Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIRATH G., KJELLMER I., SANDQVIST L. Spirometric studies in normal subjects. II. Ventilatory capacity tests in adults. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Feb;173:193–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPER N. G., FOWLER W. S., HELMHOLZ H. F., Jr Relationship of height to lung volume in healthy men. Dis Chest. 1960 Mar;37:314–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORY R. C., CALLAHAN R., BOREN H. G., SYNER J. C. The Veterans Administration-Army cooperative study of pulmonary function. I. Clinical spirometry in normal men. Am J Med. 1961 Feb;30:243–258. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(61)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
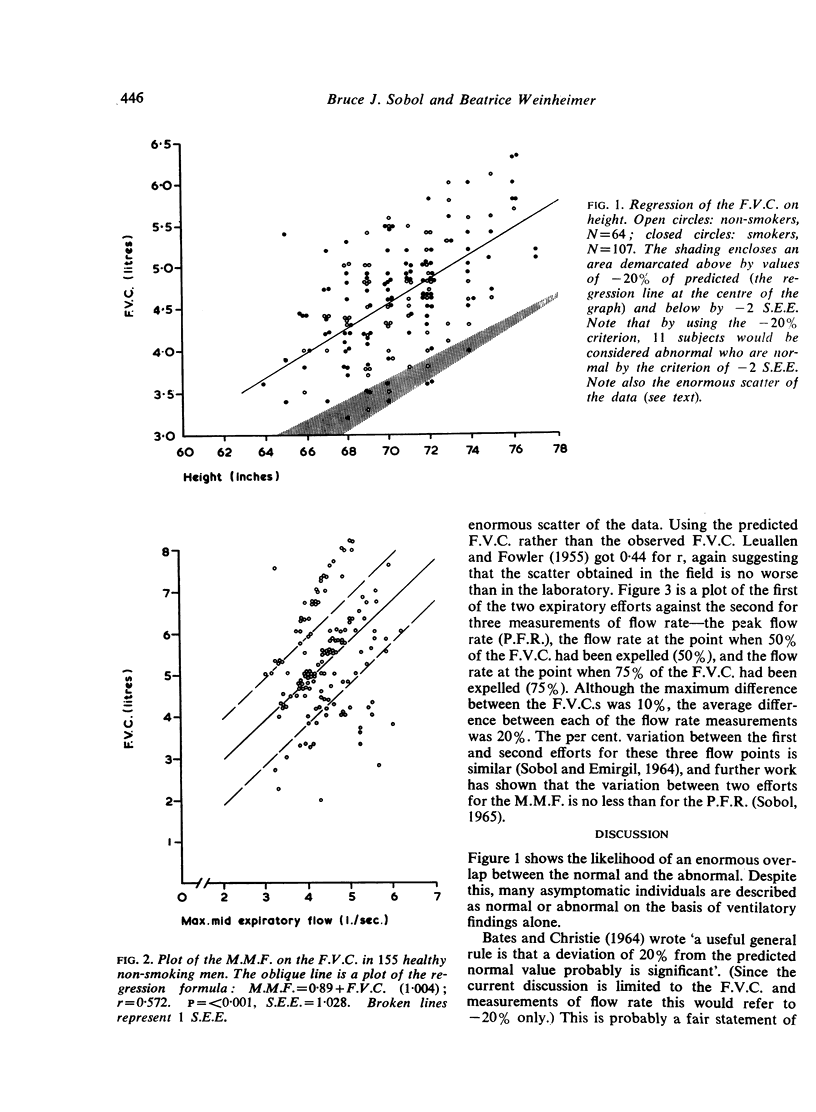
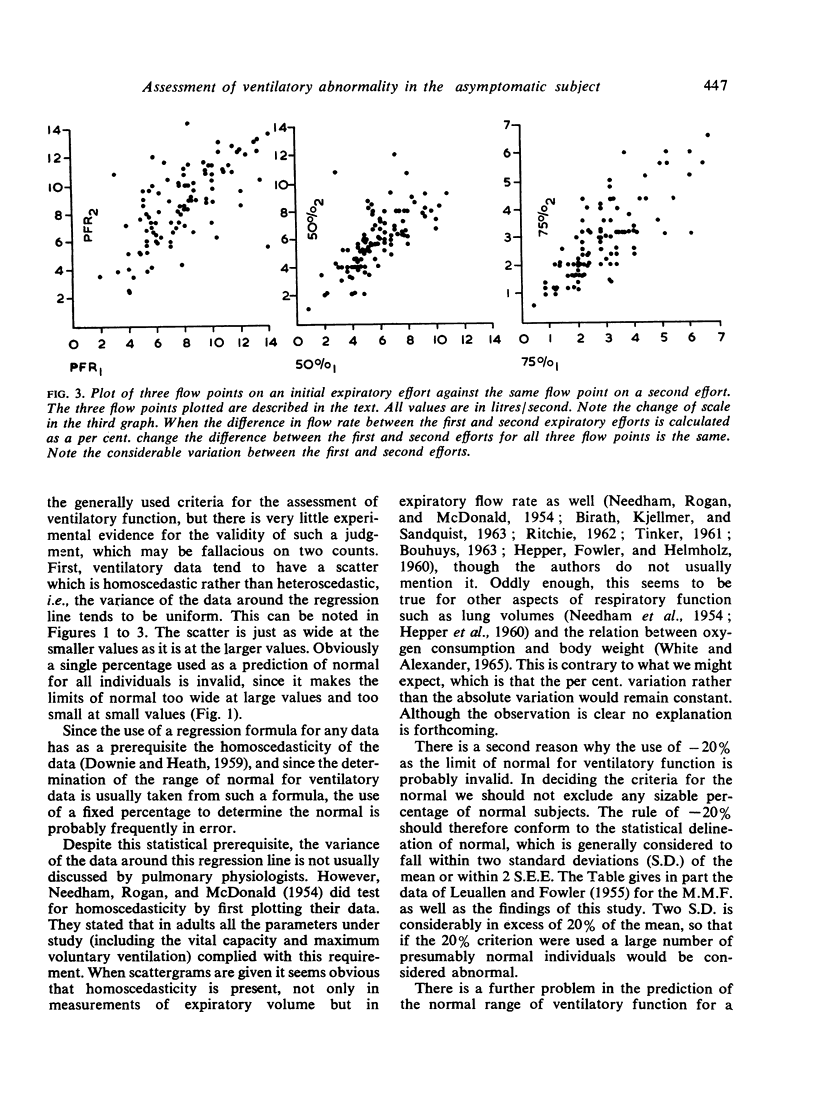
- LEUALLEN E. C., FOWLER W. S. Maximal midexpiratory flow. Am Rev Tuberc. 1955 Dec;72(6):783–800. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1955.72.6.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEDHAM C. D., ROGAN M. C., McDONALD I. Normal standards for lung volumes, intrapulmonary gas-mixing, and maximum breathing capacity. Thorax. 