Abstract
OBJECTIVE--Fetal twin-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) presenting in the second trimester has been associated with almost no perinatal survival until recently, when serial drainage of amniotic fluid has improved the prognosis to 70%-80%. Most recipient twins now survive but develop cardiac dysfunction. The study was undertaken to evaluate the abnormal echocardiographic features and clinical complications of cardiac disease in the recipient twin of TTTS. DESIGN--Antenatal and postnatal echocardiographic and clinical observational study. SETTING--Antenatal studies in a tertiary referral centre. Postnatal management and follow up were performed by the same paediatric cardiologist, either at the obstetric hospital or at the regional referral centre. PATIENTS--Twin pregnancies complicated by TTTS with severe polyhydramnios diagnosed earlier than 25 weeks that proceeded until viability (n = 5). INTERVENTION--Serial fetal echocardiography with colour Doppler. Postnatal echocardiography in the first week and between two and seven months. Serial amnioreduction was performed in all pregnancies. Digoxin treatment, pericardiocentesis, paracentesis, or laser ablation of placental anastomoses was undertaken when there was hydrops. RESULTS--Increased cardiothoracic ratio and tricuspid regurgitation were seen in all recipient twins. High pulmonary artery velocities developed in three. One recipient twin died a week after delivery of endocardial fibroelastosis and infundibular pulmonary stenosis. Two other had balloon dilatation for pulmonary stenosis, one shortly after birth and one at four months. A further twin has apical thickening of the right ventricle at six months. The remaining recipient twin had normal echocardiographic findings at follow up. CONCLUSION--This report characterises for the first time a cardiac disease acquired in utero in the recipient twin in pregnancies complicated by TTTS. Clinical manifestations in utero range from mild to critical pulmonary stenosis or lethal cardiomyopathy. Although perinatal prognosis seems to be related to the severity of dysfunction when first diagnosed in utero, follow up in infancy is recommended in view of the possibility of progressive pulmonary stenosis.
Full text
PDF
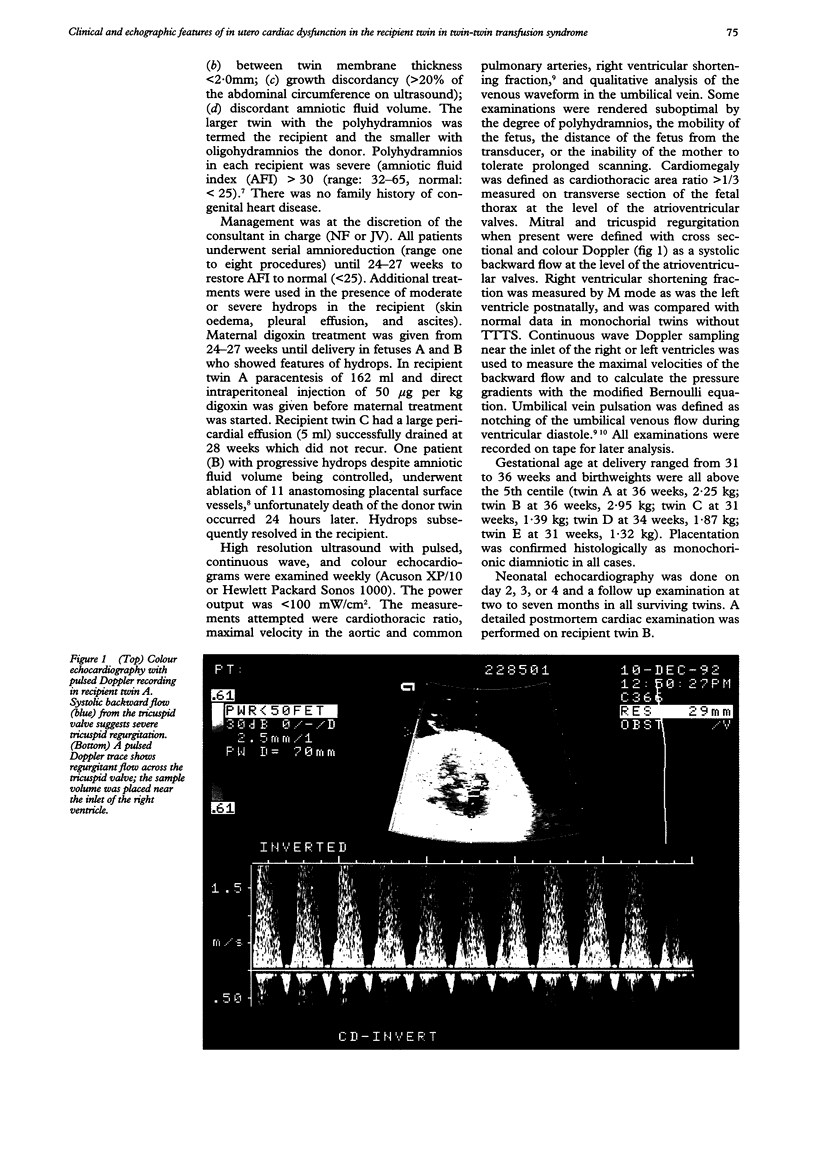




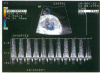
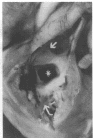
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achiron R., Rabinovitz R., Aboulafia Y., Diamant Y., Glaser J. Intrauterine assessment of high-output cardiac failure with spontaneous remission of hydrops fetalis in twin-twin transfusion syndrome: use of two-dimensional echocardiography, Doppler ultrasound, and color flow mapping. J Clin Ultrasound. 1992 May;20(4):271–277. doi: 10.1002/jcu.1870200408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey L. L., Gundry S. R. Hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1990 Feb;37(1):137–150. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)36836-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lia J. E., Cruikshank D. P., Keye W. R., Jr Fetoscopic neodymium:YAG laser occlusion of placental vessels in severe twin-twin transfusion syndrome. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Jun;75(6):1046–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lia J., Emery M. G., Sheafor S. A., Jennison T. A. Twin transfusion syndrome: successful in utero treatment with digoxin. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1985 Jun;23(3):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0020-7292(85)90104-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. P., Urig M. A., Clewell W. H. Aggressive therapeutic amniocentesis for treatment of twin-twin transfusion syndrome. Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Apr;77(4):537–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eronen M., Pesonen E., Kurki T., Ylikorkala O., Hallman M. The effects of indomethacin and a beta-sympathomimetic agent on the fetal ductus arteriosus during treatment of premature labor: a randomized double-blind study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Jan;164(1 Pt 1):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(91)90644-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrans V. J., Rodríguez E. R. Specificity of light and electron microscopic features of hypertrophic obstructive and nonobstructive cardiomyopathy. Qualitative, quantitative and etiologic aspects. Eur Heart J. 1983 Nov;4 (Suppl F):9–22. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/4.suppl_f.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisk N. M., Borrell A., Hubinont C., Tannirandorn Y., Nicolini U., Rodeck C. H. Fetofetal transfusion syndrome: do the neonatal criteria apply in utero? Arch Dis Child. 1990 Jul;65(7 Spec No):657–661. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.7_spec_no.