Abstract
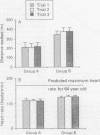
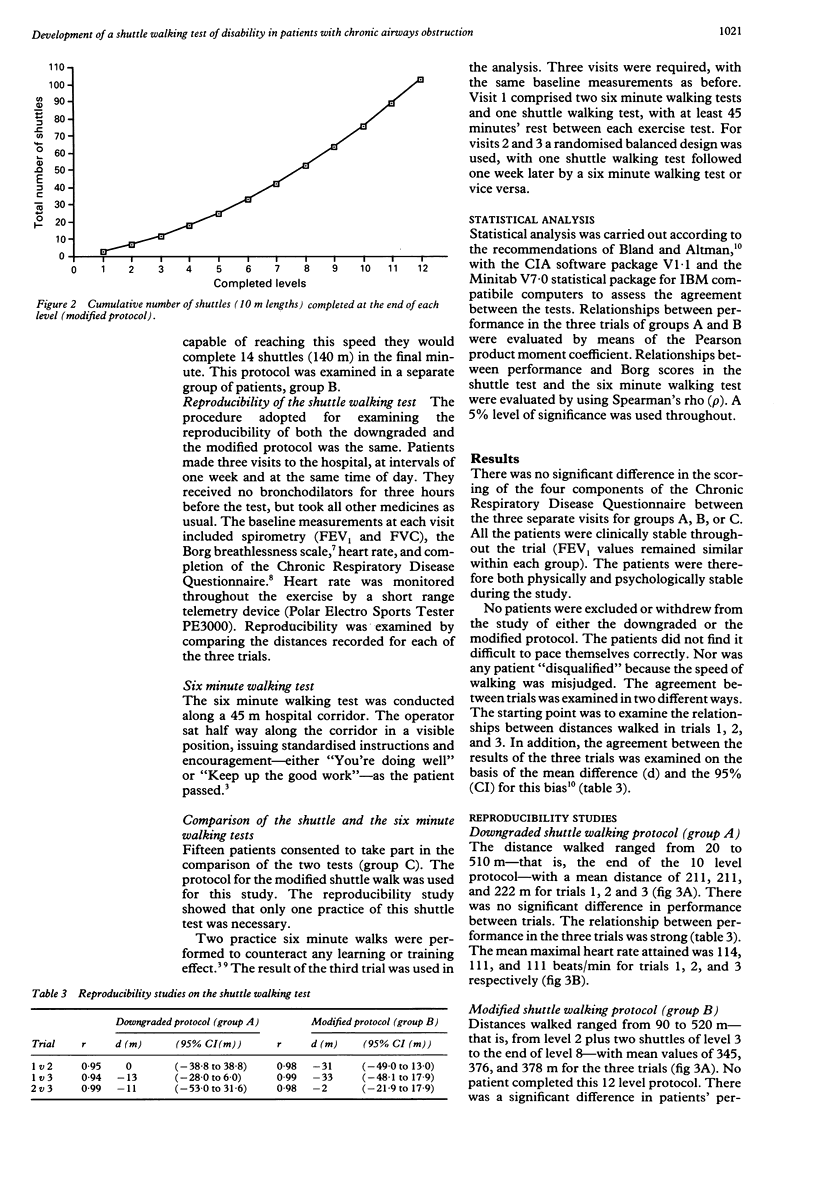
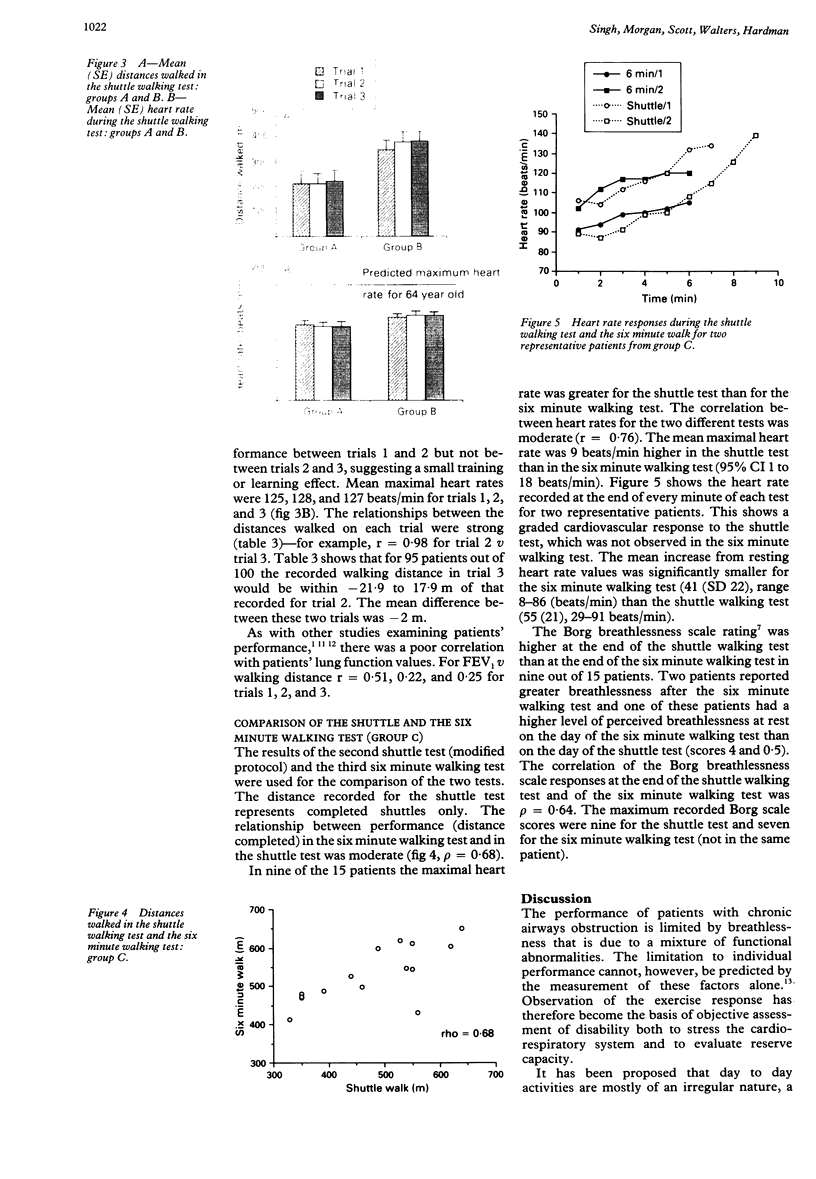
BACKGROUND: The aim was to develop a standardised and externally paced field walking test, incorporating an incremental and progressive structure, to assess functional capacity in patients with chronic airways obstruction. METHODS: The usefulness of two different shuttle walking test protocols was examined in two separate groups of patients. The initial 10 level protocol (group A, n = 10) and a subsequent, modified, 12 level protocol (group B, n = 10) differed in the number of increments and in the speeds of walking. Patients performed three shuttle walking tests one week apart. Then the performance of patients (group C, n = 15) in the six minute walking test was compared with that in the second (modified) shuttle walking test protocol. Heart rate was recorded during all the exercise tests with a short range telemetry device. RESULTS: The 12 level modified protocol provided a measure of functional capacity in patients with a wide range of disability and was reproducible after just one practice walk; the mean difference between trial 2 v 3 was -2.0 (95% CI -21.9 to 17.9) m. There was a significant relation between the distance walked in the six minute walking test and the shuttle walking test (rho = 0.68) but the six minute walking test appeared to overestimate the extent of disability in some patients. The shuttle test provoked a graded cardiovascular response not evident in the six minute test. Moreover, the maximal heart rates attained were significantly higher for the shuttle walking test than for the six minute test. CONCLUSIONS: The shuttle walking test constitutes a standardised incremental field walking test that provokes a symptom limited maximal performance. It provides an objective measurement of disability and allows direct comparison of patients' performance.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaumont A., Cockcroft A., Guz A. A self paced treadmill walking test for breathless patients. Thorax. 1985 Jun;40(6):459–464. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.6.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg G. A. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1982;14(5):377–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butland R. J., Pang J., Gross E. R., Woodcock A. A., Geddes D. M. Two-, six-, and 12-minute walking tests in respiratory disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 May 29;284(6329):1607–1608. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6329.1607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyatt G. H., Berman L. B., Townsend M., Pugsley S. O., Chambers L. W. A measure of quality of life for clinical trials in chronic lung disease. Thorax. 