Abstract
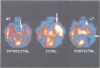
The ictal increase of regional cerebral blood flow has yet to be fully utilised in the investigation of focal seizures. Although single photon emission tomography (SPECT) is being increasingly used in the localisation of epileptic foci, the evolution and time courses of the peri-ictal perfusion changes have yet to be clarified. We performed serial SPECT studies in the interictal, ictal and immediate postictal states in 12 patients with refractory temporal lobe epilepsy to define the patterns and duration of peri-ictal cerebral blood flow changes. Visual analysis showed a constant pattern of unilateral global increases in temporal lobe perfusion during seizures which suddenly switched to a pattern of relative mesial temporal (hippocampal) hyperperfusion and lateral temporal hypoperfusion in the immediate postictal period. Quantitative analysis confirmed the visual assessment. Lateral temporal cortex ictal/normal side to side ratios were increased by mean 35.1% (95% confidence interval 21.8% to 48.4%) more in the ictal studies than in the interictal studies and mesial temporal cortex ratios increased by mean 30.8% (22.4% to 39.2%). In the postictal state, however, lateral temporal ratios were reduced by mean 7.7% (-15.8% to 0.4%) compared with interictal values, whereas mesial temporal perfusion was maintained compared with the interictal studies. These observations provide critical information for interpreting scans which can be used in the localisation of epileptic foci. This postictal switch in blood flow patterns may reflect the underlying metabolic processes of neuronal activation and recovery and have implications for understanding the neurobiology of human epileptic seizures.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann R. F., Lear J. L. Glycolysis-induced discordance between glucose metabolic rates measured with radiolabeled fluorodeoxyglucose and glucose. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1989 Dec;9(6):774–785. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1989.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumhardt L. D., Smith P. E., Owen L. Electrocardiographic accompaniments of temporal lobe epileptic seizures. Lancet. 1986 May 10;1(8489):1051–1056. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91328-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Patterson J., Hadley D. M., Macpherson P., Brodie M. J., Bone I., McGeorge A. P., Wyper D. J. CT, MR and SPECT imaging in temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990 Jan;53(1):11–15. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.53.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Jr, Kuhl D. E., Phelps M. E. Patterns of human local cerebral glucose metabolism during epileptic seizures. Science. 1982 Oct 1;218(4567):64–66. doi: 10.1126/science.6981843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Raichle M. E., Mintun M. A., Dence C. Nonoxidative glucose consumption during focal physiologic neural activity. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):462–464. doi: 10.1126/science.3260686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson G. D., Berkovic S. F., Tress B. M., Kalnins R. M., Fabinyi G. C., Bladin P. F. Hippocampal sclerosis can be reliably detected by magnetic resonance imaging. Neurology. 1990 Dec;40(12):1869–1875. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.12.1869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl D. E., Engel J., Jr, Phelps M. E., Selin C. Epileptic patterns of local cerebral metabolism and perfusion in humans determined by emission computed tomography of 18FDG and 13NH3. Ann Neurol. 1980 Oct;8(4):348–360. doi: 10.1002/ana.410080403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. I., Markand O. N., Siddiqui A. R., Park H. M., Mock B., Wellman H. H., Worth R. M., Edwards M. K. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) brain imaging using N,N,N'-trimethyl-N'-(2 hydroxy-3-methyl-5-123I-iodobenzyl)-1,3-propanediamine 2 HCl (HIPDM): intractable complex partial seizures. Neurology. 1986 Nov;36(11):1471–1477. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.11.1471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leniger-Follert E. Mechanisms of regulation of cerebral microflow during bicuculline-induced seizures in anaesthetized cats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1984 Jun;4(2):150–165. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1984.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesney L. F. Clinical and EEG features of complex partial seizures of temporal lobe origin. Epilepsia. 1986;27 (Suppl 2):S27–S45. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1986.tb05738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe C. C., Berkovic S. F., Austin M., McKay W. J., Bladin P. F. Postictal SPET in epilepsy. Lancet. 1989 Feb 18;1(8634):389–390. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91769-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. F., Smith F. W., Gemmell H. G., Lyall D., Evans N. T., Gvozdanovic D., Davidson J., Tyrrell D. A., Pickett R. D., Neirinckx R. D. Technetium-99m HM-PAO stereoisomers as potential agents for imaging regional cerebral blood flow: human volunteer studies. J Nucl Med. 1986 Feb;27(2):171–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer S. S., Williamson P. D., Spencer D. D., Mattson R. H. Human hippocampal seizure spread studied by depth and subdural recording: the hippocampal commissure. Epilepsia. 1987 Sep-Oct;28(5):479–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1987.tb03676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefan H., Bauer J., Feistel H., Schulemann H., Neubauer U., Wenzel B., Wolf F., Neundörfer B., Huk W. J. Regional cerebral blood flow during focal seizures of temporal and frontocentral onset. Ann Neurol. 1990 Feb;27(2):162–166. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodore W. H., Newmark M. E., Sato S., Brooks R., Patronas N., De La Paz R., DiChiro G., Kessler R. M., Margolin R., Manning R. G. [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in refractory complex partial seizures. Ann Neurol. 1983 Oct;14(4):429–437. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uren R. F., Magistretti P. L., Royal H. D., Parker J. A., Front D., Hill T. C., Holman B. L., Jones A. G., Kolodny G. M. Single-photon emission computed tomography. A method of measuring cerebral blood flow in three dimensions (preliminary results of studies in patients with epilepsy and stroke). Med J Aust. 1983 Apr 30;1(9):411–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]