Abstract
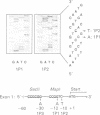
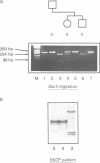
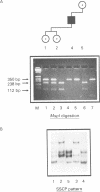
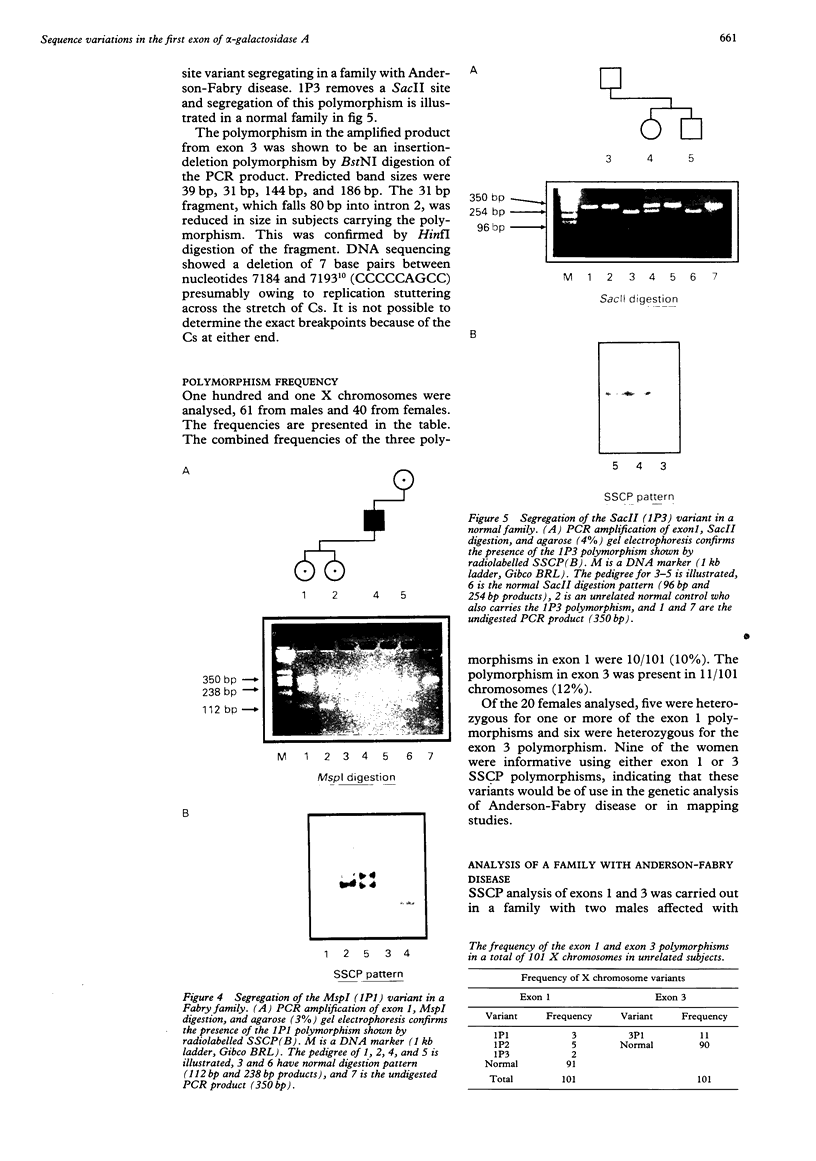
The alpha-galactosidase A gene (GALA), which is deficient in males with Anderson-Fabry disease, is shown to be remarkably polymorphic in the 5' untranslated region. GALA contains seven exons. The first exon contains 60 bp of 5' untranslated sequence before the methionine initiation codon. Single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) screening has shown three polymorphic variants from the published sequence within the 60 base pairs. The sequence changes involved are C to T at -10, G to A at -12 (which removes an MspI site), and G to A at -30 (which removes a SacII site). The combined frequency of these is 10%. A further insertion-deletion polymorphism is detected by SSCP of a 400 bp fragment including exon 3. Both polymorphisms can be easily detected using small polyacrylamide gels and ethidium bromide staining. Nine of 20 women were informative for one of these polymorphisms and this simple SSCP analysis should be of great assistance in family studies of Anderson-Fabry disease. Such a high level of polymorphism has not been previously reported in the 5' untranslated region of a human gene and is unusual in any such short stretch of DNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein H. S., Bishop D. F., Astrin K. H., Kornreich R., Eng C. M., Sakuraba H., Desnick R. J. Fabry disease: six gene rearrangements and an exonic point mutation in the alpha-galactosidase gene. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1390–1399. doi: 10.1172/JCI114027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. F., Calhoun D. H., Bernstein H. S., Hantzopoulos P., Quinn M., Desnick R. J. Human alpha-galactosidase A: nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the mature enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4859–4863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. F., Kornreich R., Desnick R. J. Structural organization of the human alpha-galactosidase A gene: further evidence for the absence of a 3' untranslated region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. H., Bishop D. F., Bernstein H. S., Quinn M., Hantzopoulos P., Desnick R. J. Fabry disease: isolation of a cDNA clone encoding human alpha-galactosidase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7364–7368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desnick R. J., Allen K. Y., Desnick S. J., Raman M. K., Bernlohr R. W., Krivit W. Fabry's disease: enzymatic diagnosis of hemizygotes and heterozygotes. Alpha-galactosidase activities in plasma, serum, urine, and leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Feb;81(2):157–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desnick R. J., Bernstein H. S., Astrin K. H., Bishop D. F. Fabry disease: molecular diagnosis of hemizygotes and heterozygotes. Enzyme. 1987;38(1-4):54–64. doi: 10.1159/000469190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejiofor A., Robinson D., Wise D., Hamers M., Tager J. M. Anderson-Fabry disease: rapid detection of carriers by hair bulb analysis. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1978;1(2):71–74. doi: 10.1007/BF01801848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Richards S., Verkerk A. J., Holden J. J., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Warren S. T. Variation of the CGG repeat at the fragile X site results in genetic instability: resolution of the Sherman paradox. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1047–1058. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Sakuraba H., Suzuki Y. Point mutations in the upstream region of the alpha-galactosidase A gene exon 6 in an atypical variant of Fabry disease. Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;89(1):29–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00207037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkilionis A. J., Riddell D. C., Spence M. W., Fenwick R. G. Fabry disease in a large Nova Scotia kindred: carrier detection using leucocyte alpha-galactosidase activity and an NcoI polymorphism detected by an alpha-galactosidase cDNA clone. J Med Genet. 1991 Apr;28(4):232–240. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.4.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide T., Ishiura M., Iwai K., Inoue M., Kaneda Y., Okada Y., Uchida T. A case of Fabry's disease in a patient with no alpha-galactosidase A activity caused by a single amino acid substitution of Pro-40 by Ser. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 1;259(2):353–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80046-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornreich R., Desnick R. J., Bishop D. F. Nucleotide sequence of the human alpha-galactosidase A gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3301–3302. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemansky P., Bishop D. F., Desnick R. J., Hasilik A., von Figura K. Synthesis and processing of alpha-galactosidase A in human fibroblasts. Evidence for different mutations in Fabry disease. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2062–2065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt R. C. Polymorphisms in the transcribed 3' untranslated region of eukaryotic genes. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90168-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermot K. D., Morgan S. H., Cheshire J. K., Wilson T. M. Anderson Fabry disease, a close linkage with highly polymorphic DNA markers DXS17, DXS87 and DXS88. Hum Genet. 1987 Nov;77(3):263–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00284482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty E. M., Carstens R., Bale A. E. Ornithine transcarbamylase polymorphism detected by PCR introduction of DraI site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):690–690. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuraba H., Eng C. M., Desnick R. J., Bishop D. F. Invariant exon skipping in the human alpha-galactosidase A pre-mRNA: Ag+1 to t substitution in a 5'-splice site causing Fabry disease. Genomics. 1992 Apr;12(4):643–650. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuraba H., Oshima A., Fukuhara Y., Shimmoto M., Nagao Y., Bishop D. F., Desnick R. J., Suzuki Y. Identification of point mutations in the alpha-galactosidase A gene in classical and atypical hemizygotes with Fabry disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Nov;47(5):784–789. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trofatter J. A., Pratt V. M., Dlouhy S. R., Hodes M. E. AhaII polymorphism in human X-linked proteolipid protein gene (PLP). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):6057–6057. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.6057-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoi T., Shinoda K., Ohno I., Kato K., Miyawaki T., Taniguchi N. A 3' splice site consensus sequence mutation in the intron 3 of the alpha-galactosidase A gene in a patient with Fabry disease. Jinrui Idengaku Zasshi. 1991 Sep;36(3):245–250. doi: 10.1007/BF01910542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Scheidt W., Eng C. M., Fitzmaurice T. F., Erdmann E., Hübner G., Olsen E. G., Christomanou H., Kandolf R., Bishop D. F., Desnick R. J. An atypical variant of Fabry's disease with manifestations confined to the myocardium. N Engl J Med. 1991 Feb 7;324(6):395–399. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102073240607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]