Abstract
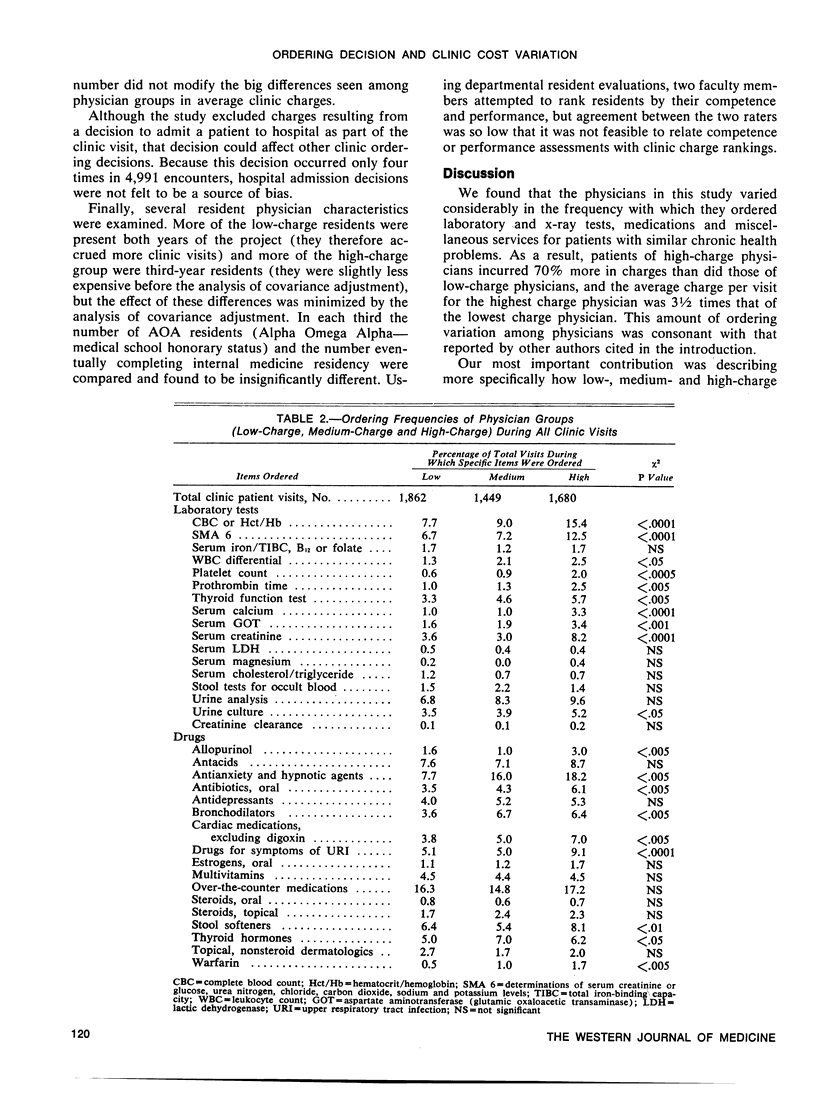
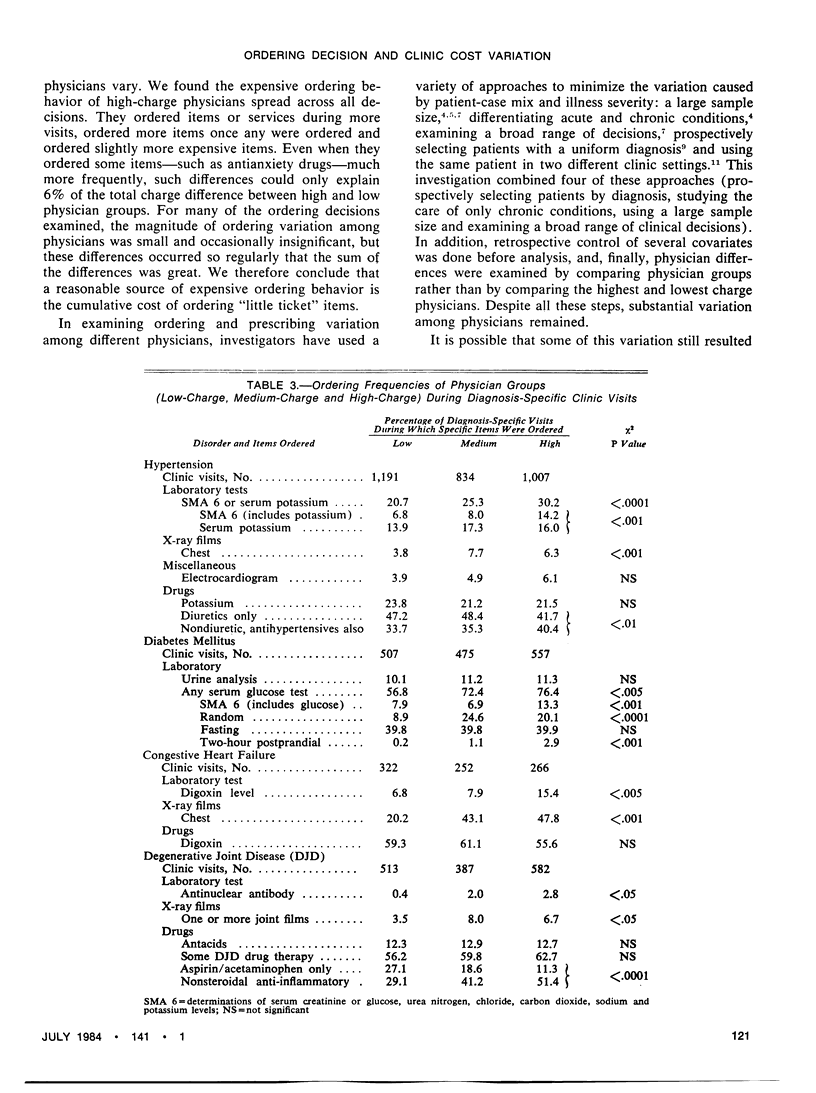
Physicians vary considerably in the services they order for their patients. We examined ordering variation among 47 resident physicians during 4,991 continuity clinic visits with patients who had specific, chronic medical problems. We ranked the physicians by their average charge per visit and grouped them into three equal categories. High-charge physicians averaged $164 per visit, medium-charge $124 and low-charge $97. In comparing the frequencies with which physicians in each group ordered a wide array of specific laboratory tests, x-ray studies, medications and miscellaneous items, we found that ordering variation among the physician groups was not confined to certain decisions or categories of services. High-charge physicians ordered a little more of nearly every item or service. Although the magnitude of ordering variation for each item was small, the sum over many items was great, suggesting that cost-containment efforts may have to focus on the “little ticket” decision-making style of expensive physicians.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Applegate W. B., Bennett M. D., Chilton L., Skipper B. J., White R. E. Impact of a cost-containment educational program on housestaff ambulatory clinic charges. Med Care. 1983 May;21(5):486–496. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198305000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton L. A., Applegate W. B., Bennett M. D., Skipper B. E., White R. E. Evaluation of educational methods in a comprehensive cost-containment project in ambulatory care. South Med J. 1982 Oct;75(10):1251–1255. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198210000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins R. O. Clinicians' reasons for overuse of skull radiographs. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1980 Sep;135(3):549–552. doi: 10.2214/ajr.135.3.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels M., Schroeder S. A. Variation among physicians in use of laboratory tests. II. Relation to clinical productivity and outcomes of care. Med Care. 1977 Jun;15(6):482–487. doi: 10.1097/00005650-197706000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg J. M., Rosoff A. J. Physician responsibility for the cost of unnecessary medical services. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jul 13;299(2):76–80. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197807132990205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg J. M., Williams S. V. Cost containment and changing physicians' practice behavior. Can the fox learn to guard the chicken coop? JAMA. 1981 Nov 13;246(19):2195–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeborn D. K., Baer D., Greenlick M. R., Bailey J. W. Determinants of medical care utilization: physicians' use of laboratory services. Am J Public Health. 1972 Jun;62(6):846–853. doi: 10.2105/ajph.62.6.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich T. J., Gorry G. A. The process of ambulatory care: a comparison of the hospital and the community health center. Am J Public Health. 