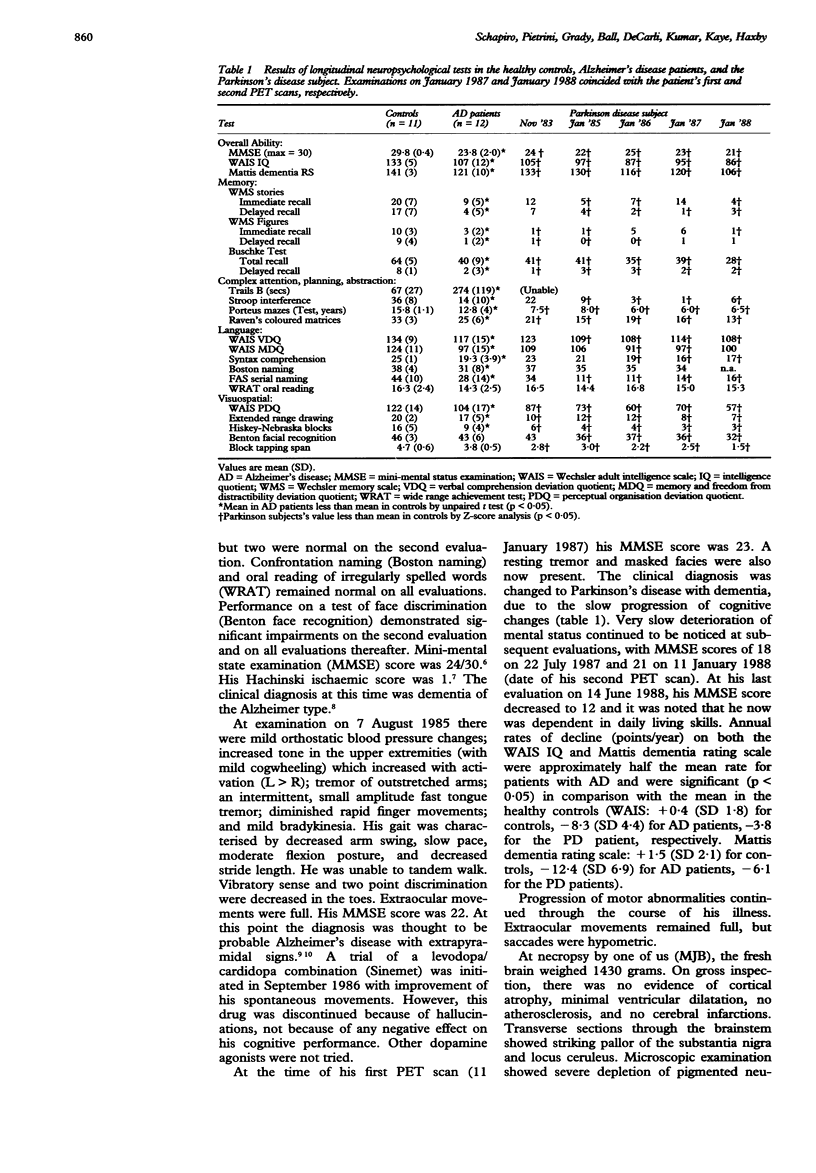
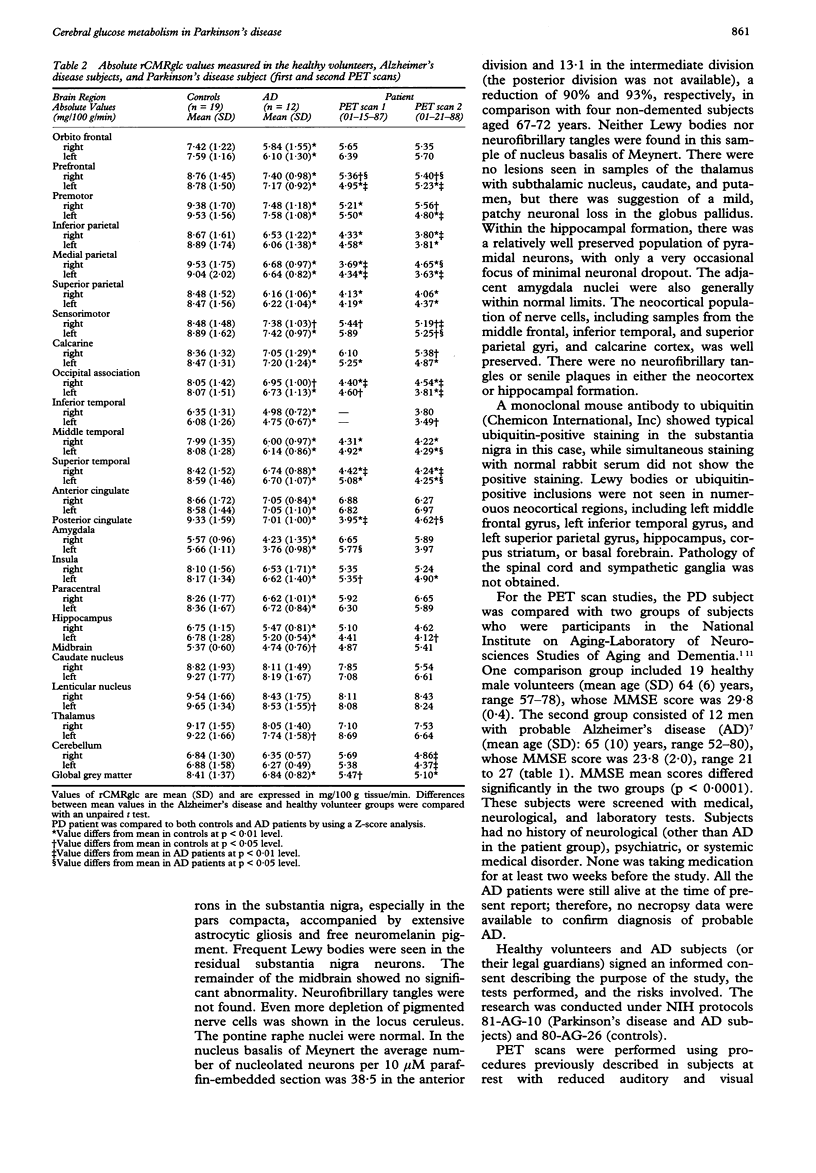
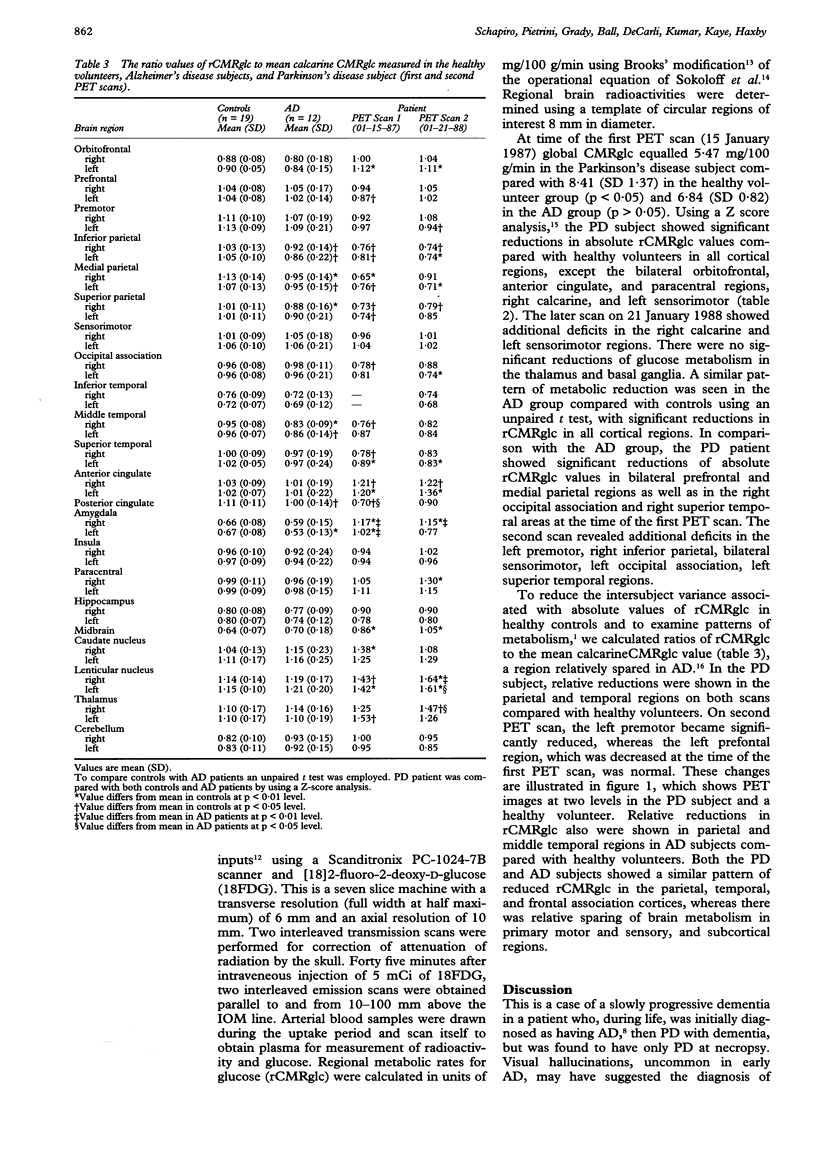
Abstract
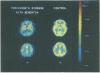
Reduction in the regional cerebral metabolic rate for glucose (rCMRglc) in the parietal and temporal regions has been shown in Alzheimer's disease (AD). The specificity of these findings for this disease state is uncertain. We repeatedly measured rCMRglc with positron emission tomography and [18F]2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose in the resting state in a 68 year old man with slowly progressive dementia who, during life, was initially diagnosed as having dementia of the Alzheimer type, then Parkinson disease with dementia, but was found to have only Parkinson's disease at necropsy. Metabolic ratios (rCMRglc/mean grey CMRglc) were significantly (p < 0.05) reduced in parietal and temporal regions, as well as in the prefrontal and premotor areas. This pattern was similar in regional distribution and magnitude of the defect to that seen in patients with probable AD. These results suggest that reductions of glucose metabolism in association neocortex in AD are not specific to the disease process, but may be related to the dementia state.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander G. E., DeLong M. R., Strick P. L. Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:357–381. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball M. J. The morphological basis of dementia in Parkinson's disease. Can J Neurol Sci. 1984 Feb;11(1 Suppl):180–184. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100046370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks R. A. Alternative formula for glucose utilization using labeled deoxyglucose. J Nucl Med. 1982 Jun;23(6):538–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. W., White C. L., 3rd, Manz H. J., Parhad I. M., Curry B., Whitehouse P. J., Lehmann J., Coyle J. T. Primary degenerative dementia without Alzheimer pathology. Can J Neurol Sci. 1986 Nov;13(4 Suppl):462–470. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100037136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duara R., Margolin R. A., Robertson-Tchabo E. A., London E. D., Schwartz M., Renfrew J. W., Koziarz B. J., Sundaram M., Grady C., Moore A. M. Cerebral glucose utilization, as measured with positron emission tomography in 21 resting healthy men between the ages of 21 and 83 years. Brain. 1983 Sep;106(Pt 3):761–775. doi: 10.1093/brain/106.3.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland R. P. 'Normal'-pressure hydrocephalus and the saga of the treatable dementias. JAMA. 1989 Nov 10;262(18):2577–2581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland R. P., Prusiner S. B., Jagust W. J., Budinger T. F., Davis R. L. Bitemporal hypometabolism in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease measured by positron emission tomography with [18F]-2-fluorodeoxyglucose. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1984 Oct;8(5):978–981. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198410000-00034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady C. L., Haxby J. V., Schlageter N. L., Berg G., Rapoport S. I. Stability of metabolic and neuropsychological asymmetries in dementia of the Alzheimer type. Neurology. 1986 Oct;36(10):1390–1392. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.10.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachinski V. C., Iliff L. D., Zilhka E., Du Boulay G. H., McAllister V. L., Marshall J., Russell R. W., Symon L. Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch Neurol. 1975 Sep;32(9):632–637. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490510088009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haxby J. V., Grady C. L., Duara R., Schlageter N., Berg G., Rapoport S. I. Neocortical metabolic abnormalities precede nonmemory cognitive defects in early Alzheimer's-type dementia. Arch Neurol. 1986 Sep;43(9):882–885. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520090022010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haxby J. V., Grady C. L., Koss E., Horwitz B., Heston L., Schapiro M., Friedland R. P., Rapoport S. I. Longitudinal study of cerebral metabolic asymmetries and associated neuropsychological patterns in early dementia of the Alzheimer type. Arch Neurol. 