Abstract
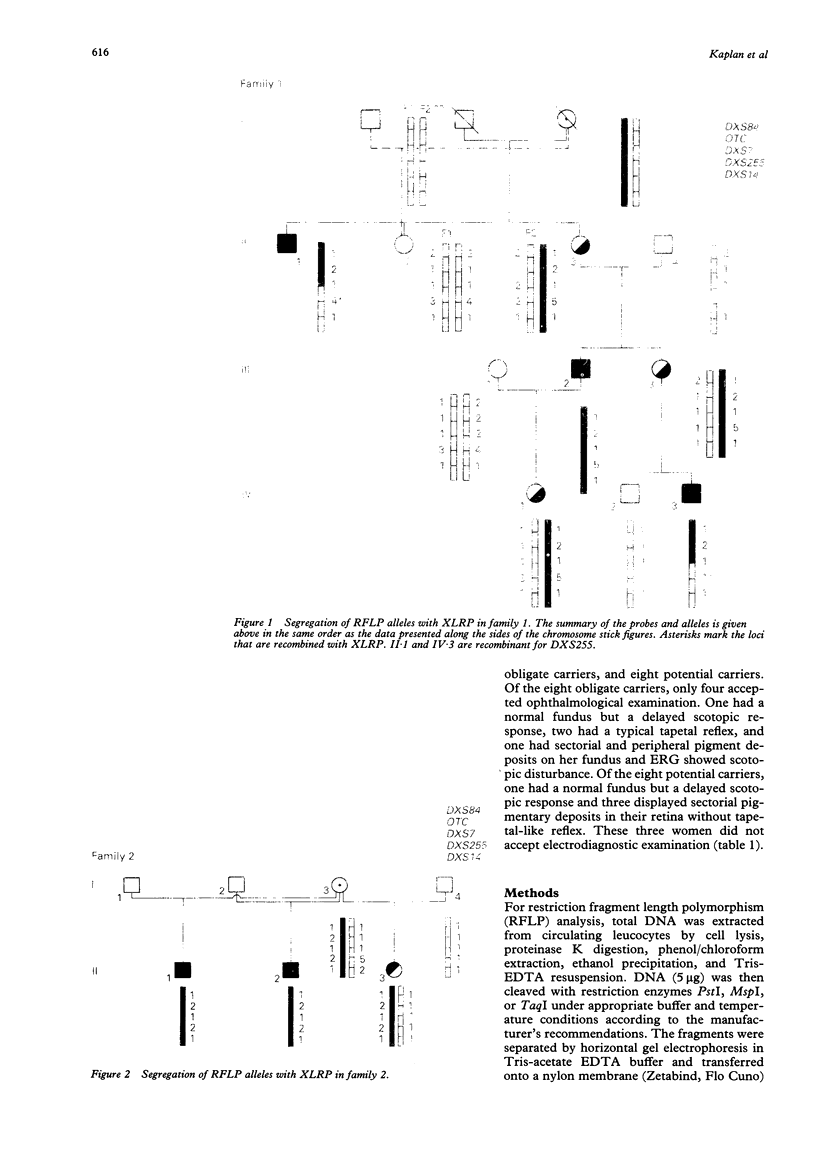
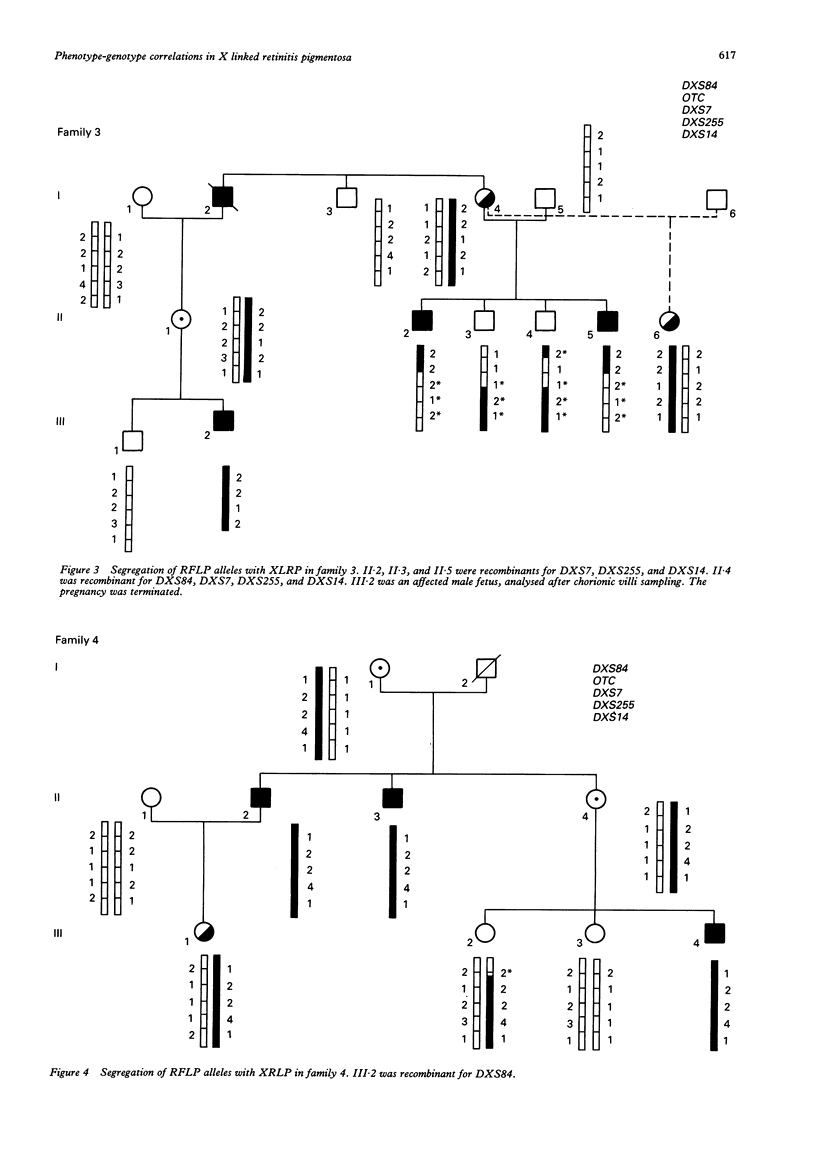
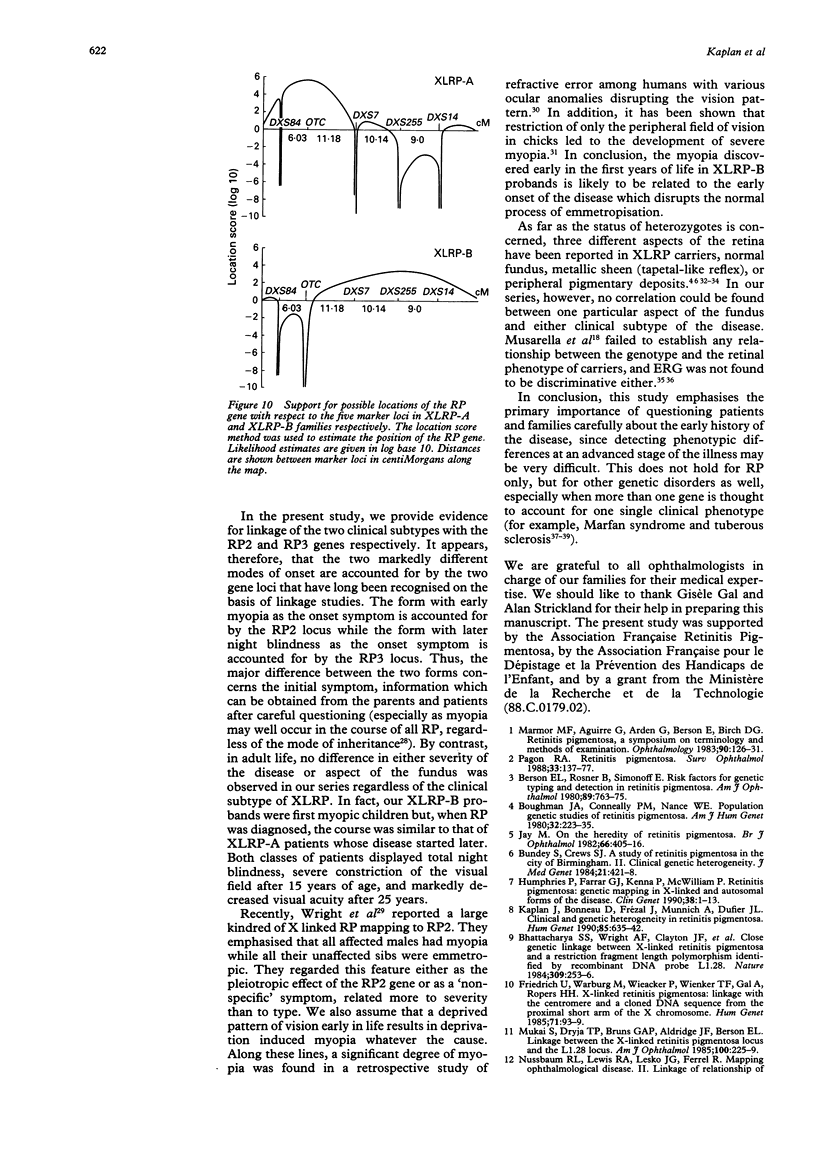
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) represents a group of clinically heterogeneous retinal degenerations in which all modes of inheritance have been described. We have previously found two different clinical profiles in X linked RP as a function of age and mode of onset. The first clinical form has very early onset with severe myopia. The second form starts later with night blindness with mild myopia or none. At least two genes have been identified in X linked forms, namely RP2 (linked to DXS7, DXS255, and DXS14) and RP3 (linked to DXS84 and OTC) on the short arm of the X chromosome. In order to contribute to phenotype-genotype correlations in X linked RP, we tested the hypothesis that the two clinical profiles could be accounted for by the two different gene loci. The present study provides evidence for linkage of the clinical form with early myopia as the onset symptom with the RP2 gene (pairwise linkage to DXS255: Z = 3.13 at theta = 0), while the clinical form with later night blindness as the onset symptom is linked to the RP3 gene (pairwise linkage to OTC: Z = 4.16 at theta = 0).
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arden G. B., Carter R. M., Hogg C. R., Powell D. J., Ernst W. J., Clover G. M., Lyness A. L., Quinlan M. P. A modified ERG technique and the results obtained in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Br J Ophthalmol. 1983 Jul;67(7):419–430. doi: 10.1136/bjo.67.7.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson E. L., Rosen J. B., Simonoff E. A. Electroretinographic testing as an aid in detection of carriers of X-chromosome-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Ophthalmol. 1979 Apr;87(4):460–468. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(79)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson E. L., Rosner B., Simonoff E. Risk factors for genetic typing and detection in retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Ophthalmol. 1980 Jun;89(6):763–775. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(80)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. C. X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Br J Ophthalmol. 1975 Apr;59(4):177–199. doi: 10.1136/bjo.59.4.