Abstract
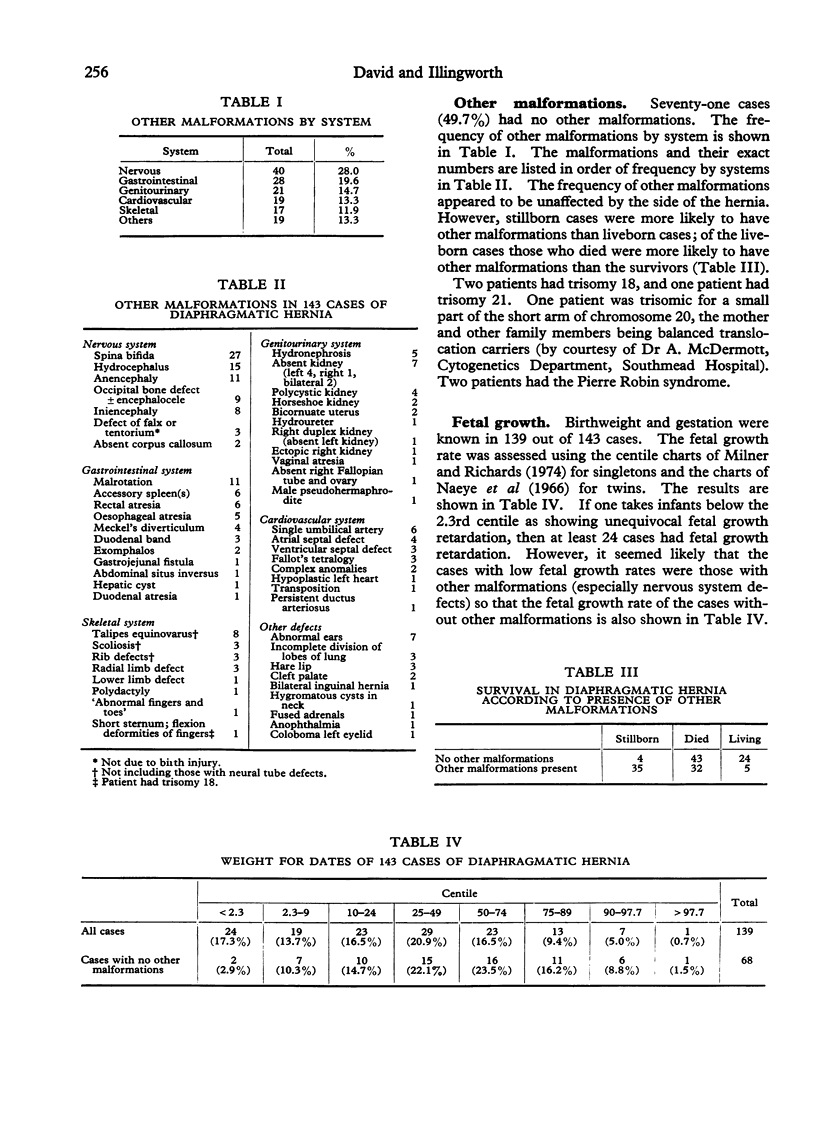
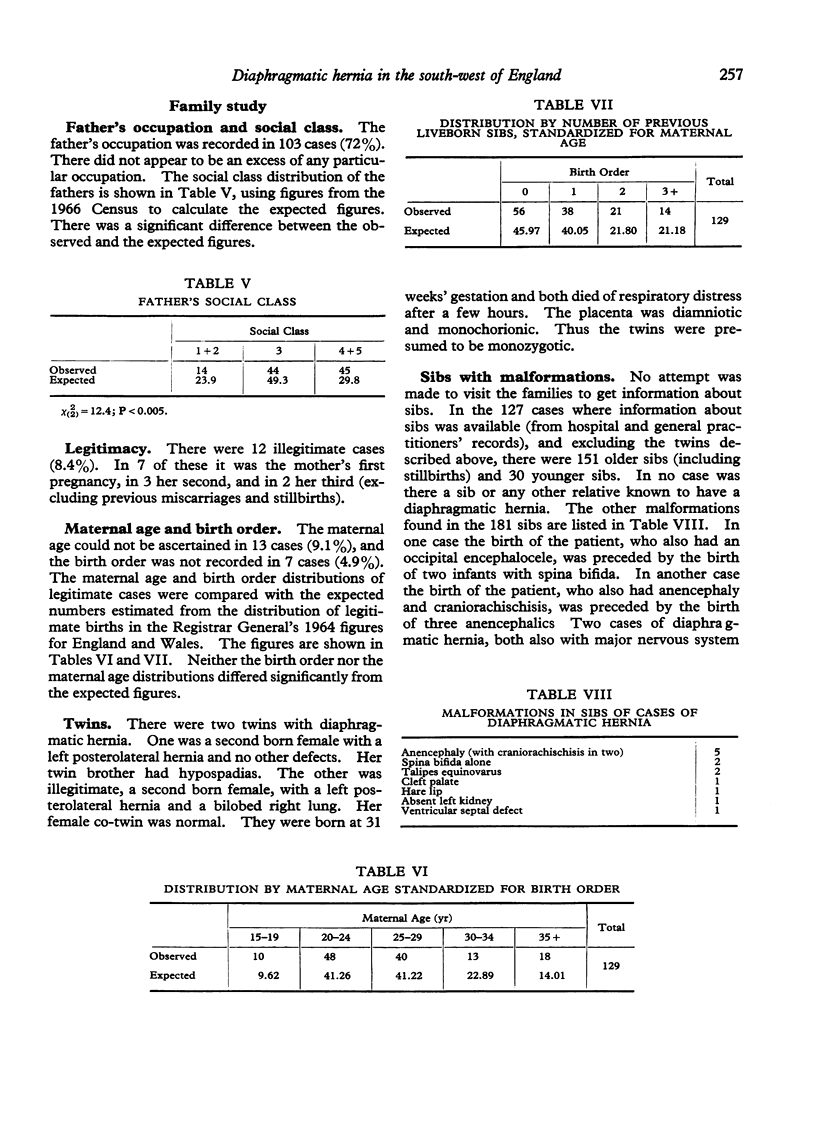
A retrospective anatomical, family, and epidemiological study was made of 143 patients (81 female and 62 male) with diaphragmatic hernia who were born in the south-west of England between 1943 and 1974. Thirty-nine cases were stillborn. Seventy-five per cent of patients had a left-sided diaphragmatic defect, 22% had a right-sided defect, and 3% had a bilateral defect. Fifty per cent of the patients had other congenital malformations, most frequently of the nervous system. No maternal age or birth order effect was noted. Cases of diaphragmatic hernia without other malformations had in general a normal fetal growth rate. Eight per cent of the cases were illegitimate. There were two pairs of twins discordant for diaphragmatic hernia, one pair being dizygotic and the other monozygotic. In no case of diaphragmatic hernia was there a relative affected with a diaphragmatic hernia. The most common type of diaphragmatic defect was a posterolateral hernia (92%), followed in frequency by an eventration of the diaphragm (5%), the least common defect being a retrocostosternal hernia (2%). Diaphragmatic hernia appears to be aetiologically as well as anatomically heterogeneous. In this series there were two cases of trisomy 18, one case of trisomy 21, one case trisomic for a small part of chromosome 20, and two cases with the Pierre Robin syndrome. It seems likely that diaphragmatic hernia is a non-specific consequence of several teratological processes.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN D. H. Effect of diet during pregnancy upon the incidence of congenital hereditary diaphragmatic hernia in the rat; failure to produce cystic fibrosis of the pancreas by maternal vitamin A deficiency. Am J Pathol. 1949 Jan;25(1):163–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahrend T. R., Thompson B. W. Hernia of the foramen of Bochdalek in the adult. Am J Surg. 1971 Nov;122(5):612–615. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(71)90288-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODEY R. S., RATCLIFFE H. L. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia in the tiger; two case reports. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1956 Aug 1;129(3):100–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER N., CLAIREAUX A. E. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia as a cause of perinatal mortality. Lancet. 1962 Mar 31;1(7231):659–663. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)92878-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baran E. M., Houston H. E., Lynn H. B., O'Connell E. J. Foramen of Morgagni hernias in children. Surgery. 1967 Dec;62(6):1076–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barash B. A., Freedman L., Opitz J. M. Anatomic studies in the 18-trisomy syndrome. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1970 Oct;6(4):3–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K., Dawes G. S. Fetal breathing. Br Med Bull. 1975 Jan;31(1):3–7. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyden E. A. The structure of compressed lungs in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Anat. 1972 Aug;134(4):497–507. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001340407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs V. A., Reilly B. J., Loewig K. Lung hypoplasia and membranous diaphragm in the congenital rubella syndrome--a rare case. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1973 Jun;24(2):126–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTER R. E., WATERSTON D. J., ABERDEEN E. Hernia and eventration of the diaphragm in childhood. Lancet. 1962 Mar 31;1(7231):656–659. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)92877-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalona W. J., Crowder W. L., Chretien P. B. Occurrence of hernia of Morgagni with filial cervical lung hernia: a hereditary defect of the cervical mesenchyme? Chest. 