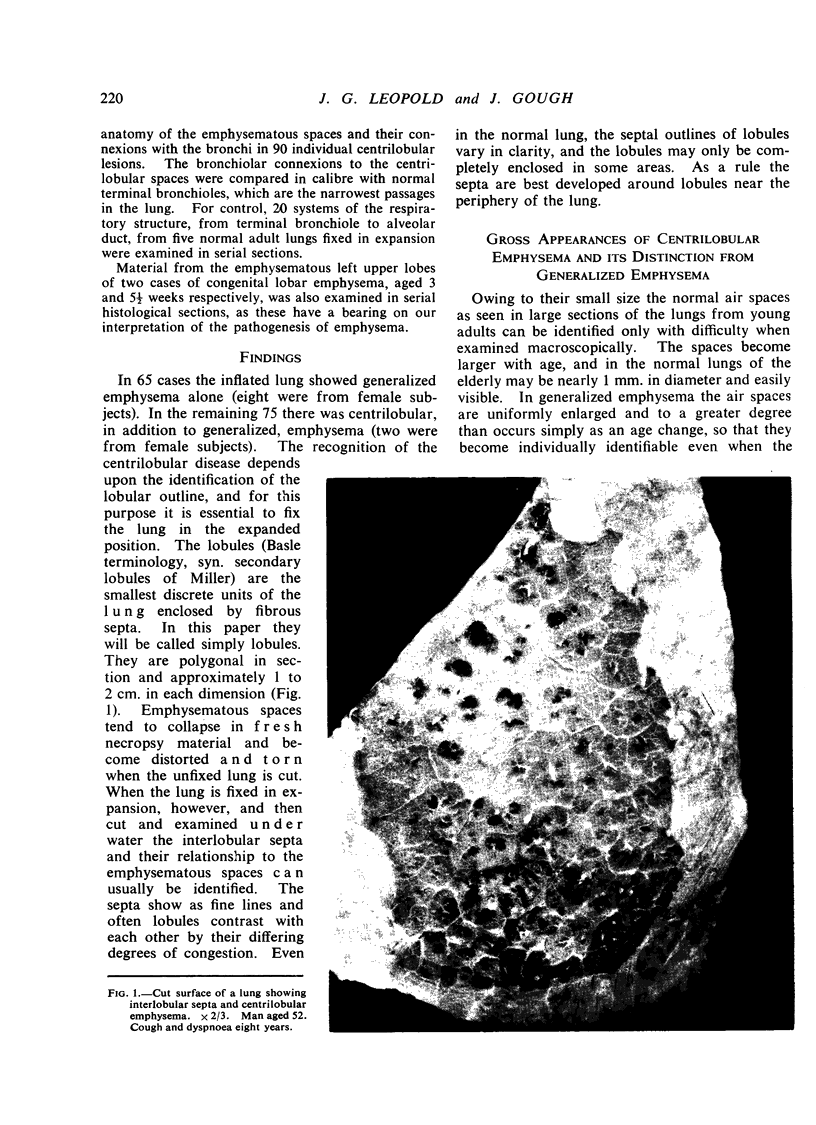
Full text
PDF
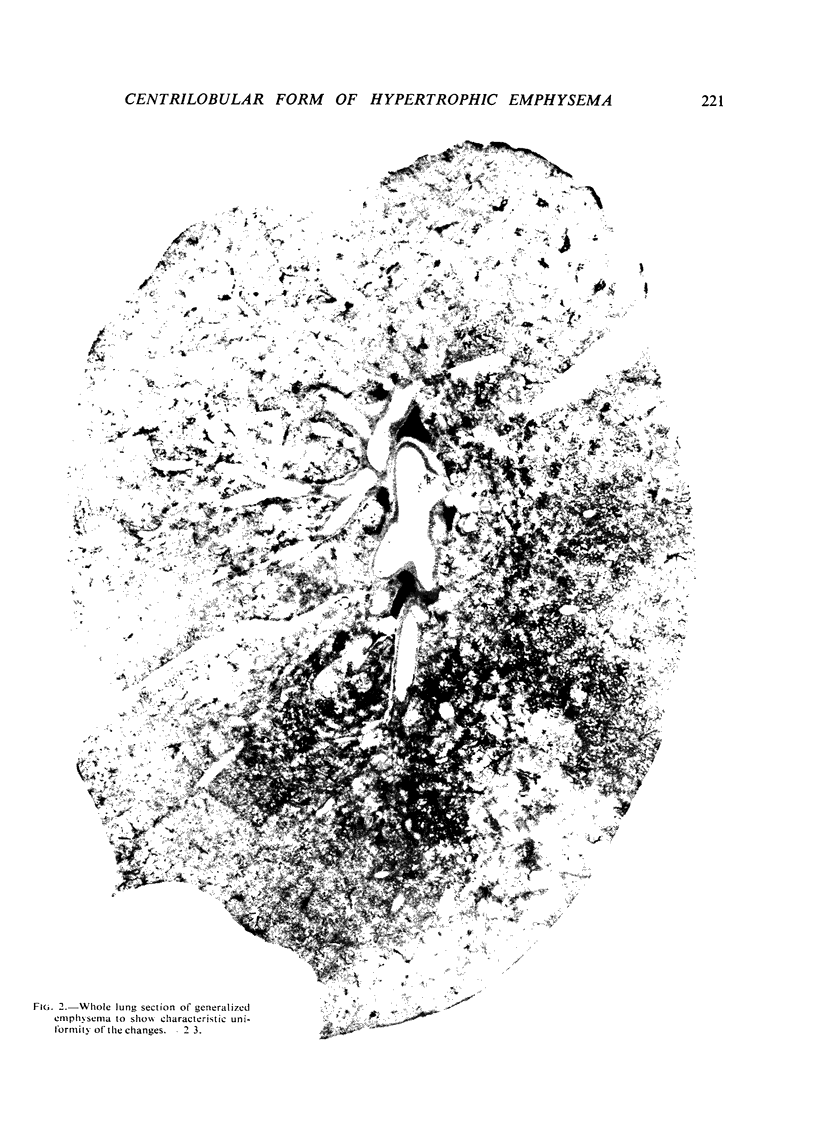
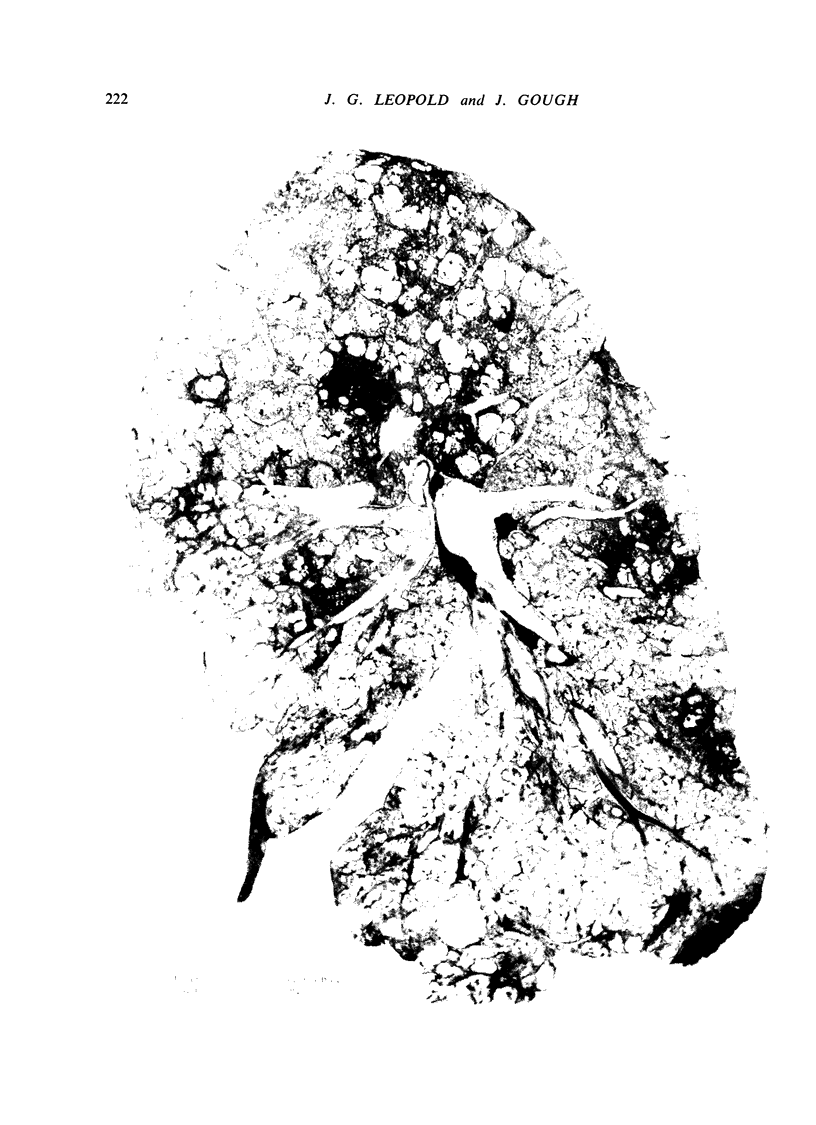








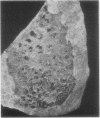
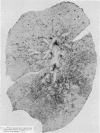
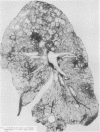
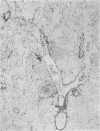
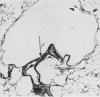
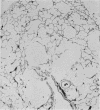
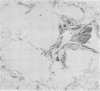
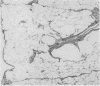
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAYMAN H. Mechanics of airflow in health and in emphysema. J Clin Invest. 1951 Nov;30(11):1175–1190. doi: 10.1172/JCI102537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRY D. L., EBERT R. V., STEAD W. W., BROWN C. C. The mechanics of pulmonary ventilation in normal subjects and in patients with emphysema. Am J Med. 1954 Jan;16(1):80–97. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(54)90325-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOUGH J. The pathological diagnosis of emphysema. Proc R Soc Med. 1952 Sep;45(9):576–577. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPLESTON A. G. The pathological anatomy of simple pneumokoniosis in coal workers. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):235–246. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMBERT M. W. Accessory bronchiolealveolar communications. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(2):311–314. doi: 10.1002/path.1700700206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLEAN K. H. The macroscopic anatomy of pulmonary emphysema. Australas Ann Med. 1956 May;5(2):73–88. doi: 10.1111/imj.1956.5.2.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McADAMS A. J., Jr Bronchiolitis obliterans. Am J Med. 1955 Aug;19(2):314–322. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(55)90430-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McILROY M. B., CHRISTIE R. V. The work of breathing in emphysema. Clin Sci. 1954 Feb;13(1):147–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAIN D. M., KAUFMAN G. The basic lesion in chronic pulmonary emphysema. Am Rev Tuberc. 1953 Jul;68(1):24–30. doi: 10.1164/art.1953.68.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]