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler H. L. Prenatal detection of genetic disorders. Adv Hum Genet. 1972;3:1–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon R., Padeh B. Prenatal diagnosis of Tay-Sachs genotypes. Br Med J. 1971 Oct 2;4(5778):17–20. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5778.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niermeijer M. F., Halley D., Sachs E., Tichelaar-Klepper C., Garver K. L. Transport and storage of amniotic fluid samples for prenatal diagnosis of metabolic diseases. Humangenetik. 1973;20(2):175–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00284856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niermeijer M. F., Koster J. F., Jahodova M., Fernandes J., Heukels-Dully M. J., Galjaard H. Prenatal diagnosis of type II glycogenosis (Pompe's disease) using microchemical analyses. Pediatr Res. 1975 May;9(5):498–503. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197505000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S., Okada S., Chen A., Fillerup D. L. Tay-sachs disease. Detection of heterozygotes and homozygotes by serum hexosaminidase assay. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jul 2;283(1):15–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197007022830104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada S., Veath M. L., Leroy J., O'Brien J. S. Ganglioside GM2 storage diseases: hexosaminidase deficiencies in cultured fibroblasts. Am J Hum Genet. 1971 Jan;23(1):55–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip J., Bang J., Hahnemann N., Mikkelsen M., Niebuhr E., Rebbe H., Weber J. Chromosome analysis of fetuses in risk pregnancies. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand Suppl. 1974;29:9–14. doi: 10.3109/00016347409157184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott G. H., Pernoll M. L., Hecht F., Nicholas A. A prenatal diagnosis clinic: an initial report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1973 Aug 1;116(7):942–948. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)33841-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Bowes W., Droegemueller W., Puck M., Goodman S., Shikes R., Greenshur A. Intrauterine diagnosis: potential complications. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1973 Aug 1;116(7):937–941. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)33840-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. B., Russell J. D., Littlefield J. W. -glucuronidase activity in fibroblasts cultured from persons with and without cystic fibrosis. J Med Genet. 1971 Dec;8(4):441–443. doi: 10.1136/jmg.8.4.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C. A., Lee S. Y., Nadler H. L. Effect of culture conditions on enzyme activities in cultivated human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1972;71(2):388–392. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90308-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAPIRO S., JONES E. W., DENSEN P. M. A life table of pregnancy terminations and correlates of fetal loss. Milbank Mem Fund Q. 1962 Jan;40:7–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. L., Stanbridge E. J., Epstein C. J., Golbus M., Abbo-Halbasch G., Rodgers G. Mycoplasma contamination of cultured amniotic fluid cells: potential hazard to prenatal chromosomal diagnosis. Science. 1974 Apr 26;184(4135):477–480. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4135.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skovby F., Niebuhr E. Presumably balanced translocations involving the same band of chromosome No. 4 found in two mentally retarded, dysmorphic individuals. Ann Genet. 1974 Dec;17(4):243–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele M. W., Breg W. R., Jr Chromosome analysis of human amniotic-fluid cells. Lancet. 1966 Feb 19;1(7434):383–385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91387-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therkelsen A. J., Petersen G. B., Steenstrup O. R., Jonasson J., Lindsten J., Zech L. Prenatal diagnosis of chromosome abnormalities. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1972 Jul;61(4):397–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1972.tb15854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlström J., Bartsch F. K., Lundberg J. Prenatal chromosome determination. A study of 219 cases. Clin Genet. 1974;6(3):184–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1974.tb00648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward A. M., Stewart C. R. Letter: False-positive results in antenatal diagnosis of neural-tube disorders. Lancet. 1974 Aug 10;2(7876):345–346. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91717-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendel U., Wöhler W., Goedde H. W., Langenbeck U., Passarge E., Rüdiger H. W. Rapid diagnosis of maple syrup urine disease (branched chain ketoaciduria) by micro-enzyme assay in leukocytes and fibroblasts. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 May 30;45(4):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Hagen C. B., Borresen A. L., Molne K., Oftedal G., Bjoro K., Berg K. Metachromatic leukodystrophy. I. Prenatal detection of arylsulphatase A deficiency. Clin Genet. 1973;4(3):256–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ploeg M., Ploem J. S. Filter combinations and light sources for fluorescence microscopy of quinacrine mustard or quinacrine stained chromosomes. Histochemie. 1973;33(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00304227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]