Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
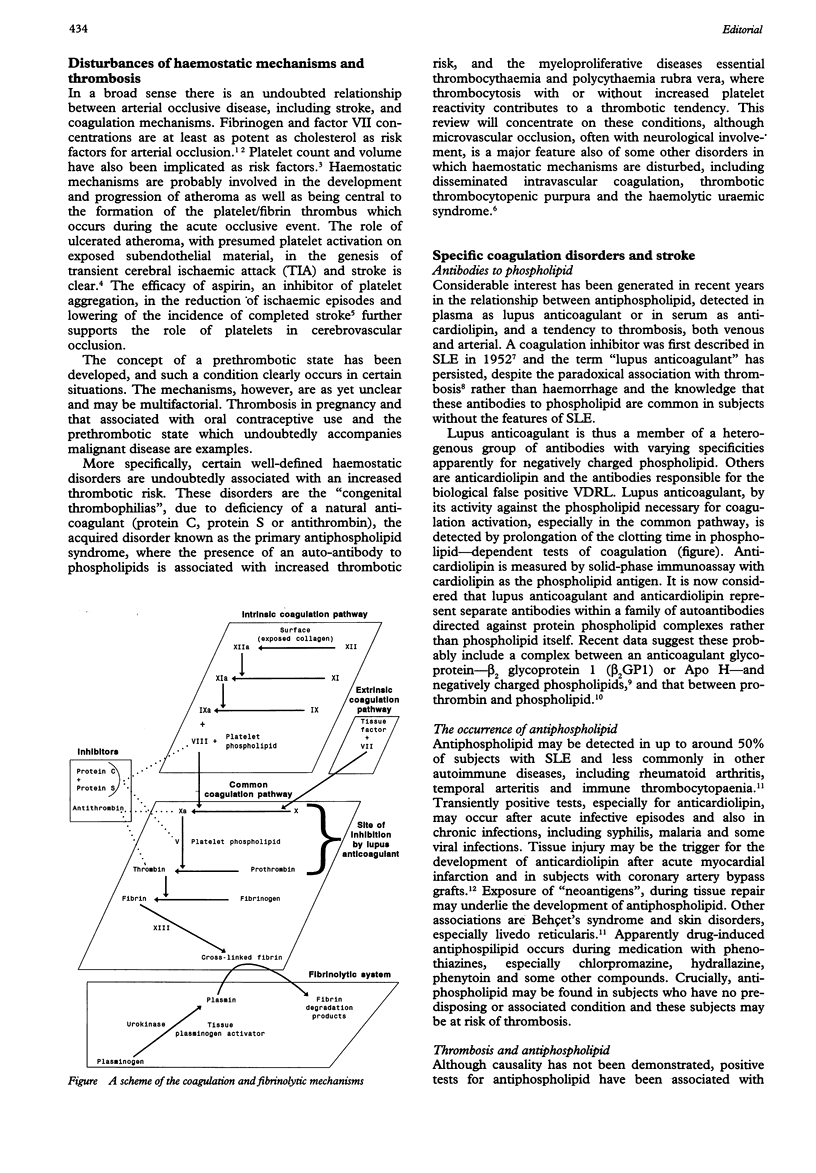
- Amarenco P., Duyckaerts C., Tzourio C., Hénin D., Bousser M. G., Hauw J. J. The prevalence of ulcerated plaques in the aortic arch in patients with stroke. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 23;326(4):221–225. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201233260402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambruso D. R., Jacobson L. J., Hathaway W. E. Inherited antithrombin III deficiency and cerebral thrombosis in a child. Pediatrics. 1980 Jan;65(1):125–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D., Bell D., Lodge R., Grant E. Recurrent cerebral ischemia and mitral valve vegetation in a patient with antiphospholipid antibodies. J Rheumatol. 1987 Aug;14(4):839–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angles-Cano E., Sultan Y., Clauvel J. P. Predisposing factors to thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: possible relation to endothelial cell damage. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Aug;94(2):312–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson R. A., Baguley E., Khamashta M. A., Hughes G. R. Multiple small-vessel occlusions in systemic lupus erythematosus. Stroke. 1989 Jan;20(1):127–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson R. A., Derksen R. H., Harris E. N., Bouma B. N., Gharavi A. E., Kater L., Hughes G. R. Chorea in systemic lupus erythematosus and "lupus-like" disease: association with antiphospholipid antibodies. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1987 May;16(4):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(87)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOWIE E. J., THOMPSON J. H., Jr, PASCUZZI C. A., OWEN C. A., Jr THROMBOSIS IN SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS DESPITE CIRCULATING ANTICOAGULANTS. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Sep;62:416–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbui T., Finazzi G., Falanga A., Cortelazzo S. Intravenous gammaglobulin, antiphospholipid antibodies, and thrombocytopenia. Lancet. 1988 Oct 22;2(8617):969–969. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92642-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbui T., Finazzi G., Mussoni L., Riganti M., Donati M. B., Colucci M., Collen D. Hereditary dysfunctional protein C (protein C Bergamo) and thrombosis. Lancet. 1984 Oct 6;2(8406):819–819. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90750-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belman A. L., Roque C. T., Ancona R., Anand A. K., Davis R. P. Cerebral venous thrombosis in a child with iron deficiency anemia and thrombocytosis. Stroke. 1990 Mar;21(3):488–493. doi: 10.1161/01.str.21.3.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benassi G., Ricci P., Calbucci F., Cacciatore F. M., D'Alessandro R. Slowly progressive ischemic stroke as first manifestation of essential thrombocythemia. Stroke. 1989 Sep;20(9):1271–1272. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.9.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevers E. M., Galli M., Barbui T., Comfurius P., Zwaal R. F. Lupus anticoagulant IgG's (LA) are not directed to phospholipids only, but to a complex of lipid-bound human prothrombin. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Dec 2;66(6):629–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch D. W., Scott J. R., Kochenour N. K., Hershgold E. Obstetric complications associated with the lupus anticoagulant. N Engl J Med. 1985 Nov 21;313(21):1322–1326. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198511213132104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. L., Hart R. G., Sherman D. G., Tegeler C. H. Antiphospholipid antibodies and cerebral ischemia in young people. Neurology. 1990 Aug;40(8):1190–1196. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.8.1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briley D. P., Coull B. M., Goodnight S. H., Jr Neurological disease associated with antiphospholipid antibodies. Ann Neurol. 1989 Mar;25(3):221–227. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIEVITZ E., THIEDE T. Complications and causes of death in polycythaemia vera. Acta Med Scand. 1962 Nov;172:513–523. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1962.tb07186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerlingo M., Finazzi G., Casto L., Laffranchi C., Barbui T., Mamoli A. Inherited protein C deficiency and nonhemorrhagic arterial stroke in young adults. Neurology. 1991 Sep;41(9):1371–1373. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.9.1371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cariou R., Tobelem G., Bellucci S., Soria J., Soria C., Maclouf J., Caen J. Effect of lupus anticoagulant on antithrombogenic properties of endothelial cells--inhibition of thrombomodulin-dependent protein C activation. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Aug 30;60(1):54–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casado Naranjo I., Martin Gonzalez R., Sancho Rieger J., Morera Guitart J., Calvo Catala J. Transient ischaemic attacks associated with thrombocytosis in active rheumatoid arthritis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Dec;51(12):1599–1599. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.12.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Nixon R. R., Cooper M. R., Esmon C. T. Familial protein S deficiency is associated with recurrent thrombosis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2082–2088. doi: 10.1172/JCI111632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conard J., Horellou M. H., Van Dreden P., Lecompte T., Samama M. Thrombosis and pregnancy in congenital deficiencies in AT III, protein C or protein S: study of 78 women. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Apr 12;63(2):319–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coull B. M., Bourdette D. N., Goodnight S. H., Jr, Briley D. P., Hart R. Multiple cerebral infarctions and dementia associated with anticardiolipin antibodies. Stroke. 1987 Nov-Dec;18(6):1107–1112. doi: 10.1161/01.str.18.6.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cros D., Comp P. C., Beltran G., Gum G. Superior sagittal sinus thrombosis in a patient with protein S deficiency. Stroke. 1990 Apr;21(4):633–636. doi: 10.1161/01.str.21.4.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alton J. G., Preston D. N., Bormanis J., Green M. S., Kraag G. R. Multiple transient ischemic attacks, lupus anticoagulant and verrucous endocarditis. Stroke. 1985 May-Jun;16(3):512–514. doi: 10.1161/01.str.16.3.512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Erasmo E., Aliberti G., Celi F. S., Romagnoli E., Vecci E., Mazzuoli G. F. Platelet count, mean platelet volume and their relation to prognosis in cerebral infarction. J Intern Med. 1990 Jan;227(1):11–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1990.tb00111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalaker K., Hjermann I., Prydz H. A novel form of factor VII in plasma from men at risk for cardiovascular disease. Br J Haematol. 1985 Oct;61(2):315–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb02831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davous P., Horellou M. H., Conard J., Samama M. Cerebral infarction and familial protein S deficiency. Stroke. 1990 Dec;21(12):1760–1761. doi: 10.1161/01.str.21.12.1760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson A. A., Ogston D. The influence of the platelet count on the incidence of thrombotic and haemorrhagic complications in polycythaemia vera. Postgrad Med J. 1970 Feb;46(532):76–78. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.46.532.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delangre T., Mihout B., Borh J. Y., Samson M. Primary thrombocythemia in a patient with cerebellar infarction. Stroke. 1985 May-Jun;16(3):524–526. doi: 10.1161/01.str.16.3.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demers C., Ginsberg J. S., Hirsh J., Henderson P., Blajchman M. A. Thrombosis in antithrombin-III-deficient persons. Report of a large kindred and literature review. Ann Intern Med. 1992 May 1;116(9):754–761. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-9-754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detection of lupus like anticoagulant: current laboratory practice in the United Kingdom. The Lupus Anticoagulant Working Party. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Jan;43(1):73–75. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digre K. B., Durcan F. J., Branch D. W., Jacobson D. M., Varner M. W., Baringer J. R. Amaurosis fugax associated with antiphospholipid antibodies. Ann Neurol. 1989 Mar;25(3):228–232. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnet A., Khalil R., Terrier G., Koeppel M. C., Njee B. T., Aillaud M. F. Cerebral infarction, livedo reticularis, and familial deficiency in antithrombin-III. Stroke. 1992 Apr;23(4):611–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusser A., Boyer-Neumann C., Wolf M. Temporary protein C deficiency associated with cerebral arterial thrombosis in childhood. J Pediatr. 1988 Nov;113(5):849–851. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGEBERG O. INHERITED ANTITHROMBIN DEFICIENCY CAUSING THROMBOPHILIA. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Jun 15;13:516–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernerudh J., Olsson J. E., von Schenck H. Antithrombin-III deficiency in ischemic stroke. Stroke. 1990 Jun;21(6):967–967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esack A., Thompson G., Burmester H. Benign intracranial hypertension and essential thrombocythaemia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989 Jul;52(7):914–914. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.52.7.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford P. M., Ford S. E., Lillicrap D. P. Association of lupus anticoagulant with severe valvular heart disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1988 Apr;15(4):597–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford S. E., Lillicrap D., Brunet D., Ford P. Thrombotic endocarditis and lupus anticoagulant. A pathogenetic possibility for idiopathic 'rheumatic type' valvular heart disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1989 Apr;113(4):350–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girolami A., Simioni P., Lazzaro A. R., Cordiano I. Severe arterial cerebral thrombosis in a patient with protein S deficiency (moderately reduced total and markedly reduced free protein S): a family study. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Feb 28;61(1):144–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladson C. L., Scharrer I., Hach V., Beck K. H., Griffin J. H. The frequency of type I heterozygous protein S and protein C deficiency in 141 unrelated young patients with venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Feb 25;59(1):18–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D., Otoya J., Oriba H., Rovner R. Protein S deficiency in middle-aged women with stroke. Neurology. 1992 May;42(5):1029–1033. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.5.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Evatt B., Zimmerman T. S., Kleiss A. J., Wideman C. Deficiency of protein C in congenital thrombotic disease. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1370–1373. doi: 10.1172/JCI110385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller D. S., Pervez N. K., Kleinerman J. Fatal cerebrovascular thrombosis in a young woman: an unusual complication associated with hypochromic anemia and thrombocytosis following surgery. Mt Sinai J Med. 1988 Sep;55(4):318–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israels S. J., Seshia S. S. Childhood stroke associated with protein C or S deficiency. J Pediatr. 1987 Oct;111(4):562–564. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabaily J., Iland H. J., Laszlo J., Massey E. W., Faguet G. B., Brière J., Landaw S. A., Pisciotta A. V. Neurologic manifestations of essential thrombocythemia. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Oct;99(4):513–518. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-4-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner R. C., Najarian L. V., Schatten S., Jabs D. A., Patz A., Kaplan H. J. Vaso-occlusive retinopathy associated with antiphospholipid antibodies (lupus anticoagulant retinopathy). Ophthalmology. 1989 Jun;96(6):896–904. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(89)32825-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelman J. H., Bakker C. M., Plandsoen W. C., Peeters F. L., Barth P. G. Hereditary protein S deficiency presenting with cerebral sinus thrombosis in an adolescent girl. J Neurol. 1992 Feb;239(2):105–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00862984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler J., Kasper J., Witt I., von Reutern G. M. Ischemic stroke due to protein C deficiency. Stroke. 1990 Jul;21(7):1077–1080. doi: 10.1161/01.str.21.7.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner M. J. Prospective study of anticardiolipin antibodies in stroke. Stroke. 1990 Feb;21(2):295–298. doi: 10.1161/01.str.21.2.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner M., Simonian N. Lupus anticoagulants, anticardiolipin antibodies, and cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 1989 Feb;20(2):225–229. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.2.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landi G., Calloni M. V., Grazia Sabbadini M., Mannuccio Mannucci P., Candelise L. Recurrent ischemic attacks in two young adults with lupus anticoagulant. Stroke. 1983 May-Jun;14(3):377–379. doi: 10.1161/01.str.14.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. K., Ng S. C. Cerebral venous thrombosis associated with antithrombin III deficiency. Aust N Z J Med. 1991 Oct;21(5):772–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1991.tb01388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J., Swanson P. D. Idiopathic thrombocytosis. A treatable cause of transient ischemic attacks. Neurology. 1968 Jul;18(7):711–713. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.7.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S. R., Brey R. L., Joseph C. L., Havstad S. Risk of recurrent thromboembolic events in patients with focal cerebral ischemia and antiphospholipid antibodies. The Antiphospholipid Antibodies in Stroke Study Group. Stroke. 