1972 Sep;62(3):340–342. doi: 10.1378/chest.62.3.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnock E. L., Doershuk C. F. Developmental aspects of the human lung. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1973 May;20(2):275–292. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)32843-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatrath R. R., el-Shafie M., Jones R. S. Fate of hypoplastic lungs after repair of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Arch Dis Child. 1971 Oct;46(249):633–635. doi: 10.1136/adc.46.249.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaurasia B. D. Single umbilical artery with caudal defects in human fetuses. Teratology. 1974 Jun;9(3):287–297. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420090308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claveau R., Chalifoux A., Bonneau N. H. Une hernie diaphragmatique avec effusion pleurale chez un chien. Can Vet J. 1973 Nov;14(11):277–279. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Jr Macroglossia, omphalocele, visceromegaly, cytomegaly of the adrenal cortex and neonatal hypoglycemia. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1971 Jun;7(7):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENNIS S. M., NAIRN M. E. TWO CASES OF CONGENITAL DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA IN AUSTRALIAN MERINO LAMBS. Vet Rec. 1965 Jun 26;77:754–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David T. J., Nixon A. Congenital malformations associated with anencephaly and iniencephaly. J Med Genet. 1976 Aug;13(4):263–265. doi: 10.1136/jmg.13.4.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Done S. H., Drew R. A. Aperture in the diaphragm with protrusion of abnormal liver tissue. A report of three cases in the ox. Br Vet J. 1972 Nov;128(11):553–559. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)36684-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan E. J. CONGENITAL DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA. Ann Surg. 1938 Sep;108(3):374–388. doi: 10.1097/00000658-193809000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan E. J. Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia. Ann Surg. 1945 Oct;122(4):569–581. doi: 10.1097/00000658-194510000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold M. Aplasia of the diaphragm. Pediatrics. 1971 Mar;47(3):601–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman D. B., Bree M. M., Cohen B. J. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia in neonatal dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1968 Oct 1;153(7):942–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. R., Crary D. D. Hereditary diaphragmatic hernia in the rabbit. J Hered. 1973 Nov-Dec;64(6):333–336. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a108435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIFFIN R. M. CONGENITAL DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA IN THE PIGLET. Vet Rec. 1965 May 1;77:492–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood R. D., Rosenthal A., Sommer A., Wolff G., Craenen J. Cardiovascular malformations in oculoauriculovertebral dysplasia (Goldenhar syndrome). J Pediatr. 1974 Dec;85(6):816–818. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80349-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. S. Congenital myotonic dystrophy in Britain. I. Clinical aspects. Arch Dis Child. 1975 Jul;50(7):505–513. doi: 10.1136/adc.50.7.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M., Altrogge H. C. Familiäre Zwerchfellagenesie. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1971 Nov;119(11):609–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Deaner R. M., Koop C. E. Diaphragmatic hernia in infancy: factors affecting the mortality rate. Surgery. 