Abstract
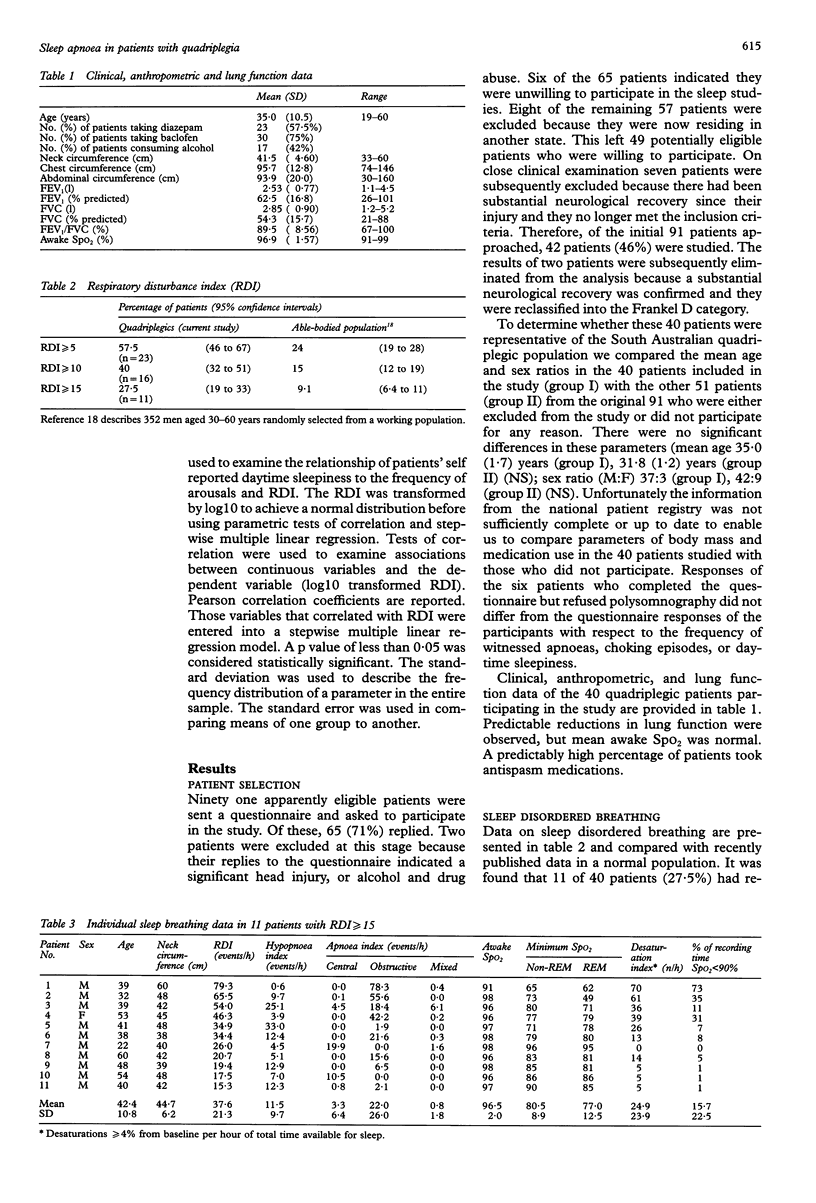
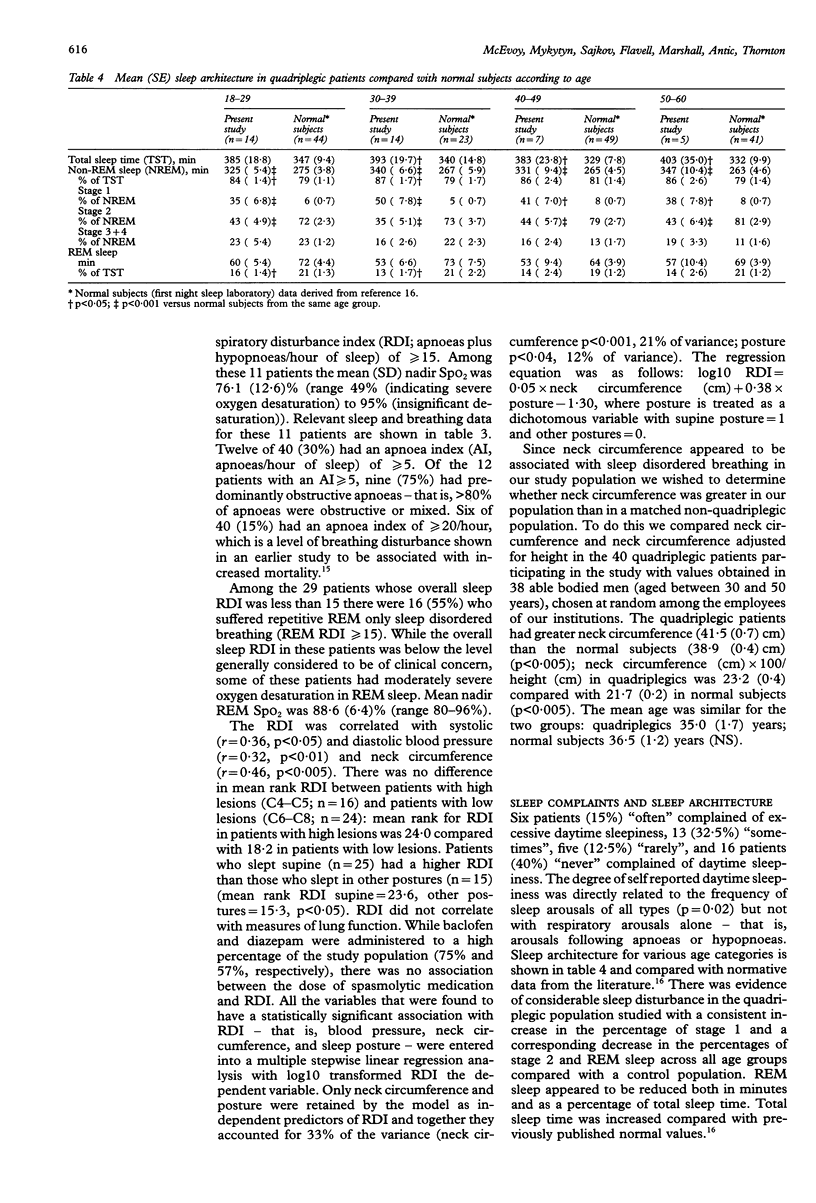
BACKGROUND--This study was undertaken to establish the prevalence of, and the factors contributing towards, sleep disordered breathing in patients with quadriplegia. METHODS--Forty representative quadriplegic patients (time since injury > 6 months, injury level C8 and above, Frankel category A, B, or C; mean (SE) age 35.0 (1.7) years) had home sleep studies in which EEG, EOG, submental EMG, body movement, nasal airflow, respiratory effort, and pulse oximetry (SpO2) were measured. Patients reporting post traumatic amnesia of > 24 hours, drug or alcohol abuse or other major medical illness were excluded from the study. A questionnaire on medications and sleep was administered and supine blood pressure, awake SpO2, spirometric values, height, and neck circumference were measured. RESULTS--A pattern of sustained hypoventilation was not observed in any of the patients. Sleep apnoeas and hypopnoeas were, however, common. Eleven patients (27.5%) had a respiratory disturbance index (RDI, apnoeas plus hypopnoeas per hour of sleep) of > or = 15, with nadir SpO2 ranging from 49% to 95%. Twelve of the 40 (30%) had an apnoea index (AI) of > or = 5 and, of these, nine (75%) had predominantly obstructive apnoeas-that is, > 80% of apnoeas were obstructive or mixed. This represents a prevalence of sleep disordered breathing more than twice that observed in normal populations. For the study population RDI correlated with systolic and diastolic blood pressure and neck circumference. RDI was higher in patients who slept supine compared with those in other postures. Daytime sleepiness was a common complaint in the study population and sleep architecture was considerably disturbed with decreased REM sleep and increased stage 1 non-REM sleep. CONCLUSIONS--Sleep disordered breathing is common in quadriplegic patients and sleep disturbance is significant. The predominant type of apnoea is obstructive. As with non-quadriplegic patients with sleep apnoea, sleep disordered breathing in quadriplegics is associated with increased neck circumference and the supine sleep posture.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonekat H. W., Andersen G., Squires J. Obstructive disordered breathing during sleep in patients with spinal cord injury. Paraplegia. 1990 Jul;28(6):392–398. doi: 10.1038/sc.1990.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun S. R., Giovannoni R., Levin A. B., Harvey R. F. Oxygen saturation during sleep in patients with spinal cord injury. Am J Phys Med. 1982 Dec;61(6):302–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahan C., Gothe B., Decker M. J., Arnold J. L., Strohl K. P. Arterial oxygen saturation over time and sleep studies in quadriplegic patients. Paraplegia. 1993 Mar;31(3):172–179. doi: 10.1038/sc.1993.