Abstract
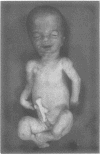
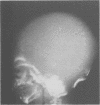
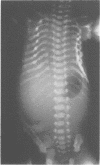
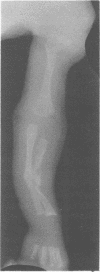
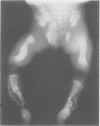
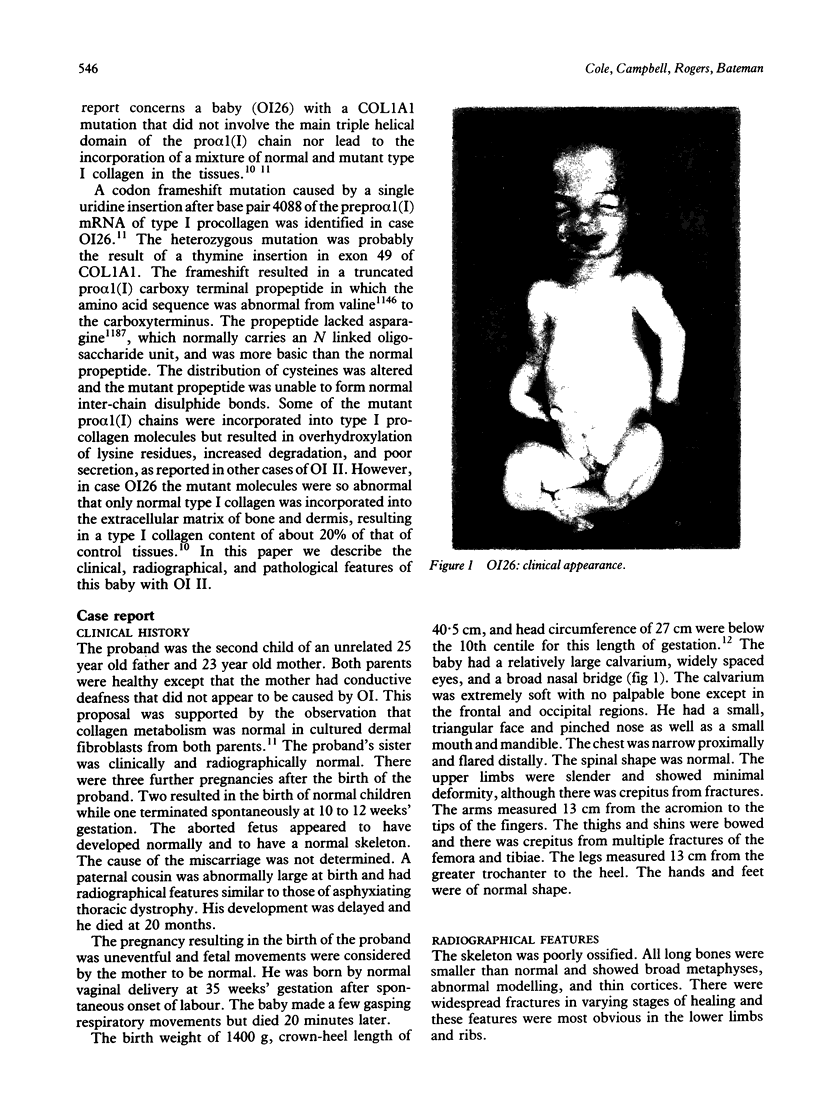
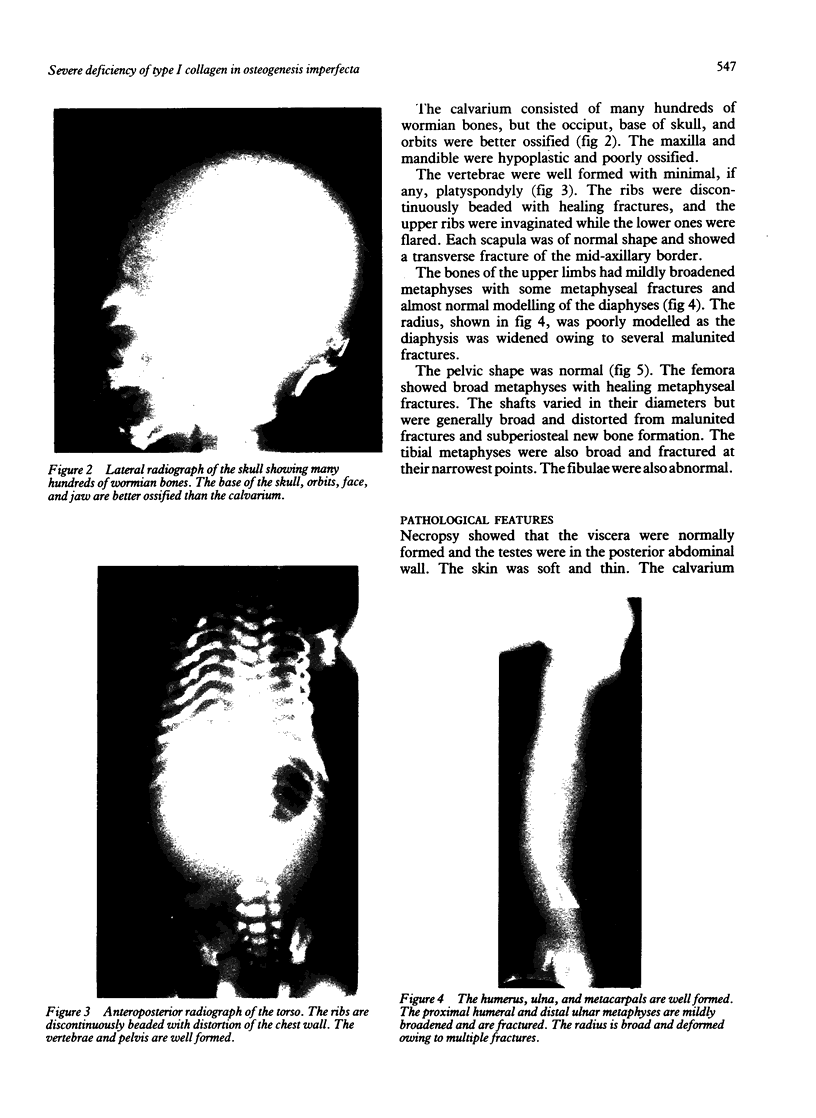
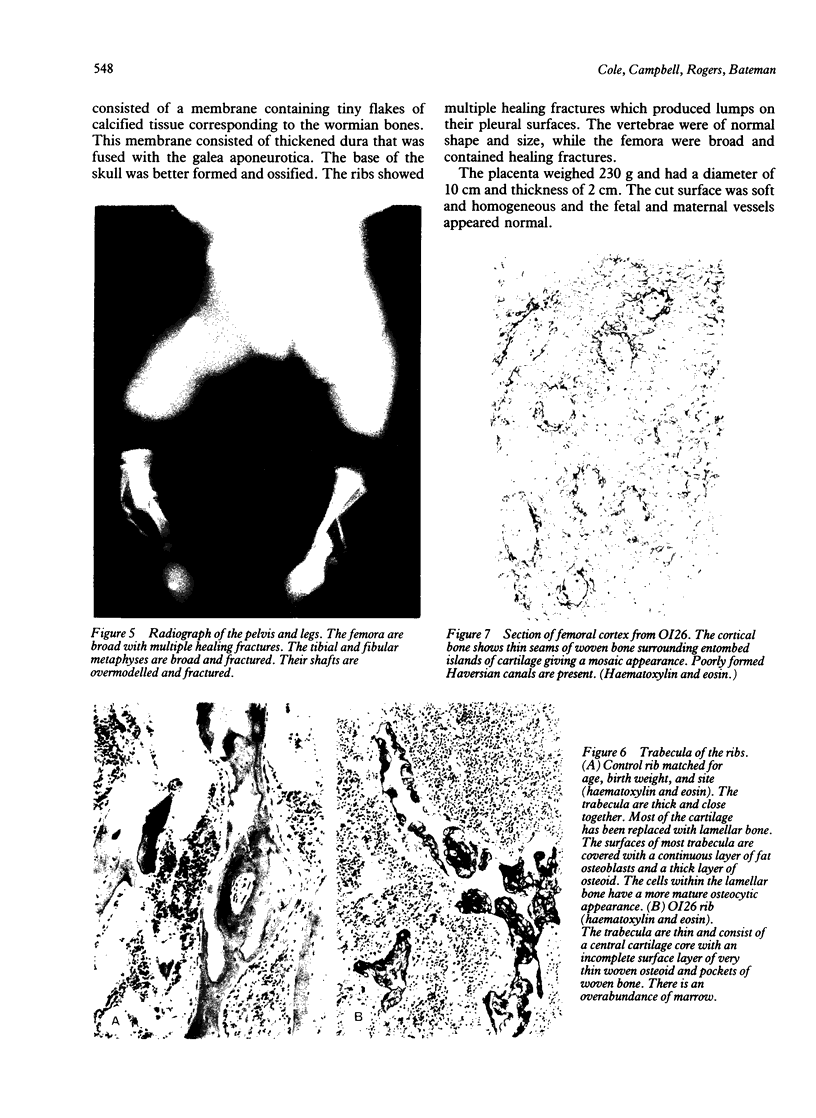
The features of a baby with lethal perinatal osteogenesis imperfecta (OI II), owing to a frameshift mutation that resulted in the production of a truncated and functionless carboxy terminal propeptide of the pro alpha 1(I) chain of type I procollagen, were studied. The baby (OI26) was heterozygous for an insertion of a single uridine nucleotide after base pair 4088 of the prepro alpha 1(I) mRNA of type I procollagen. Only normal type I collagen was incorporated into the extracellular matrix of bone and dermis resulting in a type I collagen content of about 20% of control tissues. The baby was born at 35 weeks' gestation and died shortly afterwards. He was small and had the radiographical features most like those of OI IIB. The skeleton was poorly ossified. The ribs were discontinuously beaded and the femora were broad with multiple healed fractures of the diaphyses and metaphyses. Other long bones had broad metaphyses with overmodelled diaphyses. The calvarium contained many hundreds of wormian bones. Histological examination showed grossly deficient endochondral and intramembranous ossification. The bone was of a woven type without evidence of lamellar bone or Haversian systems and the osteoblasts did not mature into osteocytes. The cortex of the femur contained Haversian canals but they were surrounded by loose collagen fibres and a mosaic pattern of woven bone and islands of cartilage. We propose that OI IIB can be sub-classified into two groups, one with helical mutations and both normal and mutant type I collagen in the tissues, and the other with carboxy terminal propeptide mutations and a severe type I collagen deficiency, but without mutant collagen in the tissues.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateman J. F., Chan D., Mascara T., Rogers J. G., Cole W. G. Collagen defects in lethal perinatal osteogenesis imperfecta. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):699–708. doi: 10.1042/bj2400699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman J. F., Chan D., Walker I. D., Rogers J. G., Cole W. G. Lethal perinatal osteogenesis imperfecta due to the substitution of arginine for glycine at residue 391 of the alpha 1(I) chain of type I collagen. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7021–7027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman J. F., Lamande S. R., Dahl H. H., Chan D., Cole W. G. Substitution of arginine for glycine 664 in the collagen alpha 1(I) chain in lethal perinatal osteogenesis imperfecta. Demonstration of the peptide defect by in vitro expression of the mutant cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11627–11630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman J. F., Lamande S. R., Dahl H. H., Chan D., Mascara T., Cole W. G. A frameshift mutation results in a truncated nonfunctional carboxyl-terminal pro alpha 1(I) propeptide of type I collagen in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):10960–10964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman J. F., Mascara T., Chan D., Cole W. G. Abnormal type I collagen metabolism by cultured fibroblasts in lethal perinatal osteogenesis imperfecta. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):103–115. doi: 10.1042/bj2170103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Tsipouras P., Bonadio J. F., Starman B. J., Schwartz R. C. Perinatal lethal osteogenesis imperfecta (OI type II): a biochemically heterogeneous disorder usually due to new mutations in the genes for type I collagen. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):237–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Williams C. J., Pepe G., Hirsch J. L., Prockop D. J., Ramirez F. Internal deletion in a collagen gene in a perinatal lethal form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):78–80. doi: 10.1038/304078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. H., Byers P. H., Steinmann B., Gelinas R. E. Lethal osteogenesis imperfecta resulting from a single nucleotide change in one human pro alpha 1(I) collagen allele. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6045–6047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole W. G., Chow C. W., Rogers J. G., Bateman J. F. The clinical features of three babies with osteogenesis imperfecta resulting from the substitution of glycine by arginine in the pro alpha 1(I) chain of type I procollagen. J Med Genet. 1990 Apr;27(4):228–235. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.4.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinou C. D., Nielsen K. B., Prockop D. J. A lethal variant of osteogenesis imperfecta has a single base mutation that substitutes cysteine for glycine 904 of the alpha 1(I) chain of type I procollagen. The asymptomatic mother has an unidentified mutation producing an overmodified and unstable type I procollagen. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):574–584. doi: 10.1172/JCI113920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene D. R., Sakai L. Y., Bächinger H. P., Burgeson R. E. Type III collagen can be present on banded collagen fibrils regardless of fibril diameter. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2393–2402. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchen W. H., Robinson H. P., Dickinson A. J. Revised intrauterine growth curves for an Australian hospital population. Aust Paediatr J. 1983 Sep;19(3):157–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1983.tb02082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löhler J., Timpl R., Jaenisch R. Embryonic lethal mutation in mouse collagen I gene causes rupture of blood vessels and is associated with erythropoietic and mesenchymal cell death. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90514-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A. C., Osse G., Schloon H. G., Lenard H. G., Deak S., Myers J. C., Prockop D. J., Weigel W. R., Fryer P., Pope F. M. The clinical features of homozygous alpha 2(I) collagen deficient osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet. 1984 Aug;21(4):257–262. doi: 10.1136/jmg.21.4.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pihlajaniemi T., Dickson L. A., Pope F. M., Korhonen V. R., Nicholls A., Prockop D. J., Myers J. C. Osteogenesis imperfecta: cloning of a pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene with a frameshift mutation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):12941–12944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnieke A., Dziadek M., Bateman J., Mascara T., Harbers K., Gelinas R., Jaenisch R. Introduction of the human pro alpha 1(I) collagen gene into pro alpha 1(I)-deficient Mov-13 mouse cells leads to formation of functional mouse-human hybrid type I collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):764–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillence D. O., Barlow K. K., Garber A. P., Hall J. G., Rimoin D. L. Osteogenesis imperfecta type II delineation of the phenotype with reference to genetic heterogeneity. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Feb;17(2):407–423. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillence D. O., Senn A., Danks D. M. Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet. 1979 Apr;16(2):101–116. doi: 10.1136/jmg.16.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. M., Young I. D., Hall C. M., Pembrey M. E. Recurrence risks and prognosis in severe sporadic osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet. 1987 Jul;24(7):390–405. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.7.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]