Abstract
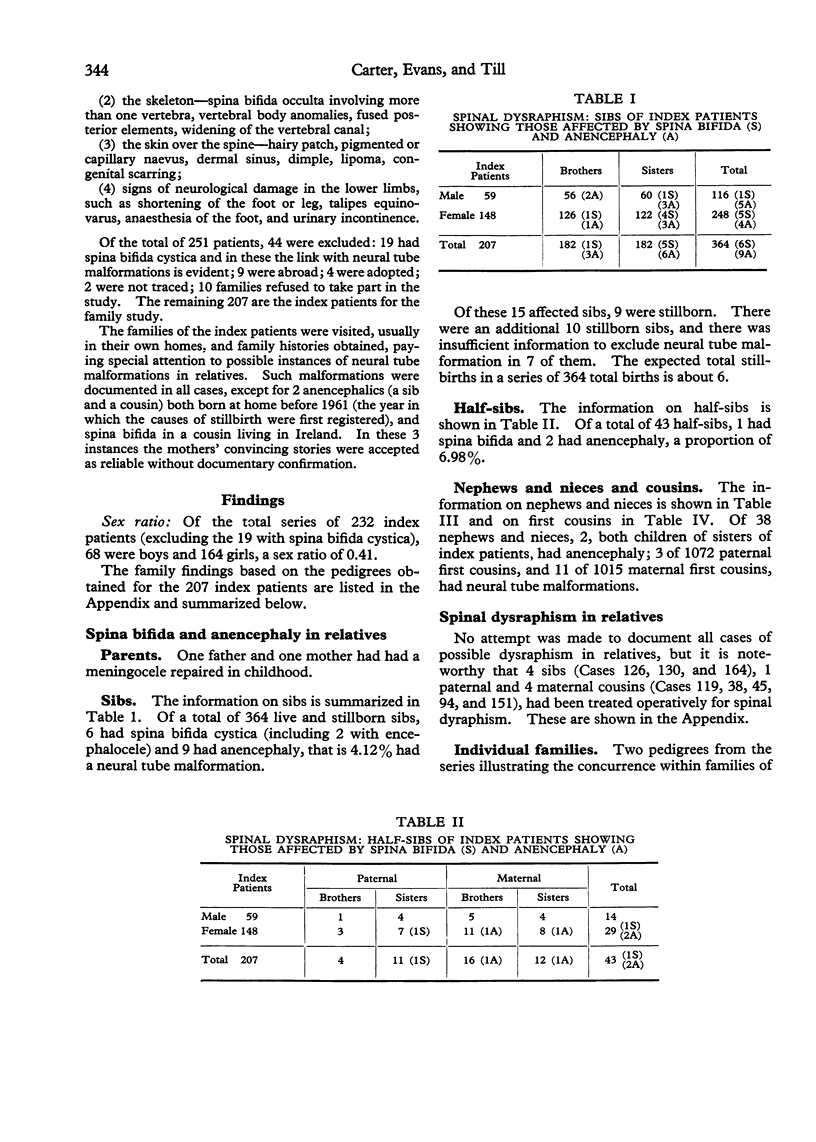
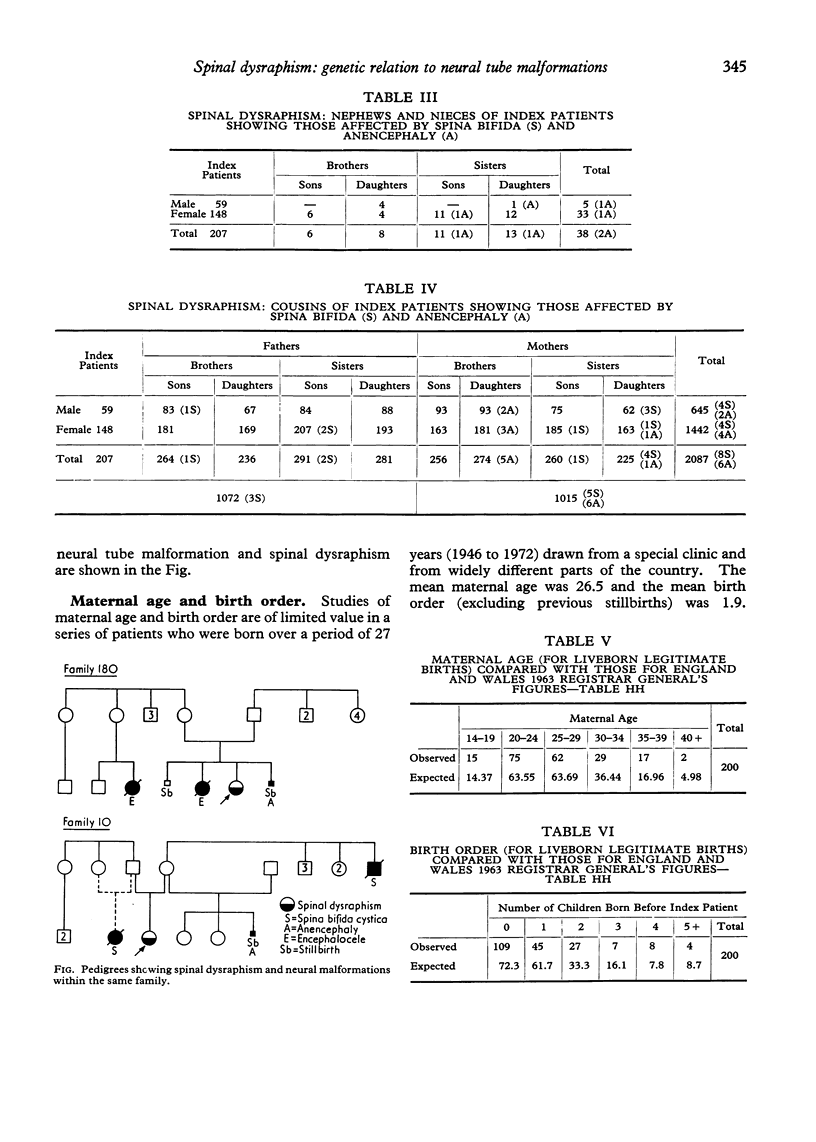
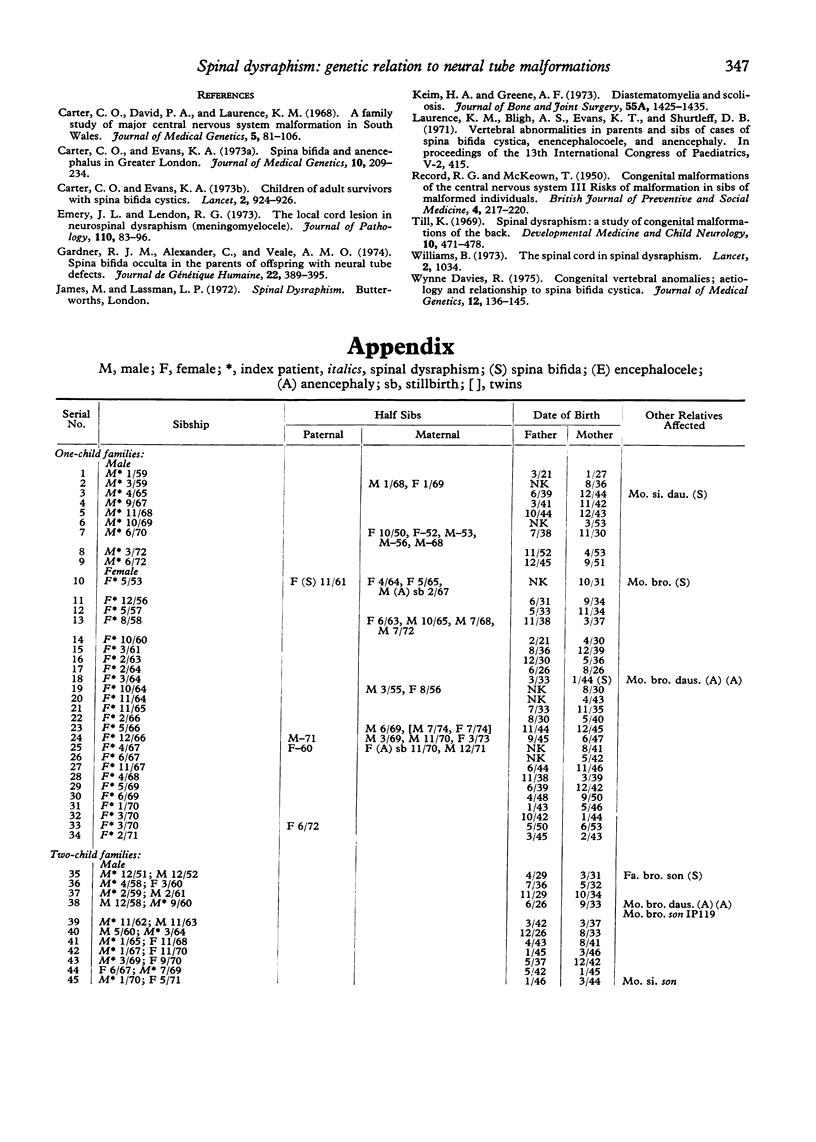
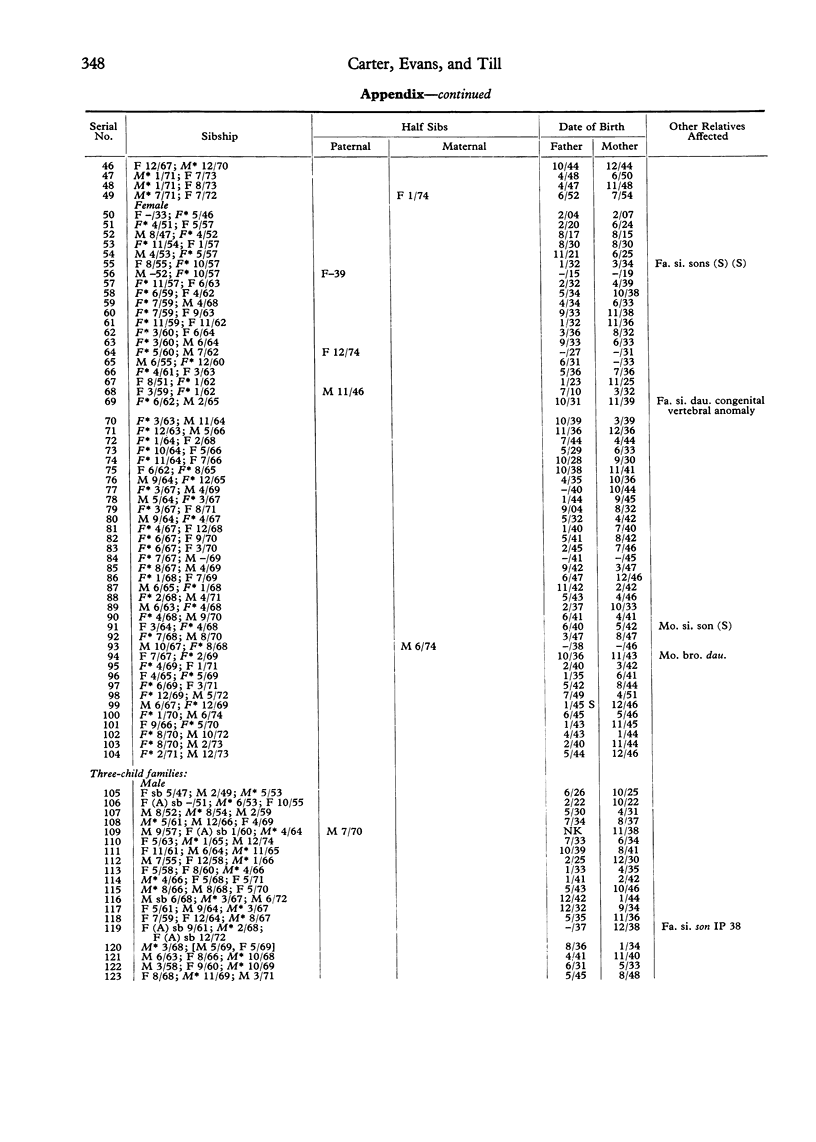
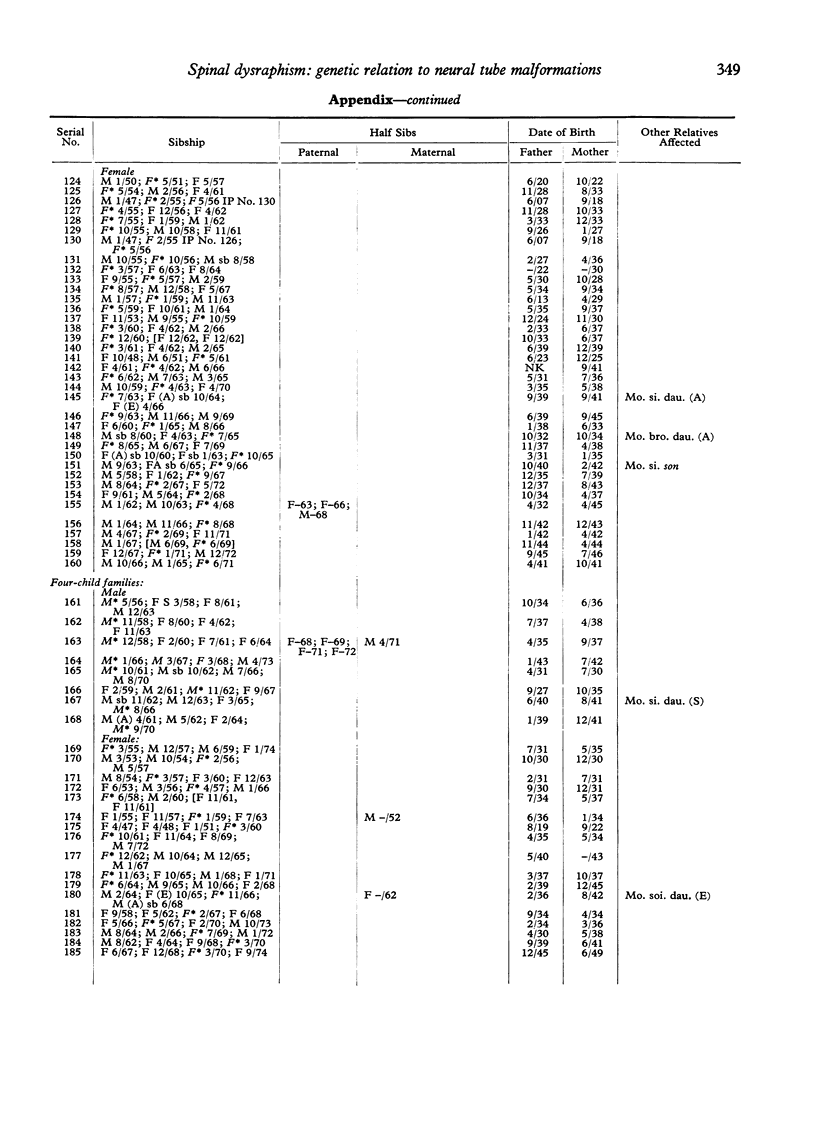
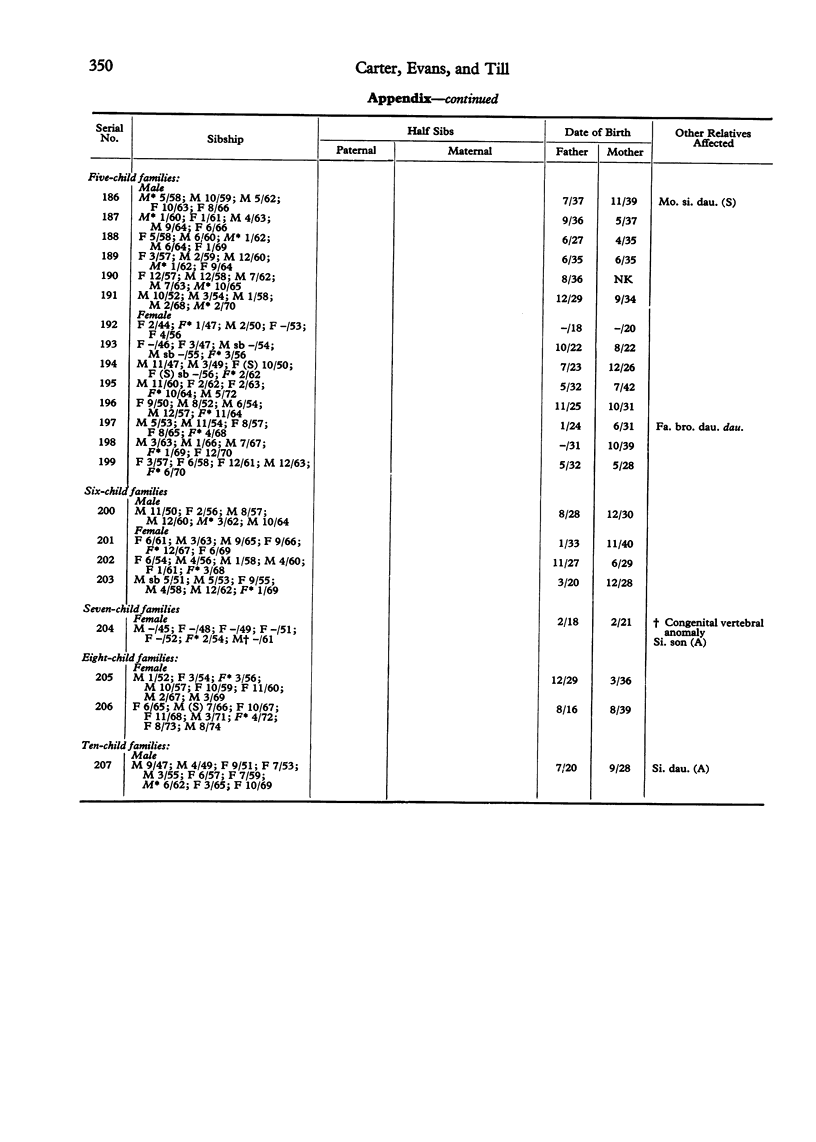
The families of 207 index patients treated for spinal dysraphism at The Hospital for Sick Children were studied to discover whether the condition was aetiologically related to the classical neural tube malformation--spina bifida cystica and anencephaly. The index patients had all