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. J., Ali N. J., Stradling J. R. Neck circumference and other clinical features in the diagnosis of the obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Thorax. 1992 Feb;47(2):101–105. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. J., Stradling J. R. The relationship between neck circumference, radiographic pharyngeal anatomy, and the obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Eur Respir J. 1990 May;3(5):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolly F. R., Block A. J. Effect of flurazepam on sleep-disordered breathing and nocturnal oxygen desaturation in asymptomatic subjects. Am J Med. 1982 Aug;73(2):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90185-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell H., Marshall R., Thornton A. T., Clements P. L., Antic R., McEvoy R. D. Hypoxia episodes during sleep in high tetraplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1992 Jul;73(7):623–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Stoohs R., Clerk A., Simmons J., Labanowski M. From obstructive sleep apnea syndrome to upper airway resistance syndrome: consistency of daytime sleepiness. Sleep. 1992 Dec;15(6 Suppl):S13–S16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He J., Kryger M. H., Zorick F. J., Conway W., Roth T. Mortality and apnea index in obstructive sleep apnea. Experience in 385 male patients. Chest. 1988 Jul;94(1):9–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirshkowitz M., Moore C. A., Hamilton C. R., 3rd, Rando K. C., Karacan I. Polysomnography of adults and elderly: sleep architecture, respiration, and leg movement. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1992 Jan;9(1):56–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoelscher T. J., McCall W. V., Powell J., Marsh G. R., Erwin C. W. Two methods of scoring sleep with the Oxford Medilog 9000: comparison to conventional paper scoring. Sleep. 1989 Apr;12(2):133–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstein V., Chan C. K., Slutsky A. S. Sleep apnea and systemic hypertension: a causal association review. Am J Med. 1991 Aug;91(2):190–196. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90014-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung J., Whitford E. G., Parsons R. W., Hillman D. R. Association of sleep apnoea with myocardial infarction in men. Lancet. 1990 Aug 4;336(8710):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91799-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelling J. S., DiMarco A. F., Gottfried S. B., Altose M. D. Respiratory responses to ventilatory loading following low cervical spinal cord injury. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Dec;59(6):1752–1756. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.6.1752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie P. Incidence of sleep apnea in a presumably healthy working population: a significant relationship with excessive daytime sleepiness. Sleep. 