1954 Dec;9(4):313–325. doi: 10.1136/thx.9.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHIE B. A comparison of forced expiratory volume and peak flow in clinical practice. Lancet. 1962 Aug 11;2(7250):271–273. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
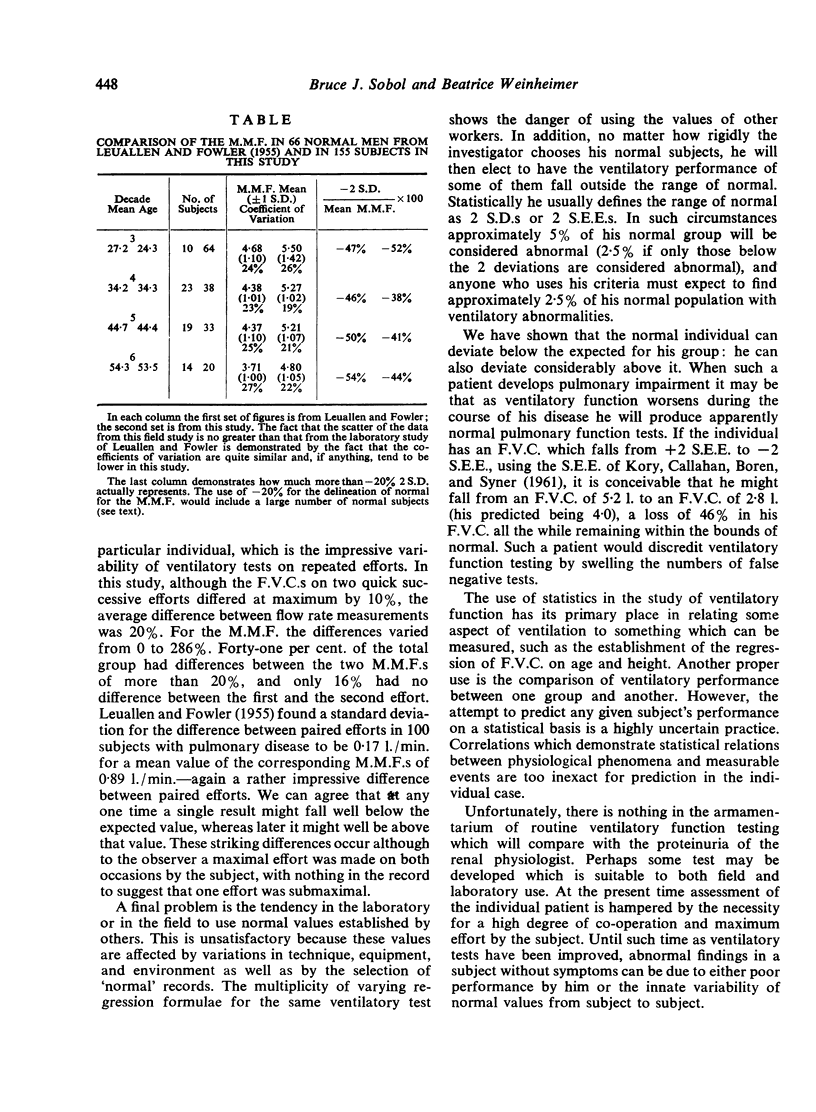
- SOBOL B. J., EMIRGIL C. SUBJECT EFFORT AND THE EXPIRATORY FLOW RATE. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1964 Mar;89:402–408. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1964.89.3.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobol B. J. The maximal midexpiratory flow: a re-examination. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Dec;92(6):914–918. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.92.6P1.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TINKER C. M. Peak expiratory flow measured by the Wright peak flow meter. Distribution of values in men aged 30-59 who denied respiratory symptoms. Br Med J. 1961 May 13;1(5236):1365–1366. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5236.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