had a tethered conus medullaris and one or more of a variety of anomalies of the spinal cord, vertebrae, or skin overlying the vertebral column. Of 364 sibs of index patients, 9 had an encephaly and 6 spina bifida cystica, a pro-proportion of 4.12%. This approximates to the proportion of sibs affected by neural tube malformations in the London region when the index patients themselves have spina bifida or anencephaly. It is, therefore, appropriate that the mothers of children with spinal dysraphism should be offered prenatal screening for neural tube malformations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter C. O., David P. A., Laurence K. M. A family study of major central nervous system malformations in South Wales. J Med Genet. 1968 Jun;5(2):81–106. doi: 10.1136/jmg.5.2.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. O., Evans K. Children of adult survivors with spina bifida cystica. Lancet. 1973 Oct 27;2(7835):924–926. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. O., Evans K. Spina bifida and anencephalus in greater London. J Med Genet. 1973 Sep;10(3):209–234. doi: 10.1136/jmg.10.3.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery J. L., Lendon R. G. The local cord lesion in neurospinal dysraphism (meningomyelocele). J Pathol. 1973 May;110(1):83–96. doi: 10.1002/path.1711100110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. J., Alexander C., Veale A. M. Spina bifida occulta in the parents of offspring with neural tube defects. J Genet Hum. 1974 Dec;22(4):389–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keim H. A., Greene A. F. Diastematomyelia and scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973 Oct;55(7):1425–1435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECORD R. G., McKEOWN T. Congenital malformations of the central nervous system. III. Risk of malformation in sibs of malformed individuals. Br J Soc Med. 1950 Oct;4(4):217–220. doi: 10.1136/jech.4.4.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. Letter: The spinal cord in spina bifida. Lancet. 1973 Nov 3;302(7836):1034–1035. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


