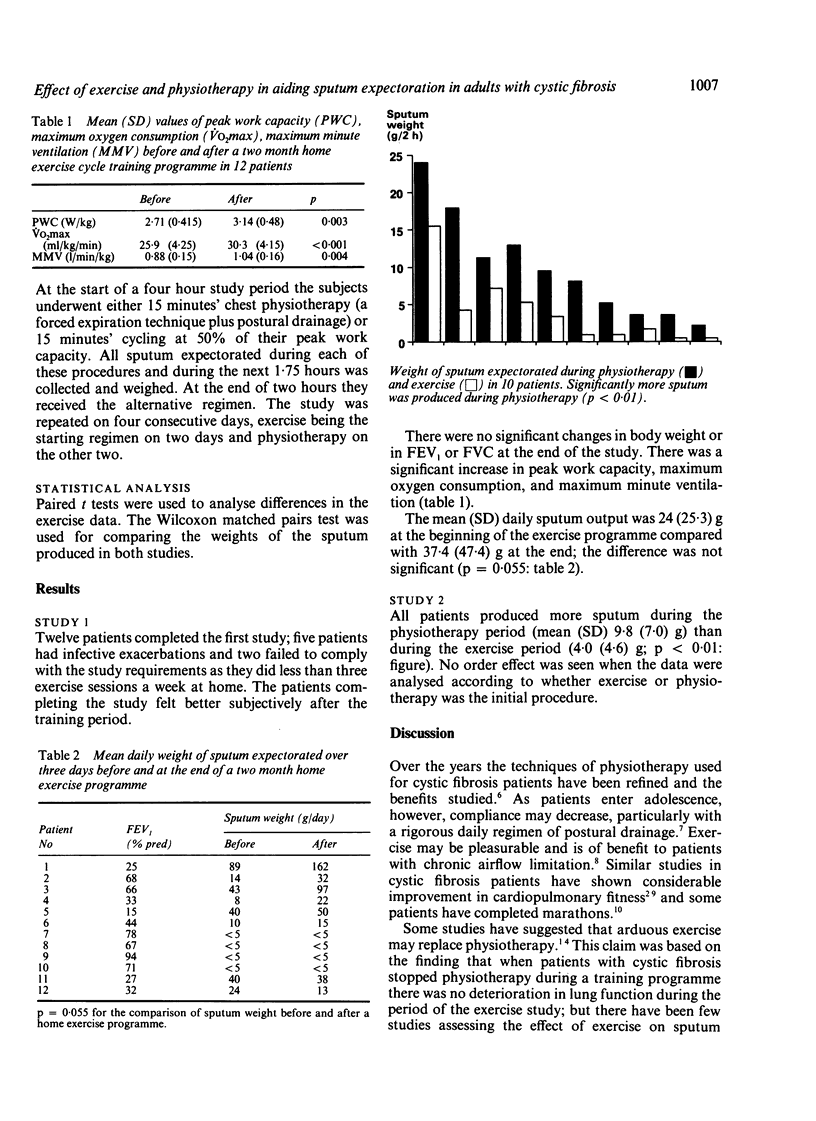
Abstract
The role of exercise in aiding sputum expectoration in patients with cystic fibrosis and the comparative roles of exercise and physiotherapy in sputum expectoration were assessed in two studies. In the first study 19 adult patients undertook a two month programme of home exercise using a cycle ergometer. In the 12 patients completing the study peak work capacity, maximum oxygen consumption, and maximum minute ventilation had increased significantly by the end of the exercise programme; the increase in daily sputum weight (from 24 to 37 g) was not significant (p = 0.055). In the second study (with 10 patients) more sputum was expectorated during and after physiotherapy than during and after exercise (9.8 v 4.0 g). Exercise may have a role in aiding sputum expectoration in patients with cystic fibrosis but should not be considered as a replacement for physiotherapy.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andréasson B., Jonson B., Kornfält R., Nordmark E., Sandström S. Long-term effects of physical exercise on working capacity and pulmonary function in cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1987 Jan;76(1):70–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1987.tb10417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cropp G. J., Pullano T. P., Cerny F. J., Nathanson I. T. Exercise tolerance and cardiorespiratory adjustments at peak work capacity in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Aug;126(2):211–216. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie D. C., Munro C., Gaskell D., Cole P. J. Practice, problems and compliance with postural drainage: a survey of chronic sputum producers. Br J Dis Chest. 1986 Jul;80(3):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(86)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mungall I. P., Hainsworth R. An objective assessment of the value of exercise training to patients with chronic obstructive airways disease. Q J Med. 1980 Winter;49(193):77–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill P. A., Dodds M., Phillips B., Poole J., Webb A. K. Regular exercise and reduction of breathlessness in patients with cystic fibrosis. Br J Dis Chest. 1987 Jan;81(1):62–69. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(87)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldenburg F. A., Jr, Dolovich M. B., Montgomery J. M., Newhouse M. T. Effects of postural drainage, exercise, and cough on mucus clearance in chronic bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Oct;120(4):739–745. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.4.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein D. M., Franklin B. A., Doershuk C. F., Hellerstein H. K., Germann K. J., Horowitz J. G., Stern R. C. Exercise conditioning and cardiopulmonary fitness in cystic fibrosis. The effects of a three-month supervised running program. Chest. 1981 Oct;80(4):392–398. doi: 10.1378/chest.80.4.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor J. A., Webber B. A., Hodson M. E., Batten J. C. Evaluation of the forced expiration technique as an adjunct to postural drainage in treatment of cystic fibrosis. Br Med J. 1979 Aug 18;2(6187):417–418. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6187.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanghelle J. K., Skyberg D. Cystic fibrosis patients running a marathon race. Int J Sports Med. 1988 Feb;9 (Suppl 1):37–40. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1025060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff R. K., Dolovich M. B., Obminski G., Newhouse M. T. Effects of exercise and eucapnic hyperventilation on bronchial clearance in man. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Jul;43(1):46–50. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.43.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zach M. S., Purrer B., Oberwaldner B. Effect of swimming on forced expiration and sputum clearance in cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1981 Nov 28;2(8257):1201–1203. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zach M., Oberwaldner B., Häusler F. Cystic fibrosis: physical exercise versus chest physiotherapy. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Aug;57(8):587–589. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.8.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