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed M. D., Rosenthal A., Bernhard W. F., Litwin S. B., Nadas A. S. Critical pulmonary stenosis with a diminutive right ventricle in neonates. Circulation. 1973 Oct;48(4):875–881. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.48.4.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. F. The frontiers of cardiomyopathy. Br Heart J. 1982 Jul;48(1):1–18. doi: 10.1136/hrt.48.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudmundsson S., Huhta J. C., Wood D. C., Tulzer G., Cohen A. W., Weiner S. Venous Doppler ultrasonography in the fetus with nonimmune hydrops. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Jan;164(1 Pt 1):33–37. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(91)90618-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornberger L. K., Sahn D. J., Kleinman C. S., Copel J. A., Reed K. L. Tricuspid valve disease with significant tricuspid insufficiency in the fetus: diagnosis and outcome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991 Jan;17(1):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(91)90722-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman T. W., Stewart P. A., Wladimiroff J. W. Ductus venosus blood flow velocity waveforms in the human fetus--a Doppler study. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1992;18(1):33–37. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(92)90005-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimatsu J., Yoshimura O., Manabe A., Matsuzaki T., Tanabe R., Hamada T. Ultrasonography and Doppler studies in twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome. Asia Oceania J Obstet Gynaecol. 1992 Dec;18(4):325–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.1992.tb00327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai C., Yui Y., Hoshino T., Sasayama S., Matsumori A. Myocardial catecholamines in hypertrophic and dilated (congestive) cardiomyopathy: a biopsy study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1983 Nov;2(5):834–840. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(83)80229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony B. S., Petty C. N., Nyberg D. A., Luthy D. A., Hickok D. E., Hirsch J. H. The "stuck twin" phenomenon: ultrasonographic findings, pregnancy outcome, and management with serial amniocenteses. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Nov;163(5 Pt 1):1513–1522. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)90617-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. R., Cayle J. E. The amniotic fluid index in normal human pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 May;162(5):1168–1173. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)90009-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAEYE R. L. Human intrauterine parabiotic syndrome and its complications. N Engl J Med. 1963 Apr 11;268:804–809. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196304112681502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai Y., Miyazaki Y., Matsuoka Y., Matsumoto M., Imanaka M., Ogita S. Pulsatile umbilical venous flow and its clinical significance. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1992 Dec;99(12):977–980. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1992.tb13701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo G., Arduini D., Romanini C. Accelerated cardiac growth and abnormal cardiac flow in fetuses of type I diabetic mothers. Obstet Gynecol. 1992 Sep;80(3 Pt 1):369–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo G., Arduini D., Romanini C. Doppler echocardiographic assessment of fetal cardiac function. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1992 Nov 1;2(6):434–445. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0705.1992.02060434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson E. G., Neer K. J. Placental injection studies in twin gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983 Sep 15;147(2):170–174. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(83)90111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders N. J., Snijders R. J., Nicolaides K. H. Twin-twin transfusion syndrome during the 2nd trimester is associated with small intertwin hemoglobin differences. Fetal Diagn Ther. 1991;6(1-2):34–36. doi: 10.1159/000263622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urig M. A., Clewell W. H., Elliott J. P. Twin-twin transfusion syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Nov;163(5 Pt 1):1522–1526. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)90618-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner C. P. Umbilical pressure measurement in the evaluation of nonimmune hydrops fetalis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Mar;168(3 Pt 1):817–823. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(12)90827-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]