Abstract
Analysis of many families with linked DNA markers has provided support for the Huntington's disease (HD) gene being close to the telomere on the short arm of chromosome 4. However, analysis of recombination events in particular families has provided conflicting results about the precise location of the HD gene relative to these closely linked DNA markers. Here we report an investigation of linkage disequilibrium between six DNA markers and the HD gene in 75 separate families of varied ancestry. We show significant non-random association between alleles detected at D4S95 and D4S98 and the mutant gene. These data suggest that it may be possible to construct high and low risk haplotypes, which may be helpful in DNA analysis and genetic counselling for HD, and represent independent evidence that the gene for HD is centromeric to more distally located DNA markers such as D4S90. This information may be helpful in defining a strategy to clone the gene for HD based on its location in the human genome.
Full text
PDF

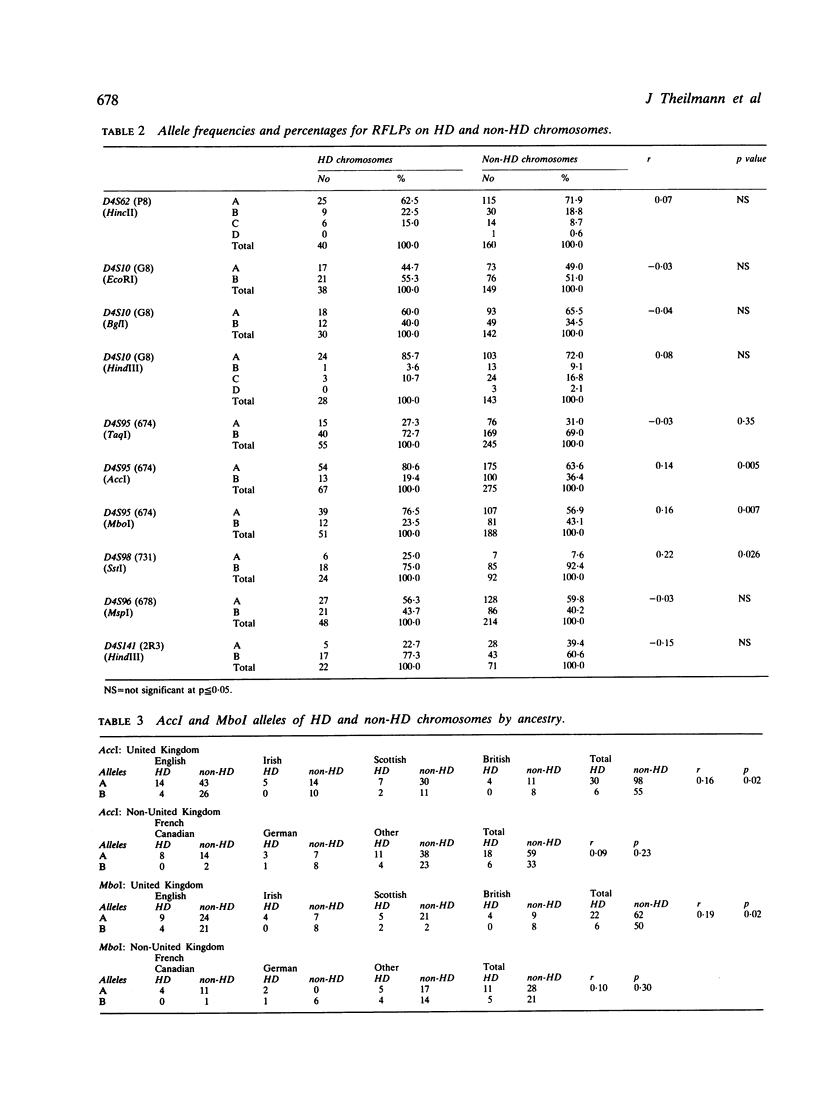
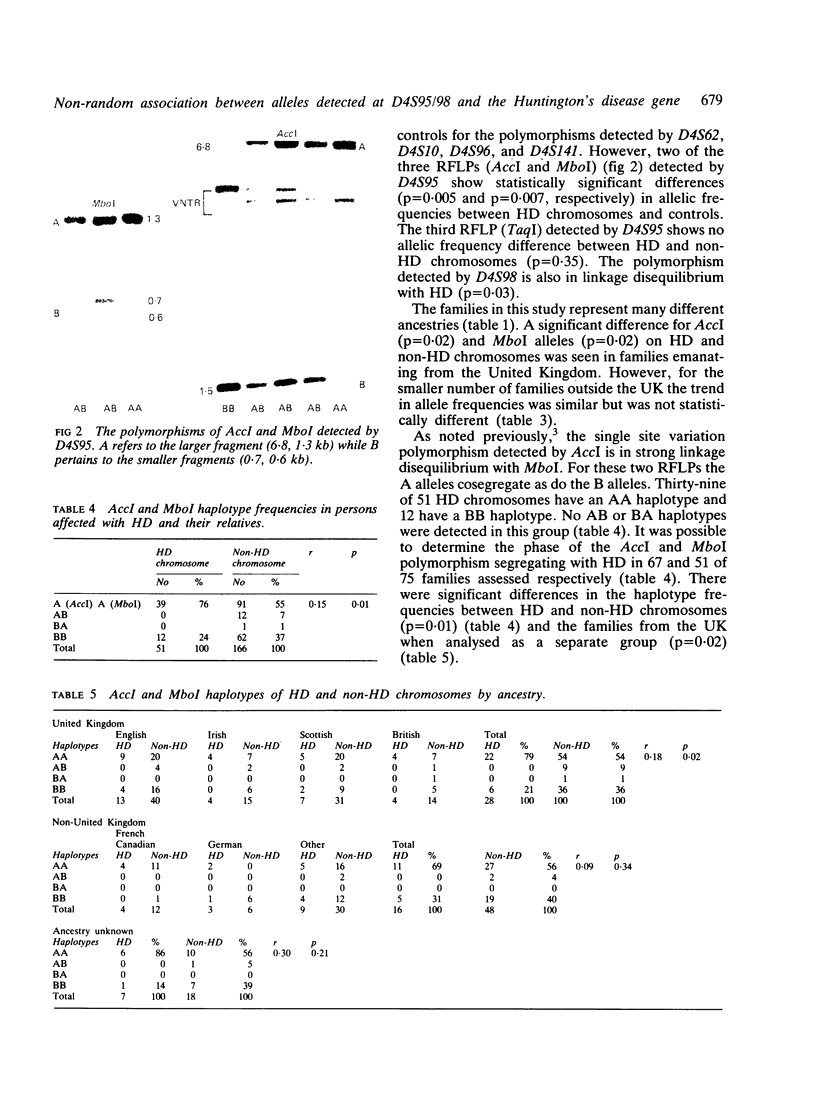


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARBEAU A., FULLUM G. Origin and migration of Huntington's chorea in Canada: preliminary report. Can Med Assoc J. 1962 Dec 8;87:1242–1243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROTHERS C. R. HUNTINGTON'S CHOREA IN VICTORIA AND TASMANIA. J Neurol Sci. 1964 Sep-Oct;1(5):405–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(64)90110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaudet A. L., Feldman G. L., Fernbach S. D., Buffone G. J., O'Brien W. E. Linkage disequilibrium, cystic fibrosis, and genetic counseling. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):319–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam T. C., Tanzi R. E., Haines J. L., Bonner T. I., Faryniarz A. G., Hobbs W. J., MacDonald M. E., Cheng S. V., Folstein S. E., Conneally P. M. Localization of the Huntington's disease gene to a small segment of chromosome 4 flanked by D4S10 and the telomere. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Naylor S. L., Anderson M. A., Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Ottina K., Wallace M. R., Sakaguchi A. Y. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington's disease. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):234–238. doi: 10.1038/306234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden M. R., Hewitt J., Wasmuth J. J., Kastelein J. J., Langlois S., Conneally M., Haines J., Smith B., Hilbert C., Allard D. A polymorphic DNA marker that represents a conserved expressed sequence in the region of the Huntington disease gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;42(1):125–131. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden M. R., Hopkins H. C., Macrea M., Beighton P. H. The origin of Huntington's chorea in the Afrikaner population of South Africa. S Afr Med J. 1980 Aug 2;58(5):197–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden M. R., Kirk H., Clark C., Frohlich J., Rabkin S., McLeod R., Hewitt J. DNA polymorphisms in and around the Apo-A1-CIII genes and genetic hyperlipidemias. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 May;40(5):421–430. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden M. R., Robbins C., Allard D., Haines J., Fox S., Wasmuth J., Fahy M., Bloch M. Improved predictive testing for Huntington disease by using three linked DNA markers. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):689–694. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C., Buetow K. H., Donovan M., Hornung S., Motulsky A. G., Disteche C., Dyer K., Swisshelm K., Anderson J., Giblett E. Linkage disequilibrium of plasminogen polymorphisms and assignment of the gene to human chromosome 6q26-6q27. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;40(4):338–350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Lathrop M., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Kamboh M. I., Lalouel J. M., White R. Frequent recombination is observed in the distal end of the long arm of chromosome 14. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):76–81. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90317-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins C., Theilmann J., Youngman S., Haines J., Altherr M. J., Harper P. S., Payne C., Junker A., Wasmuth J., Hayden M. R. Evidence from family studies that the gene causing Huntington disease is telomeric to D4S95 and D4S90. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):422–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B., Skarecky D., Bengtsson U., Magenis R. E., Carpenter N., Wasmuth J. J. Isolation of DNA markers in the direction of the Huntington disease gene from the G8 locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):335–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Hewitt J., Smith B., Allard D., Haines J. L., Skarecky D., Partlow E., Hayden M. R. A highly polymorphic locus very tightly linked to the Huntington's disease gene. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):734–736. doi: 10.1038/332734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley W. L., Michiels F., MacDonald M. E., Romano D., Zimmer M., Smith B., Leavitt J., Bucan M., Haines J. L., Gilliam T. C. Mapping of D4S98/S114/S113 confines the Huntington's defect to a reduced physical region at the telomere of chromosome 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11769–11780. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman S., Shaw D. J., Gusella J. F., MacDonald M., Stanbridge E. J., Wasmuth J., Harper P. S. A DNA probe, D5 [D4S90] mapping to human chromosome 4p16.3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1648–1648. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]