1987 Oct;42(10):773–778. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.10.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyatt G. H., Pugsley S. O., Sullivan M. J., Thompson P. J., Berman L., Jones N. L., Fallen E. L., Taylor D. W. Effect of encouragement on walking test performance. Thorax. 1984 Nov;39(11):818–822. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.11.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. W., Wakefield J. M., Kontaki E. A simple and portable paced step test for reproducible measurements of ventilation and oxygen consumption during exercise. Thorax. 1987 Feb;42(2):136–143. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox A. J., Morrison J. F., Muers M. F. Reproducibility of walking test results in chronic obstructive airways disease. Thorax. 1988 May;43(5):388–392. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.5.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léger L. A., Lambert J. A maximal multistage 20-m shuttle run test to predict VO2 max. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1982;49(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00428958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGavin C. R., Artvinli M., Naoe H., McHardy G. J. Dyspnoea, disability, and distance walked: comparison of estimates of exercise performance in respiratory disease. Br Med J. 1978 Jul 22;2(6132):241–243. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6132.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGavin C. R., Gupta S. P., McHardy G. J. Twelve-minute walking test for assessing disability in chronic bronchitis. Br Med J. 1976 Apr 3;1(6013):822–823. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6013.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mungall I. P., Hainsworth R. Assessment of respiratory function in patients with chronic obstructive airways disease. Thorax. 1979 Apr;34(2):254–258. doi: 10.1136/thx.34.2.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S. G. Exercise testing in clinical medicine. Br J Dis Chest. 1977 Jul;71(3):145–172. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(77)90106-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swerts P. M., Mostert R., Wouters E. F. Comparison of corridor and treadmill walking in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Phys Ther. 1990 Jul;70(7):439–442. doi: 10.1093/ptj/70.7.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinburn C. R., Wakefield J. M., Jones P. W. Performance, ventilation, and oxygen consumption in three different types of exercise test in patients with chronic obstructive lung disease. Thorax. 1985 Aug;40(8):581–586. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.8.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]