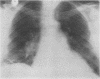
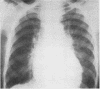
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER J. K., WEST J. R., WOOD J. A., RICHARDS D. W. Analysis of the respiratory response to carbon dioxide inhalation in varying clinical states of hypercapnia, anoxia, and acid-base derangement. J Clin Invest. 1955 Apr;34(4):511–532. doi: 10.1172/JCI103100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNSTEIN L., D'SILVA J. L., MENDEL D. The effect of the rate of breathing on the maximum breathing capacity determined with a new spirometer. Thorax. 1952 Sep;7(3):255–262. doi: 10.1136/thx.7.3.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAKEMORE W. S., FORSTER R. E., MORTON J. W., OGILVIE C. M. A standardized breath holding technique for the clinical measurement of the diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jan;36(1 Pt 1):1–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI103402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL E. J., HOWELL J. B. Simple rapid methods of estimating arterial and mixed venous pCO2. Br Med J. 1960 Feb 13;1(5171):458–462. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5171.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL E. J., SHORT D. S. The cause of oedema in "corpulmonale". Lancet. 1960 May 28;1(7135):1184–1186. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)91062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL E. J. Simplification of Haldane's apparatus for measuring carbon dioxide concentration in respired gases in clinical practice. Br Med J. 1960 Feb 13;1(5171):457–458. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5171.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNIACK R. M., SNIDAL D. P. The effect of obstruction to breathing on the ventilatory response to CO2. J Clin Invest. 1956 Nov;35(11):1286–1290. doi: 10.1172/JCI103383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EFRON R., KENT D. C. Chronic respiratory acidosis due to brain disease; reversal of normal electroencephalographic response to hyperventilation. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1957 Jun;77(6):575–587. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1957.02330360033002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EHRNER L., GARLIND T., LINDERHOLM H. Chronic cor pulmonale following thromboembolism: a clinical and pathophysiological study of three cases. Acta Med Scand. 1959 Jul 25;164:279–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN A. P. Respiratory gases in the regulation of the pulmonary circulation. Physiol Rev. 1961 Jan;41:214–280. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1961.41.1.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARLIND T., LINDERHOLM H. Hypoventilation syndrome in a case of chronic epidemic encephalitis. Acta Med Scand. 1958 Nov 27;162(5):333–349. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1958.tb01780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT R., SIPPLE J. H., AUCHINCLOSS J. H., Jr Respiratory control and work of breathing in obese subjects. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Jan;16:21–26. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODWIN J. F., ABDIN Z. H. The cardiogram of congenital and acquired right ventricular hypertrophy. Br Heart J. 1959 Oct;21:523–544. doi: 10.1136/hrt.21.4.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HADORN W., SCHERRER M. [Essential alveolar hypoventilation with cor pulmonale]. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1959 Jun 20;89:647–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGH-JONES P., LAMBERT A. V. A simple standard exercise test and its use for measuring exertion dyspnoea. Br Med J. 1952 Jan 12;1(4749):65–71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4749.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEMSLEY W. F. F. Body weight at different ages and heights. Ann Eugen. 1952 May;16(4):316–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1951.tb02484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh M. The diffusion of gases through the lungs of man. J Physiol. 1915 May 12;49(4):271–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1915.sp001710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWRENCE L. T. Idiopathic hypoventilation, polycythemia, and cor pulmonale. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1959 Oct;80:575–581. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1959.80.4P1.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWENSTEIN L., PARE P. Polycythemia associated with disturbed function of the respiratory center. Blood. 1956 Dec;11(12):1077–1084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGRATH M. W., THOMSON M. L. The effect of age, body size and lung volume change on alveolar-capillary permeability and diffusing capacity in man. J Physiol. 1959 Jun 11;146(3):572–582. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAEYE R. L. Alveolar hypoventilation and cor pulmonale secondary to damage to the respiratory center. Am J Cardiol. 1961 Sep;8:416–419. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(61)90161-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEDHAM C. D., ROGAN M. C., McDONALD I. Normal standards for lung volumes, intrapulmonary gas-mixing, and maximum breathing capacity. Thorax. 1954 Dec;9(4):313–325. doi: 10.1136/thx.9.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWMAN W., FELTMAN J. A., DEVLIN B. Pulmonary function studies in polycythemia vera; results in five probable cases. Am J Med. 1951 Dec;11(6):706–714. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(51)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWEN W. R., THOMAS W. A., CASTLEMAN B., BLAND E. F. Unrecognized emboli to the lungs with subsequent cor pulmonale. N Engl J Med. 1953 Dec 3;249(23):919–926. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195312032492302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIME F. J., WESTLAKE E. K. The respiratory response to CO2 in emphysema. Clin Sci. 1954 Aug;13(3):321–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATTO O., BRISCOE W. A., MORTON J. W., COMROE J. H., Jr Anoxemia secondary to polycythemia and polycythemia secondary to anoxemia. Am J Med. 1955 Dec;19(6):958–965. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(55)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- READ J. Pulmonary ventilation and perfusion in normal subjects and in patients with emphysema. Clin Sci. 1959 Aug;18:465–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDS D. W., FRITTS H. W., Jr, DAVIS A. L. Observations on the control of respiration in emphysema: the effects of oxygen on ventilatory response to CO2 inhalation. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1958;71:142–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHTER T., WEST J. R., FISHMAN A. P. The syndrome of alveolar hypoventilation and diminished sensitivity of the respiratory center. N Engl J Med. 1957 Jun 20;256(25):1165–1170. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195706202562501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODMAN T., CLOSE H. P. The primary hypoventilation syndrome. Am J Med. 1959 May;26(5):808–817. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODMAN T., RESNICK M. E., BERKOWITZ R. D., FENNELLY J. F., OLIVIA J. Alveolar hypoventilation due to involvement of the respiratory center by obscure disease of the central nervous system. Am J Med. 1962 Feb;32:208–217. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(62)90290-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSSIER P. H., BUHLMANN A. Cor pulmonale et pathophysiologie alvéolaire. Cardiologia. 1954;25(2-3):132–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARNOFF S. J., WHITTENBERGER J. L., AFFELDT J. E. Hypoventilation syndrome in bulbar poliomyelitis. J Am Med Assoc. 1951 Sep 1;147(1):30–34. doi: 10.1001/jama.1951.03670180036007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEST J. B., FOWLER K. T., HUGH-JONES P., O'DONNELL T. V. Measurement of the ventilation-perfusion ratio inequality in the lung by the analysis of a single expirate. Clin Sci. 1957 Aug;16(3):529–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON R. H., BORDEN C. W., EBERT R. V., WELLS H. S. A comparison of the effect of voluntary hyperventilation in normal persons, patients with pulmonary emphysema, and patients with cardiac disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1950 Jul;36(1):119–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]