Abstract
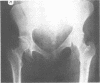
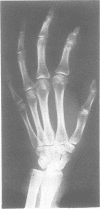
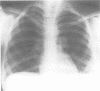
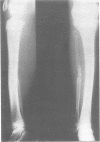
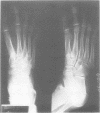
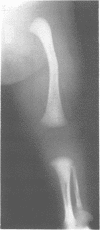
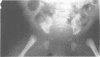
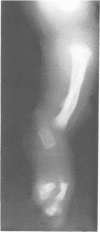
We present a mother and daughter with clinical and radiological findings consistent with the diagnosis of campomelic dysplasia. Milder tibial bowing and significant shortening of the phalangeal bones of both hands and feet may distinguish this from the classical autosomal recessive form of the disease.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cremin B. J., Orsmond G., Beighton P. Autosomal recessive inheritance in camptomelic dwarfism. Lancet. 1973 Mar 3;1(7801):488–489. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91918-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. D., Spranger J. W. Campomelic dysplasia. Further elucidation of a distinct entity. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Mar;134(3):285–289. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130150039010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston C. S., Opitz J. M., Spranger J. W., Macpherson R. I., Reed M. H., Gilbert E. F., Herrmann J., Schinzel A. The campomelic syndrome: review, report of 17 cases, and follow-up on the currently 17-year-old boy first reported by Maroteaux et al in 1971. Am J Med Genet. 1983 May;15(1):3–28. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320150103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafai T. Letter: Camptomelic syndrome in siblings. J Pediatr. 1976 Sep;89(3):512–513. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80568-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stüve A., Wiedemann H. R. Congenital bowing of the long bones in two sisters. Lancet. 1971 Aug 28;2(7722):495–495. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92666-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurmon T. F., DeFraites E. B., Anderson E. E. Familial camptomelic dwarfism. J Pediatr. 1973 Nov;83(5):841–843. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]