1967 Dec;62(6):1082–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAJII T., OIKAWA K., ITAKURA K., OHSAWA T. A PROBABLE 17-18 TRISOMY SYNDROME WITH PHOCOMELIA, EXOMPHALOS, AND AGENESIS OF HEMIDIAPHRAGM. Arch Dis Child. 1964 Oct;39:519–522. doi: 10.1136/adc.39.207.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRKLAND J. A. Congenital posterolateral diaphragmatic hernia in the adult. Br J Surg. 1959 Jul;47:16–22. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004720103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOX G. Secular pattern of congenital oesophageal atresia. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1959 Oct;13:222–226. doi: 10.1136/jech.13.4.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J. Rate and type of congenital anomalies among offspring of diabetic women. J Reprod Med. 1971 Aug;7(2):73–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kup J. Zwerchfelldefekt nach Abtreibungsversuch mit Chinin. Kasuistische Beobachtung. Munch Med Wochenschr. 1967 Dec 8;109(49):2582–2583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESTER J., VESTERDAL J., SMITH C. C. W. Twenty-one cases of anterior and posterior diaphragmatic hernias in children. Acta Paediatr. 1959 Mar;48(2):175–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leck I., Record R. G., McKeown T., Edwards J. H. The incidence of malformations in Birmingham, England, 1950-1959. Teratology. 1968 Aug;1(3):263–280. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420010305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M. Letter: congenital diaphragmatic hernia in the calf. Vet Rec. 1974 Feb 2;94(5):102–102. doi: 10.1136/vr.94.5.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTINS H. Uber eine familiäre Zwerchfellmissbildung. Zentralbl Gynakol. 1952;74(24):951–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. D., Richards B. An analysis of birth weight by gestational age of infants born in England and Wales, 1967 to 1971. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1974 Dec;81(12):956–967. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1974.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeye R. L., Benirschke K., Hagstrom J. W., Marcus C. C. Intrauterine growth of twins as estimated from liveborn birth-weight data. Pediatrics. 1966 Mar;37(3):409–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILIPP E. E., SKELTON M. O. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia in siblings. Br Med J. 1952 Jun 14;1(4771):1283–1284. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4771.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUTSCHAR W. G., MANION W. C. Congenital absence of the spleen and associated anomalies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1956 May;26(5):429–470. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/26.5.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passarge E., Halsey H., German J. Unilateral agenesis of the diaphragm. Humangenetik. 1968;5(3):226–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00281959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priester W. A., Glass A. G., Waggoner N. S. Congenital defects in domesticated animals: general considerations. Am J Vet Res. 1970 Oct;31(10):1871–1879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reale F. R., Esterly J. R. Pulmonary hypoplasia: a morphometric study of the lungs of infants with diaphragmatic hernia, anencephaly, and renal malformations. Pediatrics. 1973 Jan;51(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLATER B. C., WATSON G. I., MCDONALD J. C. SEASONAL VARIATION IN CONGENITAL ABNORMALITIES. PRELIMINARY REPORT OF A SURVEY CONDUCTED BY THE RESEARCH COMMITTEE OF COUNCIL OF THE COLLEGE OF GENERAL PRACTITIONERS. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1964 Jan;18:1–7. doi: 10.1136/jech.18.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER R., ROGERSON M. M. Perforated peptic ulcer in a mongoloid infant associated with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Arch Dis Child. 