1983;6(4):312–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter J. C., Knuth S. L., Krol R. C., Bartlett D., Jr The effect of diazepam on genioglossal muscle activity in normal human subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):216–219. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson W. B., Garnett D., Gillin J. C. Flurazepam-induced sleep apnea syndrome in a patient with insomnia and mild sleep-related respiratory changes. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1981 Apr;169(4):261–264. doi: 10.1097/00005053-198104000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millman R. P., Redline S., Carlisle C. C., Assaf A. R., Levinson P. D. Daytime hypertension in obstructive sleep apnea. Prevalence and contributing risk factors. Chest. 1991 Apr;99(4):861–866. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.4.861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partinen M., Guilleminault C. Daytime sleepiness and vascular morbidity at seven-year follow-up in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Chest. 1990 Jan;97(1):27–32. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid K., Böhmer G., Gebauer K. GABAB receptor mediated effects on central respiratory system and their antagonism by phaclofen. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 8;99(3):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90464-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short D. J., Stradling J. R., Williams S. J. Prevalence of sleep apnoea in patients over 40 years of age with spinal cord lesions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992 Nov;55(11):1032–1036. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.11.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., Gold A. R., Meyers D. A., Haponik E. F., Bleecker E. R. Weight loss in mildly to moderately obese patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Dec;103(6 ):850–855. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-6-850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan C. E., Issa F. G., Berthon-Jones M., Eves L. Reversal of obstructive sleep apnoea by continuous positive airway pressure applied through the nares. Lancet. 1981 Apr 18;1(8225):862–865. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92140-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. A., Hamosh P., Gillis R. A. Respiratory depression produced by activation of GABA receptors in hindbrain of cat. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Nov;51(5):1278–1286. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.5.1278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young T., Palta M., Dempsey J., Skatrud J., Weber S., Badr S. The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med. 1993 Apr 29;328(17):1230–1235. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199304293281704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