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughman J. A., Conneally P. M., Nance W. E. Population genetic studies of retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 Mar;32(2):223–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundey S., Crews S. J. A study of retinitis pigmentosa in the City of Birmingham. II Clinical and genetic heterogeneity. J Med Genet. 1984 Dec;21(6):421–428. doi: 10.1136/jmg.21.6.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. D., Dickinson P., Gray R., Constable I., Sheffield L., Denton M. J. Non-allelic mutations in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Clin Genet. 1989 May;35(5):338–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1989.tb02954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daish P., Hardman M. J., Lamont M. A. Hydrocephalus, tall stature, joint laxity, and kyphoscoliosis: a new inherited disorder of connective tissue? J Med Genet. 1989 Jan;26(1):51–54. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman G. A., Weinberg A. B., McMahon T. T. X-linked recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Clinical characteristics of carriers. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Sep;104(9):1329–1335. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1986.01050210083030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Ochs H. D., de Martinville B., Giacalone J., Lindgren V., Distèche C., Pagon R. A., Hofker M. H., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Minor Xp21 chromosome deletion in a male associated with expression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):250–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Davies K. E., Ropers H. H. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of the X and Y Chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):296–352. doi: 10.1159/000132178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries P., Farrar G. J., Kenna P., McWilliam P. Retinitis pigmentosa: genetic mapping in X-linked and autosomal forms of the disease. Clin Genet. 1990 Jul;38(1):1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1990.tb03541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen L. A., Sandkuyl L. A., Merkens E. C., Maat-Kievit J. A., Sampson J. R., Fleury P., Hennekam R. C., Grosveld G. C., Lindhout D., Halley D. J. Genetic heterogeneity in tuberous sclerosis. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay M. On the heredity of retinitis pigmentosa. Br J Ophthalmol. 1982 Jul;66(7):405–416. doi: 10.1136/bjo.66.7.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J., Bonneau D., Frézal J., Munnich A., Dufier J. L. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity in retinitis pigmentosa. Hum Genet. 1990 Oct;85(6):635–642. doi: 10.1007/BF00193589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert S. R., Taylor D., Kriss A. The infant with nystagmus, normal appearing fundi, but an abnormal ERG. Surv Ophthalmol. 1989 Nov-Dec;34(3):173–186. doi: 10.1016/0039-6257(89)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahtani M. M., Willard H. F. A primary genetic map of the pericentromeric region of the human X chromosome. Genomics. 1988 May;2(4):294–301. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai S., Dryja T. P., Bruns G. A., Aldridge J. F., Berson E. L. Linkage between the X-linked retinitis pigmentosa locus and the L1.28 locus. Am J Ophthalmol. 1985 Aug 15;100(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(85)90786-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musarella M. A., Anson-Cartwright L., Burghes A., Worton R. G., Lesko J. G., Nussbaum R. L. Linkage analysis of a large Latin-American family with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa and metallic sheen in the heterozygote carrier. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):601–605. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90285-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musarella M. A., Anson-Cartwright L., Leal S. M., Gilbert L. D., Worton R. G., Fishman G. A., Ott J. Multipoint linkage analysis and heterogeneity testing in 20 X-linked retinitis pigmentosa families. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):286–296. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90284-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musarella M. A., Burghes A., Anson-Cartwright L., Mahtani M. M., Argonza R., Tsui L. C., Worton R. Localization of the gene for X-linked recessive type of retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP) to Xp21 by linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Oct;43(4):484–494. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Lewis R. A., Lesko J. G., Ferrell R. Mapping X-linked ophthalmic diseases: II. Linkage relationship of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa to X chromosomal short arm markers. Hum Genet. 1985;70(1):45–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00389458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin J., Van Sluyters R. C., Malach R. Emmetropization: a vision-dependent phenomenon. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981 Apr;20(4):561–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieving P. A., Fishman G. A. Refractive errors of retinitis pigmentosa patients. Br J Ophthalmol. 1978 Mar;62(3):163–167. doi: 10.1136/bjo.62.3.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallman J., Turkel J., Trachtman J. Extreme myopia produced by modest change in early visual experience. Science. 1978 Sep 29;201(4362):1249–1251. doi: 10.1126/science.694514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth B., Denton M. J., Chen J. D., Neugebauer M., Halliday F. B., van Schooneveld M., Donald J., Bleeker-Wagemakers E. M., Pearson P. L., Gal A. Two different genes for X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Genomics. 1988 Apr;2(3):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. F., Bhattacharya S. S., Aldred M. A., Jay M., Carothers A. D., Thomas N. S., Bird A. C., Jay B., Evans H. J. Genetic localisation of the RP2 type of X linked retinitis pigmentosa in a large kindred. J Med Genet. 1991 Jul;28(7):453–457. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.7.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. F., Bhattacharya S. S., Clayton J. F., Dempster M., Tippett P., McKeown C. M., Jay M., Jay B., Bird A. C. Linkage relationships between X-linked retinitis pigmentosa and nine short-arm markers: exclusion of the disease locus from Xp21 and localization to between DXS7 and DXS14. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;41(4):635–644. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saint-Basile G., Bohler M. C., Fischer A., Cartron J., Dufier J. L., Griscelli C., Orkin S. H. Xp21 DNA microdeletion in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod phenotype. Hum Genet. 1988 Sep;80(1):85–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00451463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]