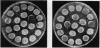
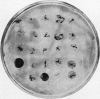
Full text
PDF

































Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDER V. G., GILLESPIE W. A., THOMPSON M. E. Virulence and phage patterns of antibiotic-resistant Staphylococci in a hospital. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(2):503–511. doi: 10.1002/path.1700700228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON E. S., FELIX A. Variation in Vi-phage II of Salmonella typhi. Nature. 1952 Sep 20;170(4325):492–494. doi: 10.1038/170492b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON E. S., FRASER A. The influence of the factors determining Vi-type specificity in Salmonella typhi on the adaptation of Vi-phage II. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Dec;13(3):519–532. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-3-519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON E. S. The significance of Vi-phage types F1 and F2 of Salmonella typhi. J Hyg (Lond) 1951 Dec;49(4):458–470. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400066778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ATKINS J. B., MARKS J. The role of staphylococcal infection in beat disorders of miners. Br J Ind Med. 1952 Oct;9(4):296–302. doi: 10.1136/oem.9.4.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANKER D. D. Paratyphoid-A phage typing. Nature. 1955 Feb 12;175(4450):309–310. doi: 10.1038/175309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER M., BURSTON J. Antibiotic-resistant staphylococcal infection; a study of antibiotic sensitivity in relation to bacteriophage types. Lancet. 1955 Sep 17;269(6890):578–583. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(55)92582-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER M., HAYHOE F. G. J., WHITEHEAD J. E. M. Penicillin-resistant staphylococcal infection in a maternity hospital. Lancet. 1949 Dec 17;2(6590):1120–1125. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(49)91144-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER M., WHITEHEAD J. E. M. Bacteriophage types in penicillin-resistant staphylococcal infection. Br Med J. 1949 Sep 10;2(4627):565–569. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4627.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER M., WILSON B. D., RIPPON J. E., WILLIAMS R. E. Spread of Staphylococcus aureus in a maternity department in the absence of severe sepsis. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1953 Aug;60(4):476–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1953.tb07223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARROW G. I. Clinical and bacteriological aspects of impetigo contagiosa. J Hyg (Lond) 1955 Dec;53(4):495–508. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400000991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTANI G., WEIGLE J. J. Host controlled variation in bacterial viruses. J Bacteriol. 1953 Feb;65(2):113–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.2.113-121.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAIR J. E., CARR M. The bacteriophage typing of staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1953 Jul-Aug;93(1):1–13. doi: 10.1093/infdis/93.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOWERS R., MASON G. A., WALLACE K. R., WALTON M. Control of wound infection in a thoracic surgery unit. Lancet. 1955 Oct 15;269(6894):786–794. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(55)92385-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD J. S. K., PARKER M. T., MAIR N. S. Symbiotic bacteriophage as a marker in the identification of strains of Salmonella typhimurium. J Hyg (Lond) 1951 Dec;49(4):442–451. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400066754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD J. S. K. The symbiotic bacteriophages of Salmonella typhi-murium. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;62(4):501–517. doi: 10.1002/path.1700620402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD J. S. K. The symbiotic bacteriophages of Salmonella typhi-murium. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;62(4):501–517. doi: 10.1002/path.1700620402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRANDIS H. Die Lysotype von Typhus-und Paratyphus-B-Bakterien. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1955 Nov;164(1-5):149–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERRY W. B., DAVIS B. R., EDWARDS P. R. Observations on the types and typing of Salmonella paratyphi B cultures in the United States. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1953 Oct;43(10):1280–1286. doi: 10.2105/ajph.43.10.1280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE BLASI R., BUOGO A. La tipizzazione fagica delle SS. typhi e paratyphi B; prime osservazioni sui tipi che ricorrono nell'Italia Centrale. Riv Ital Ig. 1952 Jan-Feb;12(1-2):16–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DHAYAGUDE R. G. Typing of locally isolated cultures of Salmonella typhi by means of Vi-bacteriophage. Indian J Med Res. 1951 Jan;39(1):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWLING H. F., LEPPER M. H., JACKSON G. G. Observations on the epidemiological spread of antibiotic-resistant staphylococci, with measurements of the changes in sensitivity to penicillin and aureomycin. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1953 Jul;43(7):860–868. doi: 10.2105/ajph.43.7.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAIRBROTHER R. W., PARKER L., EATON B. R. The stability of penicillinase-producting strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Apr;10(2):309–316. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARRANT J. L., ROUNTREE P. M. Electron microscopy of a staphylococcal bacteriophage. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Oct;9(2):288–292. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-2-288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELIX A., ANDERSON E. S. Bacteriophages carried by the Vi-phage types of Salmonella typhi. Nature. 1951 Apr 14;167(4250):603–603. doi: 10.1038/167603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON W. W., JUENKER A., FERGUSON R. A. Characterization of latent phages from strains of Salmonella typhi typable and untypable with Vi phage. Am J Hyg. 1955 Nov;62(3):306–326. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOUACE J., LUTZ A. Type bactériophagique des staphylocoques pathogènes sécréteurs de pénicillinase. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Sep;85(3):387–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN J. Mass experiments on pollens during 1949-54. Acta Allergol. 1955;8(2):156–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUSILLO M. H., ROERIG R. N., METZGER J. F., ERNST K. F. Phage typing antibiotic-resistant staphylococci. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1954 Mar;44(3):317–322. doi: 10.2105/ajph.44.3.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD J. C., McKILLOP E. J. The carriage of Staphylococcus pyogenes var. aureus in the human nose. J Hyg (Lond) 1954 Sep;52(3):304–310. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400027509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD J. C. Origin of penicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pyogenes. Nature. 1955 Jul 23;176(4473):176–176. doi: 10.1038/176176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S. Slide Technique for Bacteriophage Typing of Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1954 Dec 17;120(3129):1041–1042. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3129.1041-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON H. Leucotomy; a recent development. J Ment Sci. 1954 Jan;100(418):62–65. doi: 10.1192/bjp.100.418.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., LWOFF A., SIMINOVITCH A., WOLLMAN E. Définition de quelques termes relatifs a la lysogénie. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Jan;84(1):222–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNIGHT V., HOLZER A. R. Studies on staphylococci from hospital patients. I. Predominance of strains of group III phage patterns which are resistant to multiple antibiotics. J Clin Invest. 1954 Sep;33(9):1190–1198. doi: 10.1172/JCI102992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY E., RIPPON J. E., WILLIAMS R. E. Relation of bacteriophage pattern to some biological properties of staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Aug;9(1):97–100. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILLEENGEN K. Typing of Salmonella dublin and Salmonella enteritidis by means of bacteriophage. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1950;27(4):625–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1950.tb04934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., HOOD A. M. The acquired resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to Bacteriophage. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Dec;9(3):524–535. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-3-524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., HUMAN M. L. A nonhereditary, host-induced variation of bacterial viruses. J Bacteriol. 1952 Oct;64(4):557–569. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.4.557-569.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LWOFF A. Lysogeny. Bacteriol Rev. 1953 Dec;17(4):269–337. doi: 10.1128/br.17.4.269-337.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERCIER P., PILLET J., CHABANIER P. Détermination des types de staphylocoques par l'agglutination. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1950 Apr;78(4):457–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. B., Miller A. M. IDENTIFICATION BY BACTERIOPHAGE TYPING. Can Med Assoc J. 1946 Jul;55(1):36–39. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWELL K. W., HOBBS B. C., WALLACE E. J. G. Paratyphoid fever associated with Chinese frozen whole egg; outbreaks in two bakeries. Br Med J. 1955 Nov 26;2(4951):1296–1298. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4951.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICOLLE P., HAMON Y., EDLINGER E. Recherches sur les facteurs qui conditionnent l'appartenance des bacilles paratyphiques B aux différents types bactériophagiques de Felix et Callow. I. La lysogénéité des différents types de Salmonella paratyphi B. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1951 May;80(5):479–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICOLLE P., JUDE A., BUTTIAUX R. Stabilité des types bactériophagiques de Salmonella paratyphi B et valeur épidémiologique de la lysotypie par la méthode de Felix et Callow. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1950 Sep;79(3):246–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICOLLE P., PAVLATOU M., DIVERNEAU G. Les lysotypies auxiliaires de Salmonella typhi. I. Subdivision du type A et du groupe I+IV par une nouvelle série de phages. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1954 Nov;87(5):493–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OEDING P. Serological typing of staphylococci. III. Further investigations and comparison to phage typing. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1953;33(3):324–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER M. T., KENNEDY J. The source of infection in pemphigus neonatorum. J Hyg (Lond) 1949 Jun;47(2):213–219. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400014492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAVLATOU M., NICOLLE P. Incidence des types biochimiques parmi les types bactériophagiques de Salmonella typhi. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Aug;85(2):185–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEREIRA M. S., BLAXLAND J. D. Salmonella typhi-murium infection in man contracted from turkeys. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1955 Mar;14:52–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RISCHE H., ROHNE K., SCHNEIDER H. Ergebnisse der Vi-Phagen-Typisierung von Salmonella typhi und paratyphi B. Z Gesamte Inn Med. 1954 Sep 15;9(18):896–903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROODYN L. Staphylococcal infections in general practice. Br Med J. 1954 Dec 4;2(4900):1322–1325. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4900.1322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUNTREE P. M., BARBOUR R. G. H. Incidence of penicillin-resistant and streptomycin-resistant staphylococci in a hospital. Lancet. 1951 Feb 24;1(6652):435–436. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(51)92031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H. W. Some observations on lysogenic strains of Salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Aug;5(3):458–471. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-3-458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH M. E., HOBBS B. C. Salmonella in Chinese frozen egg. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1955 Sep;14:154–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUART-HARRIS C. H., FRANKS Z., TYRRELL D. Deaths from influenza; a statistical and laboratory investigation. Br Med J. 1950 Feb 4;1(4648):263–266. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4648.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TULLOCH L. G. Nasal carriage in staphylococcal skin infections. Br Med J. 1954 Oct 16;2(4893):912–913. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4893.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE F. C. O., HALL-SMITH S. P. Superficial staphylococcal infection. Lancet. 1952 Aug 23;2(6730):351–354. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)92245-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGELSANG T. M. Staphylococcal studies in hospital staffs. III. Bacteriophage typing. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1953;33(4):435–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAHL R., FOUACE J. Sur les principes de classification des staphylocoques pathogènes par la mèthode des phages. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1952 May;82(5):542–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAHL R., LAPEYRE-MENSIGNAC P. L'identification des staphylocoques par les bactériophages; essai de classification des staphylocoques par la méthode des phages. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1950 Jun;78(6):765–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIGLE J. J., BERTANI G. Variations des bactériophages conditionnées par les bactéries hôtes. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Jan;84(1):175–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. E. O., RIPPON J. E. Bacteriophage typing of Staphylococcus aureus. J Hyg (Lond) 1952 Sep;50(3):320–353. doi: 10.1017/s002217240001963x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISE R. I., VOIGT A. E., COLLIN M. V., CRANNY C. L. Origin of erythromycin-resistant strains of Micrococcus pyogenes in infections; bacteriophage types and in vitro resistance of cultures to antibiotics. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1955 Mar;95(3):419–426. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1955.00250090057008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]