1992 Feb;23(2 Suppl):I29–I32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S. R., Crofts J. W., Lesser G. R., Floberg J., Welch K. M. Visual symptoms associated with the presence of a lupus anticoagulant. Ophthalmology. 1988 May;95(5):686–692. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(88)33139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S. R., Deegan M. J., Futrell N., Welch K. M. Cerebrovascular and neurologic disease associated with antiphospholipid antibodies: 48 cases. Neurology. 1990 Aug;40(8):1181–1189. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.8.1181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S. R., Welch K. M. The spectrum of neurologic disease associated with antiphospholipid antibodies. Lupus anticoagulants and anticardiolipin antibodies. Arch Neurol. 1987 Aug;44(8):876–883. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520200078024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey N., Henderson F., Malia R., Greaves M., Hughes P. Serum masks the inhibition of thrombin-induced prostacyclin release produced by anticardiolipin antibodies. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Mar;31(3):179–183. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.3.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshin M. D., Druzin M. L., Goei S., Qamar T., Magid M. S., Jovanovic L., Ferenc M. Antibody to cardiolipin as a predictor of fetal distress or death in pregnant patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 18;313(3):152–156. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507183130304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLIKAN C. H., SIEKERT R. G., WHISNANT J. P. Intermittent carotid and vertebral-basilar insufficiency associated with polycythemia. Neurology. 1960 Feb;10:188–196. doi: 10.1212/wnl.10.2.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malia R. G., Kitchen S., Greaves M., Preston F. E. Inhibition of activated protein C and its cofactor protein S by antiphospholipid antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1990 Sep;76(1):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb07843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak E., Romond E. H. Impaired catalytic function of activated protein C: a new in vitro manifestation of lupus anticoagulant. Blood. 1989 Nov 15;74(7):2426–2432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita K., Kuriyama Y., Sawada T., Uchida K. Cerebral infarction associated with protein C deficiency. Stroke. 1992 Jan;23(1):108–111. doi: 10.1161/01.str.23.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. D., Tatemichi T. K., Kranzler S. J., Chi L., Hilal S. K., Mohr J. P. Thrombosis of the superior sagittal sinus associated with essential thrombocytosis followed by MRI during anticoagulant therapy. Neurology. 1989 Nov;39(11):1554–1555. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.11.1554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Simpson R. J., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Anti-phospholipid antibodies are directed against a complex antigen that includes a lipid-binding inhibitor of coagulation: beta 2-glycoprotein I (apolipoprotein H). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade T. W., Mellows S., Brozovic M., Miller G. J., Chakrabarti R. R., North W. R., Haines A. P., Stirling Y., Imeson J. D., Thompson S. G. Haemostatic function and ischaemic heart disease: principal results of the Northwick Park Heart Study. Lancet. 1986 Sep 6;2(8506):533–537. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J., Sherman L., Broze G., Jr Absence of thrombosis in subjects with heterozygous protein C deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):991–996. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D., Fisher J., Irving D., Gazzard B. G., Guiloff R. J. Lateral sinus thrombosis and intracranial hypertension in essential thrombocythaemia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Feb;49(2):218–219. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. F., Clarke C. R., Brearley R. L. Superior sagittal sinus thrombosis and essential thrombocythaemia. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Nov 5;287(6402):1344–1344. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6402.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najean Y., Mugnier P., Dresch C., Rain J. D. Polycythaemia vera in young people: an analysis of 58 cases diagnosed before 40 years. Br J Haematol. 1987 Nov;67(3):285–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb02349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquale L. R., Moster M. L., Schmaier A. Dural sinus thrombosis with abnormalities of protein S and fibrinogen. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990 May;108(5):644–644. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1990.01070070030013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T. C., Wetherley-Mein G. Vascular occlusive episodes and venous haematocrit in primary proliferative polycythaemia. Lancet. 1978 Dec 9;2(8102):1219–1222. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines A., Kaplinsky N., Olchovsky D., Bregman J., Frankl O. Recurrent transient ischemic attacks associated with thrombocytosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 1982 Dec;1(4):291–293. doi: 10.1007/BF02032089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNEDDON I. B. CEREBRO-VASCULAR LESIONS AND LIVEDO RETICULARIS. Br J Dermatol. 1965 Apr;77:180–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1965.tb14628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacco R. L., Owen J., Mohr J. P., Tatemichi T. K., Grossman B. A. Free protein S deficiency: a possible association with cerebrovascular occlusion. Stroke. 1989 Dec;20(12):1657–1661. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.12.1657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuragawa N., Takahashi K., Kondo S., Koide T. Antithrombin III Toyama: a hereditary abnormal antithrombin III of a patient with recurrent thrombophlebitis. Thromb Res. 1983 Jul 15;31(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90333-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinmyozu K., Ohkatsu Y., Maruyama Y., Osame M., Igata A. [A case of congenital antithrombin III deficiency complicated by an internal carotid artery occlusion]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1986 Feb;26(2):162–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sié P., Boneu B., Biermé R., Wiesel M. L., Grunebaum L., Cazenave J. P. Arterial thrombosis and protein S deficiency. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Nov 24;62(3):1040–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Ens G. E. Protein C deficiency: a cause of amaurosis fugax? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Mar;50(3):361–362. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.3.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripodi A., Franchi F., Krachmalnicoff A., Mannucci P. M. Asymptomatic homozygous protein C deficiency. Acta Haematol. 1990;83(3):152–155. doi: 10.1159/000205194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueyama H., Hashimoto Y., Uchino M., Sasaki Y., Uyama E., Okajima K., Araki S. Progressing ischemic stroke in a homozygote with variant antithrombin III. Stroke. 1989 Jun;20(6):815–818. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.6.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velasco F., Andres P., Cañadillas F., Fornes G., Torres A. Transient ischemic attack (T.I.A.) in a patient with non-thrombogenic hereditary protein C deficiency under oral contraceptives. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Dec 17;54(4):904–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieregge P., Schwieder G., Kömpf D. Cerebral venous thrombosis in hereditary protein C deficiency. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989 Jan;52(1):135–137. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.52.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vomberg P. P., Breederveld C., Fleury P., Arts W. F. Cerebral thromboembolism due to antithrombin III deficiency in two children. Neuropediatrics. 1987 Feb;18(1):42–44. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenburg H. C., Dekker G. A., Makovitz J. W., Rotmans P. Low-dose aspirin prevents pregnancy-induced hypertension and pre-eclampsia in angiotensin-sensitive primigravidae. Lancet. 1986 Jan 4;1(8471):1–3. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91891-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis D. E., Godwin J. Mitral valve prolapse, cerebral ischemia, and protein S deficiency. Am J Med. 1988 May;84(5):974–974. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts M. T., Greaves M., Clearkin L. G., Malia R. G., Cooper S. M. Anti-phospholipid antibodies and ischaemic optic neuropathy. Lancet. 1990 Mar 10;335(8689):613–614. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90404-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintzen A. R., Broekmans A. W., Bertina R. M., Briët E., Briët P. E., Zecha A., Vielvoye G. J., Bots G. T. Cerebral haemorrhagic infarction in young patients with hereditary protein C deficiency: evidence for "spontaneous" cerebral venous thrombosis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Feb 2;290(6465):350–352. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6465.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. M., Fisher M., Sigsbee A., Errichetti A. Cardiogenic brain embolism and lupus anticoagulant. Ann Neurol. 1989 Sep;26(3):390–392. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]