1980 Mar;70(3):251–255. doi: 10.2105/ajph.70.3.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick D. F., Vertinsky P., Barth R. T., Mitchell V. F., Bernstein M., Vertinsky I. Clinical styles and motivation: a study of laboratory test use. Med Care. 1975 May;13(5):397–408. doi: 10.1097/00005650-197505000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki E. Review of literature on the factors affecting drug prescribing. Soc Sci Med. 1975 Feb;9(2):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0037-7856(75)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce C. R., Last J. M., Weatherall M. Personal factors as a cause of differences in prescribing by general practitioners. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1968 Jul;22(3):170–177. doi: 10.1136/jech.22.3.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyle C. B., Applegate W. B., Citron D. S., Williams O. D. Practice habits in a group of eight internists. Ann Intern Med. 1976 May;84(5):594–601. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-5-594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyle C. B., Jr, Citron D. S., Sugg W. C., Jr, Williams O. D. Cost of medical care in a practice of internal medicine. A study in a group of seven internists. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jul;81(1):1–6. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moloney T. W., Rogers D. E. Medical technology -- a different view of the contentious debate over costs. N Engl J Med. 1979 Dec 27;301(26):1413–1419. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197912273012603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pineault R. The effect of medical training factors on physician utilization behavior. Med Care. 1977 Jan;15(1):51–67. doi: 10.1097/00005650-197701000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid R. A., Lantz K. H. Physician profiles in training the graduate internist. J Med Educ. 1977 Apr;52(4):301–307. doi: 10.1097/00001888-197704000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutkow I. M. Unnecessary surgery: what is it? Surg Clin North Am. 1982 Aug;62(4):613–625. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)42782-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder S. A., Kenders K., Cooper J. K., Piemme T. E. Use of laboratory tests and pharmaceuticals. Variation among physicians and effect of cost audit on subsequent use. JAMA. 1973 Aug 20;225(8):969–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder S. A., Schliftman A., Piemme T. E. Variation among physicians in use of laboratory tests: relation to quality of care. Med Care. 1974 Aug;12(8):709–713. doi: 10.1097/00005650-197408000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somers A. R., Somers H. M. A proposed framework for health and health care policies. Inquiry. 1977 Jun;14(2):115–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. D., Kane R. L., Snell G. F., Woolley F. R. Costs and outcomes for different primary care providers. JAMA. 1977 Jul 4;238(1):46–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