1990 Jul;47(7):753–760. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1990.00530070043010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haxby J. V., Grady C. L., Koss E., Horwitz B., Schapiro M., Friedland R. P., Rapoport S. I. Heterogeneous anterior-posterior metabolic patterns in dementia of the Alzheimer type. Neurology. 1988 Dec;38(12):1853–1863. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.12.1853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J. A., May C., Daly E., Atack J. R., Sweeney D. J., Luxenberg J. S., Kay A. D., Kaufman S., Milstien S., Friedland R. P. Cerebrospinal fluid monoamine markers are decreased in dementia of the Alzheimer type with extrapyramidal features. Neurology. 1988 Apr;38(4):554–557. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.4.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyosawa M., Baron J. C., Hamel E., Pappata S., Duverger D., Riche D., Mazoyer B., Naquet R., MacKenzie E. T. Time course of effects of unilateral lesions of the nucleus basalis of Meynert on glucose utilization by the cerebral cortex. Positron tomography in baboons. Brain. 1989 Apr;112(Pt 2):435–455. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.2.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl D. E., Metter E. J., Riege W. H. Patterns of local cerebral glucose utilization determined in Parkinson's disease by the [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose method. Ann Neurol. 1984 May;15(5):419–424. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Schapiro M. B., Grady C., Haxby J. V., Wagner E., Salerno J. A., Friedland R. P., Rapoport S. I. High-resolution PET studies in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1991 Jan;4(1):35–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Yates P. O. Pathological basis for neurotransmitter changes in Parkinson's disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1983 Jan-Feb;9(1):3–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1983.tb00320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielke R., Herholz K., Grond M., Kessler J., Heiss W. D. Severity of vascular dementia is related to volume of metabolically impaired tissue. Arch Neurol. 