Abstract
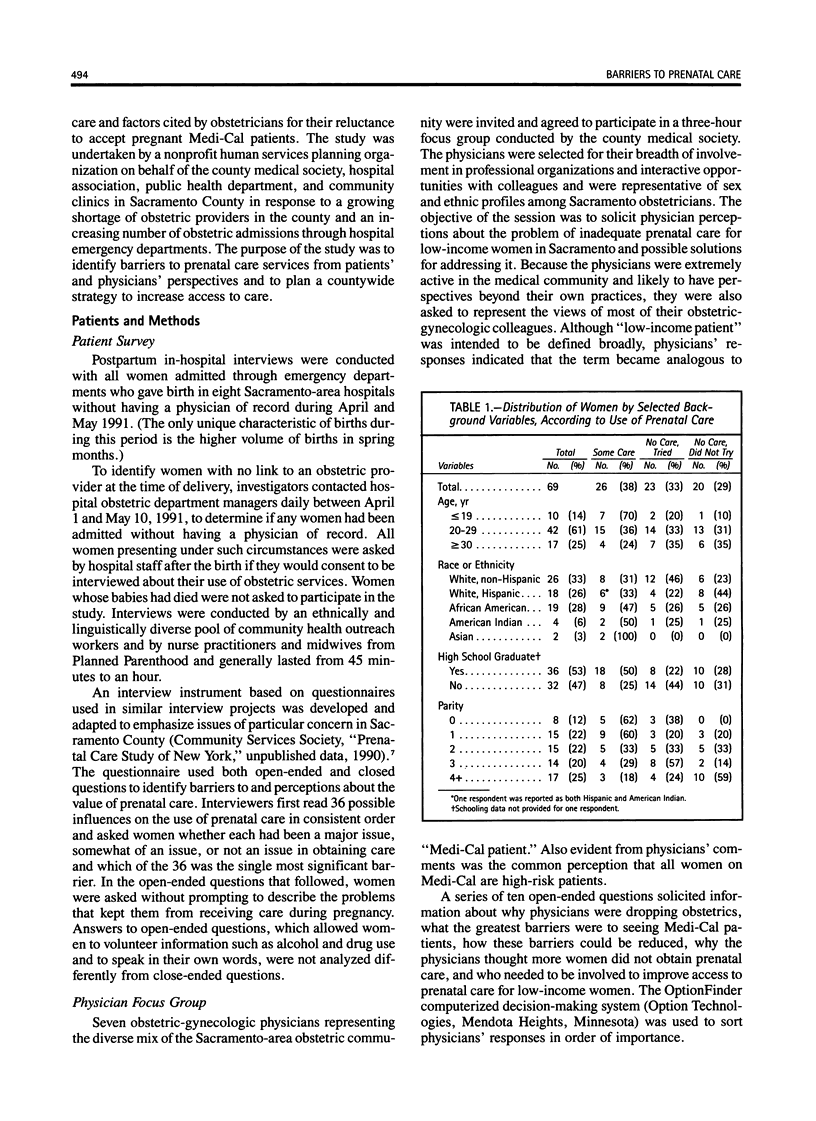
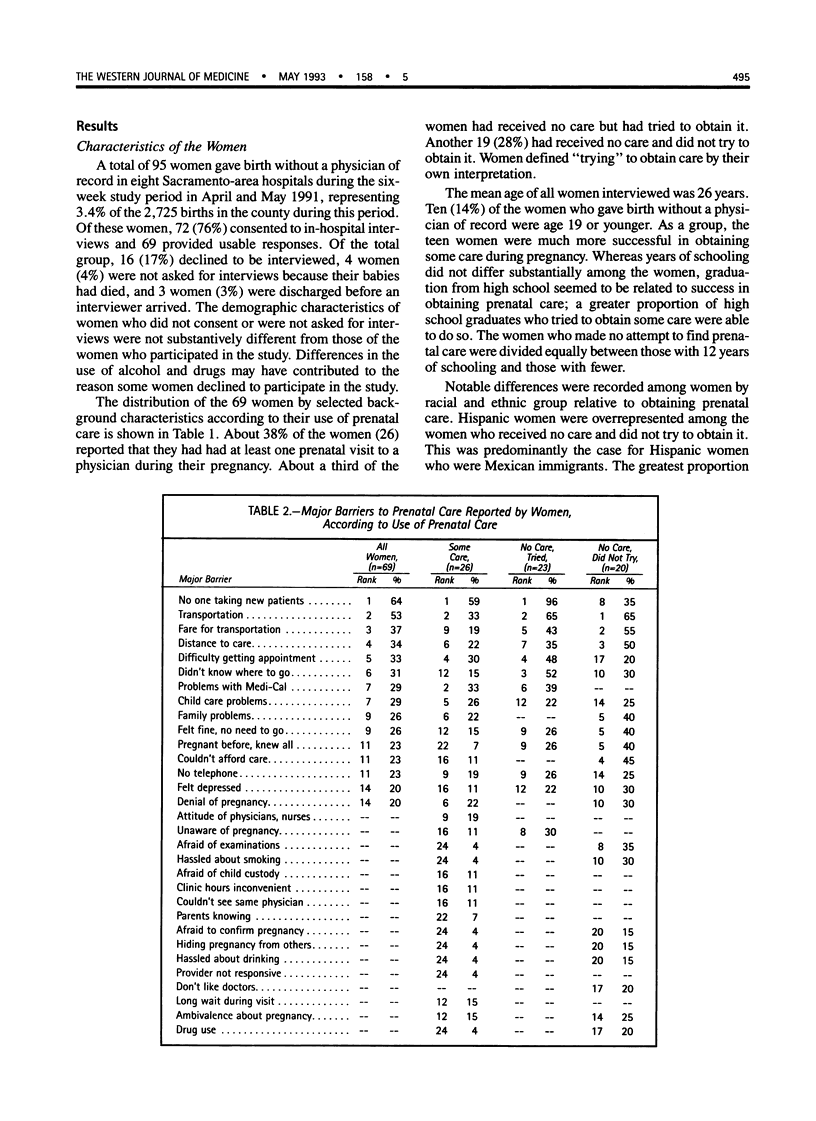
Inadequate prenatal care is associated with poor birth outcomes. Recognizing barriers to care is necessary to improve results. Postpartum in-hospital interviews were conducted with women admitted through emergency departments with no physician of record (n = 69) in 8 Sacramento hospitals during April and May 1991. A focus group of local obstetrician-gynecologists was used to determine physicians' attitudes about caring for low-income women. We undertook the study in response to an increased number of "no doc" births. The inability to find a physician willing to accept them was reported by the women as the single largest barrier to obtaining care, cited by 64% of women overall and 96% of those who tried but were unable to obtain care. Transportation difficulties were a problem regardless of women's success in obtaining care and were ranked as the top barrier by women who never tried to obtain care. Physicians cited administrative difficulties and reimbursement levels of Medi-Cal plus extra care requirements and resource dependency of low-income patients as barriers to caring for this population. The value ascribed to prenatal care by women and physicians' perceptions of women's attitudes about care contrasted sharply. The link between poor women and physicians providing obstetric services can be fragile. The difficulty finding physicians willing to take them indicates that these women need special support services to ensure adequate care during pregnancy.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chasnoff I. J., Landress H. J., Barrett M. E. The prevalence of illicit-drug or alcohol use during pregnancy and discrepancies in mandatory reporting in Pinellas County, Florida. N Engl J Med. 1990 Apr 26;322(17):1202–1206. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199004263221706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney J. P. What determines the start of prenatal care? Prenatal care, insurance, and education. Med Care. 1985 Aug;23(8):986–997. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198508000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mussman M. G., Zawistowich L., Weisman C. S., Malitz F. E., Morlock L. L. Medical malpractice claims filed by Medicaid and non-Medicaid recipients in Maryland. JAMA. 1991 Jun 12;265(22):2992–2994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


