Abstract
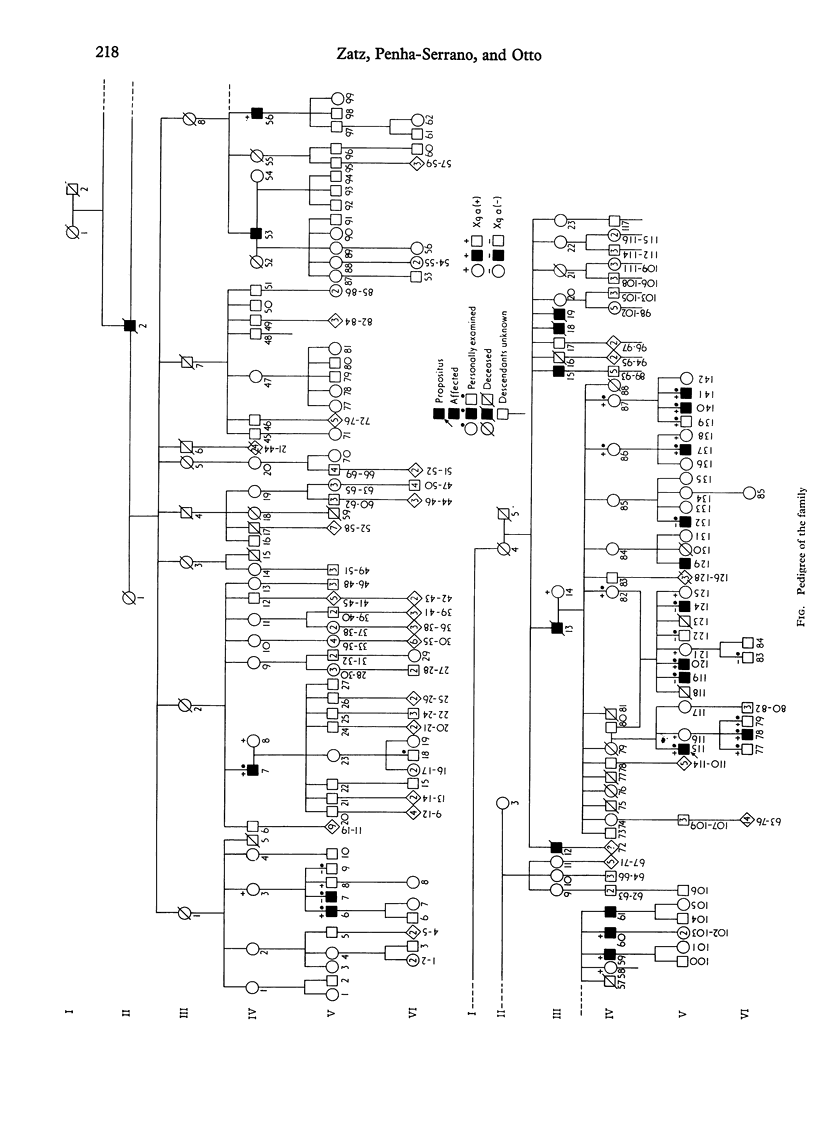
A family with 24 males affected by an X-linked type of spastic paraplegia is reported. Twelve affected members were personally examined showing the pure form of the disease. Half of the affected males had many descendants, all normal. Linkage studies strongly suggest that this X-linked form of spastic paraplegia and Xg loci are not at a measurable distance on the X chromosome.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AAGENAES O. Hereditary spastic paraplegia. A family with ten injured. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1959;34:489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1959.tb07537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLUMEL J., EVANS E. B., EGGERS G. W. Hereditary cerebral palsy; a preliminary report. J Pediatr. 1957 Apr;50(4):454–458. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(57)80255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery A. E. Genetic linkage between the loci for colour blindness and Duchenne type muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1966 Jun;3(2):92–95. doi: 10.1136/jmg.3.2.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
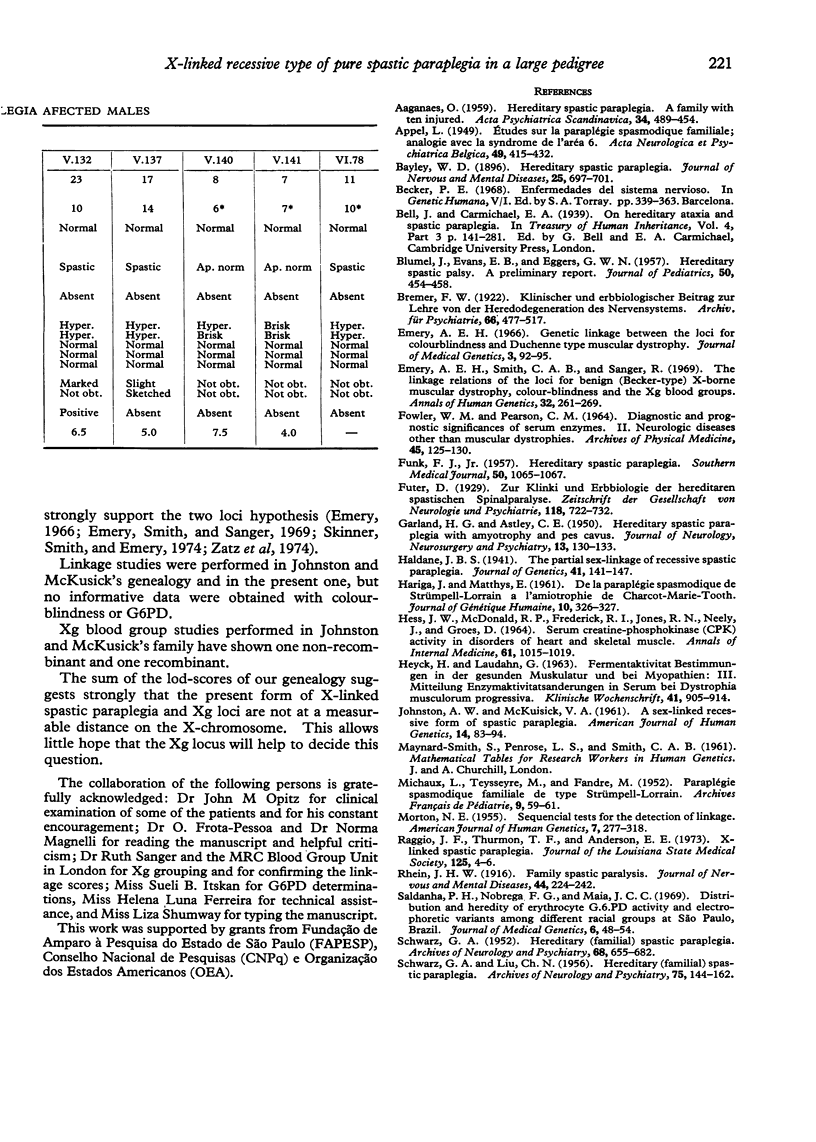
- Emery A. E., Smith C. A., Sanger R. The linkage relations of the loci for benign (Becker type) X-borne muscular dystrophy, colour blindness and the Xg blood groups. Ann Hum Genet. 1969 Jan;32(3):261–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1969.tb00075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOWLER W. M., Jr, PEARSON C. M. DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF SERUM ENZYMES. II. NEUROLOGIC DISEASES OTHER THAN MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1964 Mar;45:125–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUNK F. J., Jr Hereditary spastic paraplegia. South Med J. 1957 Aug;50(8):1065–1067. doi: 10.1097/00007611-195708000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARLAND H. G., ASTLEY C. E. Hereditary spastic paraplegia with amyotrophy and pes cavus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1950 May;13(2):130–133. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.13.2.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS J. W., MACDONALD R. P., FREDERICK R. J., JONES R. N., NEELY J., GROSS D. SERUM CREATINE PHOSPHOKINASE (CPK) ACTIVITY IN DISORDERS OF HEART AND SKELETAL MUSCLE. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Dec;61:1015–1028. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-61-6-1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
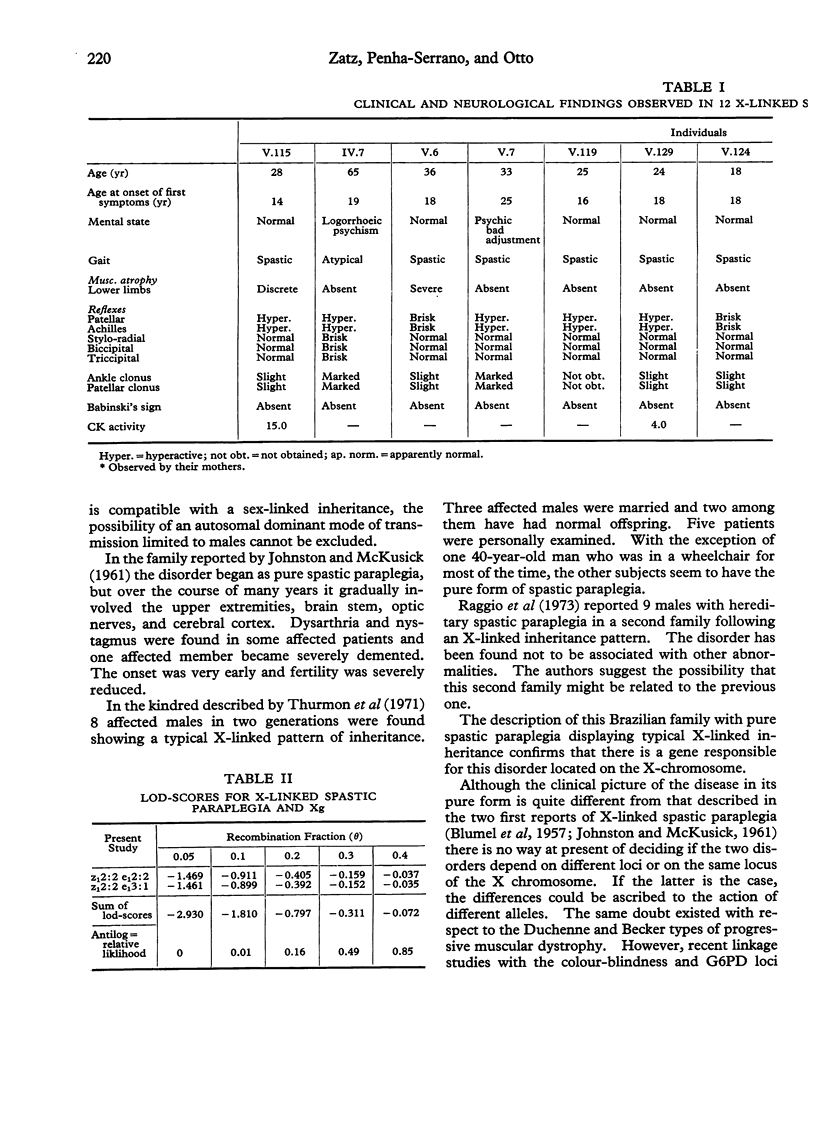
- JOHNSTON A. W., McKUSICK V. A. A sex-linked recessive form of spastic paraplegia. Am J Hum Genet. 1962 Mar;14:83–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAUX L., TEYSSEYRF, FANDRE M. Paraplégie spasmodigue familiale de type Strumpell-Lorrain. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1952;9(1):59–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. Sequential tests for the detection of linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1955 Sep;7(3):277–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raggio J. F., Thurmon T. F., Anderson E. E. X-linked hereditary spastic paraplegia. J La State Med Soc. 1973 Jan;125(1):4–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARZ G. A. Hereditary (familial) spastic paraplegia. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1952 Nov;68(5):655–662. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1952.02320230081010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARZ G. A., LIU C. N. Hereditary (familial) spastic paraplegia; further clinical and pathologic observations. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1956 Feb;75(2):144–162. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1956.02330200038005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saldanha P. H., Nóbrega F. G., Maia J. C. Distribution and heredity of erythrocyte G6PD activity and electrophoretic variants among different racial groups at São Paulo, Brazil. J Med Genet. 1969 Mar;6(1):48–54. doi: 10.1136/jmg.6.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner R., Smith C., Emery A. E. Linkage between the loci for benign (Becker-type) X-borne muscular dystrophy and deutan colour blindness. J Med Genet. 1974 Dec;11(4):317–320. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.4.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurmon T. F., Walker B. A., Scott C. I., Abbott M. H. Two kindreds with a sex-linked recessive form of spastic paraplegia. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1971 Feb;7(1):219–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN BOGAERT L. Etude génétique sur les paraplégies spasmodiques familiales. J Genet Hum. 1952 May;1(1):6–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M., Itskan S. B., Sanger R., Frota-Pessoa O., Saldanha P. H. New linkage data for the X-linked types of muscular dystrophy and G6PD variants, colour blindness, and Xg blood groups. J Med Genet. 1974 Dec;11(4):321–327. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.4.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M., Penha-Serrano C., Frota-Pessoa O., Klein D. A malignant form of neurogenic muscular atrophy in adults, with dominant inheritance. J Genet Hum. 1971 Dec;19(4):337–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