1951 Dec;26(130):566–569. doi: 10.1136/adc.26.130.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. L., Cohn R. A., Haller J. A., Jr Diaphragmatic hernia, three legs, two penises, and imperforate anus: a complete salvage problem in a newborn. J Pediatr Surg. 1974 Aug;9(4):525–529. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(74)80019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. M., Paterson L. Monozygous anencephalic triplets--a case report. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1966 Feb;73(1):147–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1966.tb05134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby L. A., Hopps H. C., Edmonds L. D. Comparative aspects of congenital malformations in man and swine. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1971 Dec 1;159(11):1485–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Grosfeld J. L. Trisomy E and T-E fistula. J Med Genet. 1970 Mar;7(1):70–74. doi: 10.1136/jmg.7.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symbas P. N., Ware R. E. A syndrome of defects of the thoracoabdominal wall, diaphragm, pericardium, and heart. One-stage surgical repair and analysis of the syndrome. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1973 Jun;65(6):914–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. I. Autosomal trisomy syndromes: a detailed study of 27 cases of Edwards' syndrome and 27 cases of Patau's syndrome. J Med Genet. 1968 Sep;5(3):227–252. doi: 10.1136/jmg.5.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorburn M. J., Wright E. S., Miller C. G., Smith-Read E. H. Exomphalos-macroglossia-gigantism syndrome in Jamaican infants. Am J Dis Child. 1970 Apr;119(4):316–321. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1970.02100050318006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyama W. M. Combined congenital defects of the anterior abdominal wall, sternum, diaphragm, pericardium, and heart: a case report and review of the syndrome. Pediatrics. 1972 Nov;50(5):778–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON J. G., ROTH C. B., WARKANY J. An analysis of the syndrome of malformations induced by maternal vitamin A deficiency. Effects of restoration of vitamin A at various times during gestation. Am J Anat. 1953 Mar;92(2):189–217. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000920202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warkany J., Passarge E., Smith L. B. Congenital malformations in autosomal trisomy syndromes. Am J Dis Child. 1966 Dec;112(6):502–517. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1966.02090150046002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. P., 3rd, Newton C. D., Burt J. K. A review of 116 diaphragmatic hernias in dogs and cats. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1971 Nov 1;159(9):1142–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. G., Gavan J. A. Congenital malformations in nonhuman primates: spontaneous and experimentally induced. Anat Rec. 1967 May;158(1):99–109. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091580111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolloch Y., Grunebaum M., Glanz I., Dintsman M. Symptomatic retrosternal (Morgagni) hernia. Am J Surg. 1974 May;127(5):601–605. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(74)90327-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannetti G., Piccinini V. [Diaphragmatic hernia in the dog]. Folia Vet Lat. 1974 Jan;4(1):71–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zólciński A., Heimrath T., Ujec M. Chinina jako przyczyna wad rozwojowych płodu. Ginekol Pol. 1965 Aug;36(8):935–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Kate L. P., Anders G. J. Unilateral agenesis of the diaphragm. Humangenetik. 1970;8(4):366–367. doi: 10.1007/BF00280341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


