Abstract
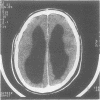
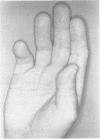
We describe a two generation family in which two males have the X linked recessive MASA syndrome (mental retardation, aphasia, shuffling gait, and adducted thumbs). A third male in this family died at the age of 15 years from congenital hydrocephalus. In the present family cerebral abnormalities are reported for the first time. Linkage analysis confirms the chromosome localisation at Xq28. A crossover between the coagulation factor VIII locus (F8C) and MASA syndrome, but not with DXS52 and DXS305, locates the gene on the same side of F8C as DXS52 and DXS305. The possible relationship between MASA syndrome and X linked hydrocephalus is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bianchine J. W., Lewis R. C., Jr The MASA syndrome: a new heritable mental retardation syndrome. Clin Genet. 1974;5(4):298–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1974.tb01697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gareis F. J., Mason J. D. X-linked mental retardation associated with bilateral clasp thumb anomaly. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jan;17(1):333–338. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt J., Ballo R., Sachs B., Moosa A. X-linked spastic paraplegia: evidence for homogeneity with a variable phenotype. Clin Genet. 1989 Feb;35(2):116–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1989.tb02915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday J., Chow C. W., Wallace D., Danks D. M. X linked hydrocephalus: a survey of a 20 year period in Victoria, Australia. J Med Genet. 1986 Feb;23(1):23–31. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenwrick S., Ionasescu V., Ionasescu G., Searby C., King A., Dubowitz M., Davies K. E. Linkage studies of X-linked recessive spastic paraplegia using DNA probes. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):264–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00401241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppen L. D., Leppert M. F., O'Connell P., Nakamura Y., Stauffer D., Lathrop M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Etiological heterogeneity in X-linked spastic paraplegia. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Nov;41(5):933–943. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landrieu P., Ninane J., Ferrière G., Lyon G. Aqueductal stenosis in X-linked hydrocephalus: a secondary phenomenon? Dev Med Child Neurol. 1979 Oct;21(5):637–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1979.tb01678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Gedeon A. K., Haan E. A., Woodroffe P., Mulley J. C. Linkage studies with the gene for an X-linked syndrome of mental retardation, microcephaly and spastic diplegia (MRX2) Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):493–508. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Kretz C., Oberlé I., Mandel J. L. A new polymorphic marker very closely linked to DXS52 in the q28 region of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):85–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00288280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems P. J., Brouwer O. F., Dijkstra I., Wilmink J. X-linked hydrocephalus. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Aug;27(4):921–928. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320270419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. M., Davies K. E., Bell M. V., Huson S. M., Patterson M. N. MASA syndrome: further clinical delineation and chromosomal localisation. Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;82(4):367–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00273999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeatman G. W. Mental retardation-clasped thumb syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jan;17(1):339–344. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]