1992 Sep;49(9):909–913. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1992.00530330031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orzi F., Diana G., Casamenti F., Palombo E., Fieschi C. Local cerebral glucose utilization following unilateral and bilateral lesions of the nucleus basalis magnocellularis in the rat. Brain Res. 1988 Oct 11;462(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90590-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. H., Tomlinson B. E., Candy J. M., Blessed G., Foster J. F., Bloxham C. A., Perry E. R. Cortical cholinergic deficit in mentally impaired Parkinsonian patients. Lancet. 1983 Oct 1;2(8353):789–790. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S. I. Integrated phylogeny of the primate brain, with special reference to humans and their diseases. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1990 Sep-Dec;15(3):267–294. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(90)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinne J. O., Rummukainen J., Paljärvi L., Rinne U. K. Dementia in Parkinson's disease is related to neuronal loss in the medial substantia nigra. Ann Neurol. 1989 Jul;26(1):47–50. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff L., Reivich M., Kennedy C., Des Rosiers M. H., Patlak C. S., Pettigrew K. D., Sakurada O., Shinohara M. The [14C]deoxyglucose method for the measurement of local cerebral glucose utilization: theory, procedure, and normal values in the conscious and anesthetized albino rat. J Neurochem. 1977 May;28(5):897–916. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swedo S. E., Schapiro M. B., Grady C. L., Cheslow D. L., Leonard H. L., Kumar A., Friedland R., Rapoport S. I., Rapoport J. L. Cerebral glucose metabolism in childhood-onset obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1989 Jun;46(6):518–523. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1989.01810060038007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]