Abstract
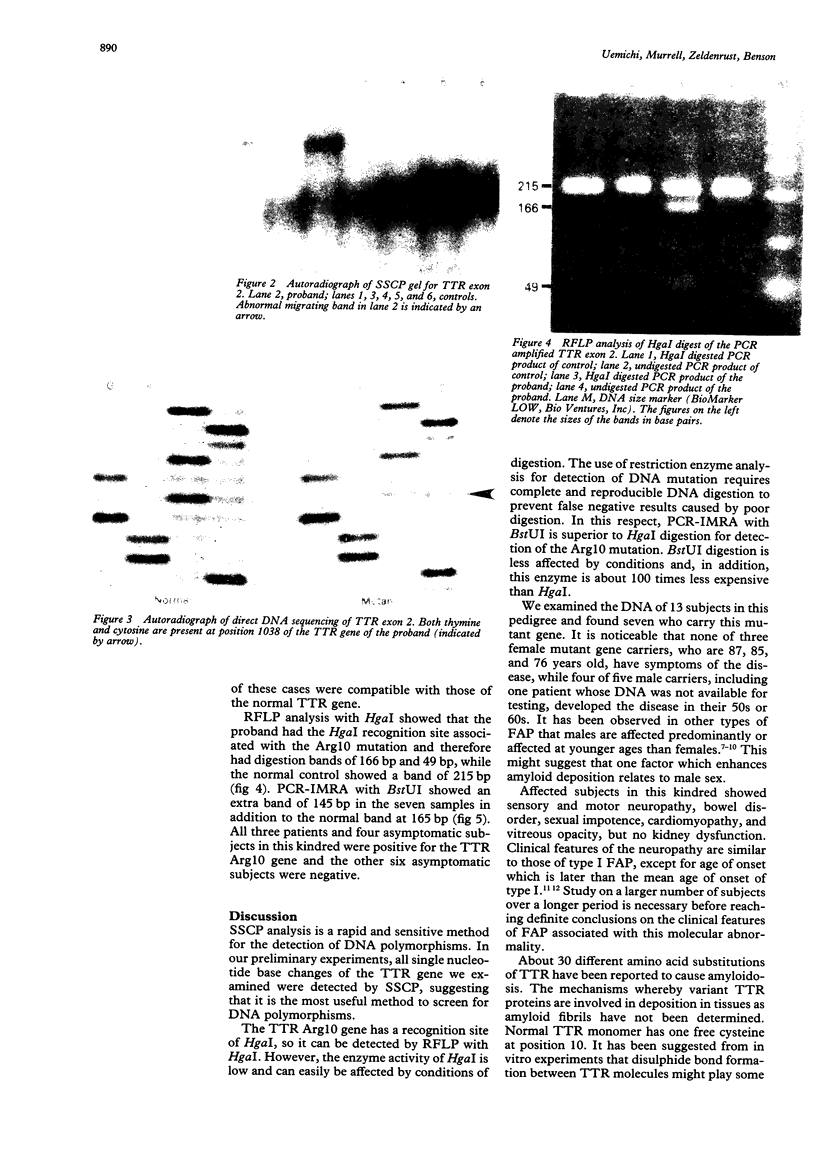
We report a new kindred with systemic amyloidosis presenting as peripheral neuropathy in the sixth and seventh decades of life. Polymorphism in exon 2 of the transthyretin (TTR) gene was suggested by single strand conformation polymorphism analysis and determined by direct DNA sequencing. We also developed restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis by polymerase chain reaction using a primer with an induced mutation. The point mutation (cytosine for thymine at position 1038 of the TTR gene) is responsible for substitution of arginine for cysteine at position 10 of the TTR molecule. It is hypothesised that the TTR molecules which have no cysteine have a unique structure in heterozygous TTR polymers and are responsible for amyloid fibril formation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson M. D. Inherited amyloidosis. J Med Genet. 1991 Feb;28(2):73–78. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.2.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S., Hanyu N., Hongo M., Yoshioka J., Oguchi H., Yanagisawa N., Kobayashi T., Tsukagoshi H., Ito N., Yokota T. Hereditary generalized amyloidosis with polyneuropathy. Clinicopathological study of 65 Japanese patients. Brain. 1987 Apr;110(Pt 2):315–337. doi: 10.1093/brain/110.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madisen L., Hoar D. I., Holroyd C. D., Crisp M., Hodes M. E. DNA banking: the effects of storage of blood and isolated DNA on the integrity of DNA. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Jun;27(2):379–390. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320270216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. C., Gregg R. E., Brewer H. B., Jr, Benson M. D. A mutation in apolipoprotein A-I in the Iowa type of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):318–323. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90288-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. C., Liepnieks J. J., McKusick V. A., Benson M. D. Direct sequencing of the gene for Maryland/German familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy type II and genotyping by allele-specific enzymatic amplification. Genomics. 1989 Oct;5(3):535–540. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Iwahana H., Kanazawa H., Hayashi K., Sekiya T. Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2766–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuzuki T., Mita S., Maeda S., Araki S., Shimada K. Structure of the human prealbumin gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12224–12227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemichi T., Ueno S., Fujimura H., Umekage T., Yorifuji S., Matsuzawa Y., Tarui S. Familial amyloid polyneuropathy related to transthyretin Gly42 in a Japanese family. Muscle Nerve. 1992 Aug;15(8):904–911. doi: 10.1002/mus.880150807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]