Abstract
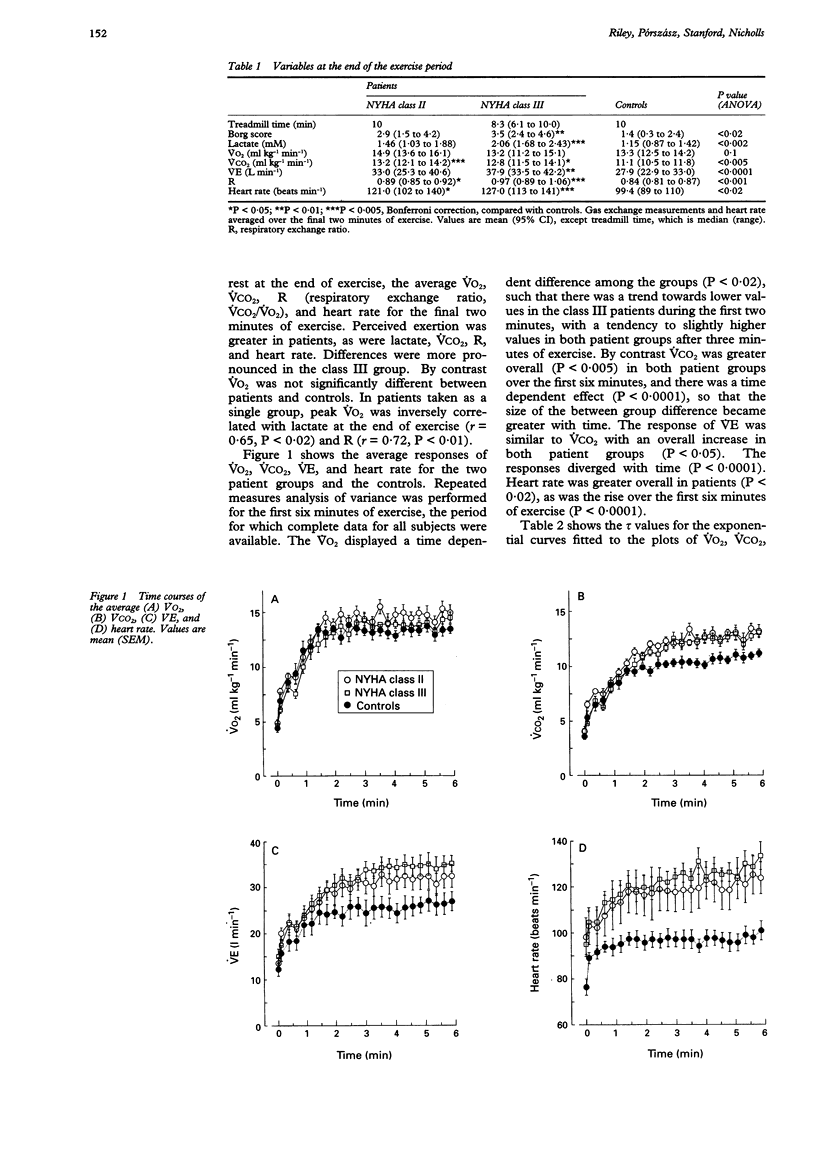
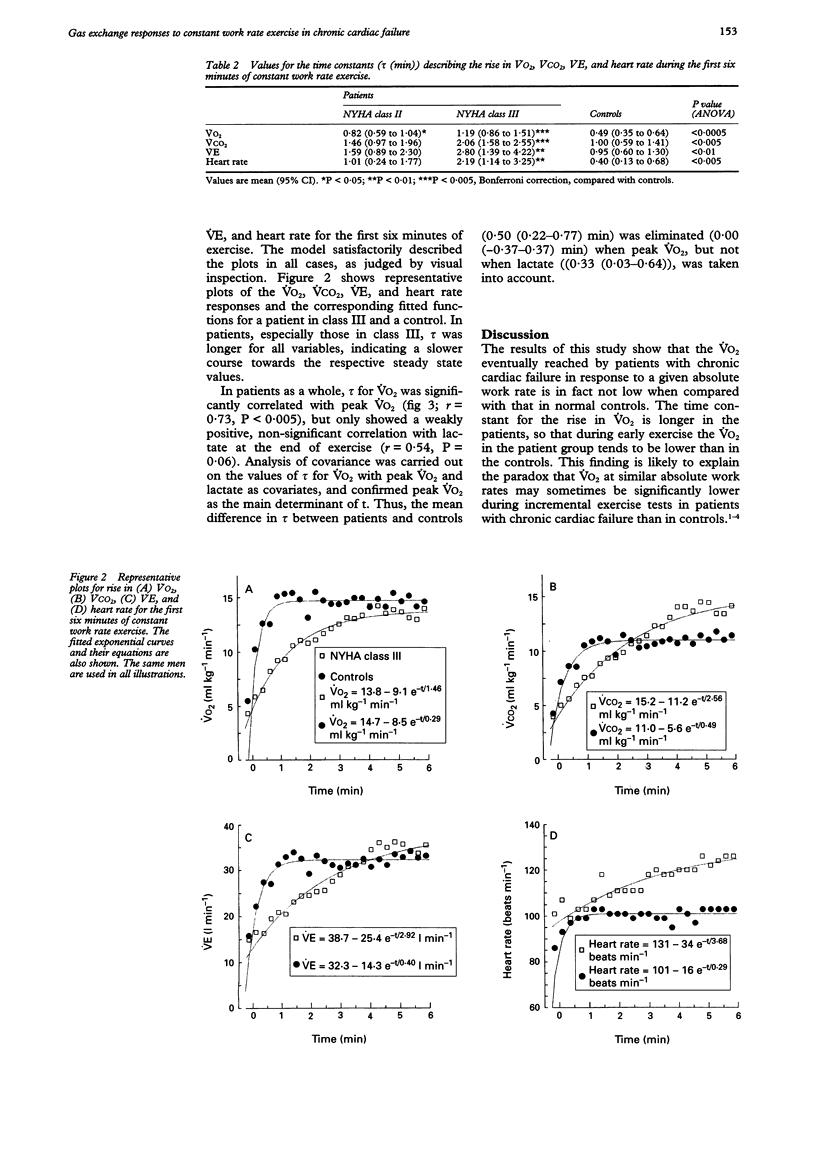
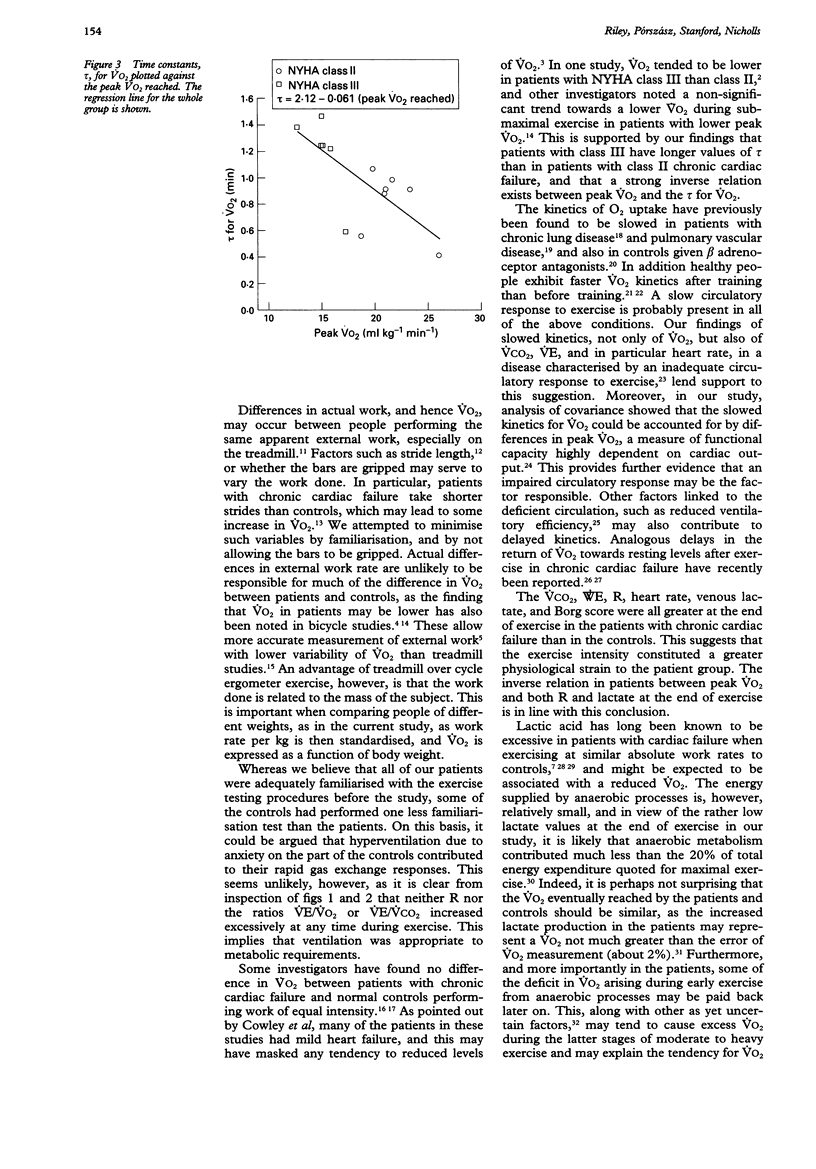
OBJECTIVE--To examine the time course of changes in minute oxygen consumption and other gas exchange variables and heart rate during constant work rate exercise in patients with chronic cardiac failure. DESIGN--Treadmill exercise with on line measurement of gas exchange and a target duration of 10 minutes. SUBJECTS--Seven men in New York Heart Association class II, six in class III, and seven controls. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Gas exchange variables and heart rate were averaged for the final two minutes of exercise. Time constants were calculated for the increase in all variables. RESULTS--Consumption of oxygen at the end of exercise (VO2) was similar in class II patients (mean (95% confidence interval (95% CI) 14.9 (13.6 to 16.1) ml kg-1 min-1), class III patients (13.2 (11.2 to 15.1) ml kg-1 min-1), and controls (13.3 (12.5 to 14.2) ml kg-1 min-1). The patients reached this VO2 more slowly with longer exponential time constants of 0.82 (0.59 to 1.04) min in class II and 1.19 (0.86 to 1.51) min in class III, than the 0.49 (0.35 to 0.64) min in the controls. Time constants of other gas exchange variables and heart rate were also longer in patients. By analysis of covariance, peak VO2 accounted for the between group difference in the time constant for VO2, suggesting that circulatory factors may be an important cause of the delayed kinetics. CONCLUSIONS--A delayed rise in VO2 in response to exercise may be responsible for subnormal values of VO2 early in exercise in patients with chronic cardiac failure.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borg G. A. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1982;14(5):377–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce R. A., Kusumi F., Hosmer D. Maximal oxygen intake and nomographic assessment of functional aerobic impairment in cardiovascular disease. Am Heart J. 1973 Apr;85(4):546–562. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(73)90502-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTES J. E. The role of oxygen, carbon dioxide and lactic acid in the ventilatory response to exercise in patients with mitral stenosis. Clin Sci. 1955 May;14(2):317–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clode M., Campbell E. J. The relationship between gas exchange and changes in blood lactate concentrations during exercise. Clin Sci. 1969 Oct;37(2):263–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley A. J., Stainer K., Rowley J. M., Hampton J. R. Abnormalities of the peripheral circulation and respiratory function in patients with severe heart failure. Br Heart J. 1986 Jan;55(1):75–80. doi: 10.1136/hrt.55.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. W., Greig C. A., Jordan S. L., Grieve D. W., Lipkin D. P. Short-stepping gait in severe heart failure. Br Heart J. 1992 Nov;68(5):469–472. doi: 10.1136/hrt.68.11.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elborn J. S., Stanford C. F., Nicholls D. P. Reproducibility of cardiopulmonary parameters during exercise in patients with chronic cardiac failure. The need for a preliminary test. Eur Heart J. 1990 Jan;11(1):75–81. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franciosa J. A., Ziesche S., Wilen M. Functional capacity of patients with chronic left ventricular failure. Relationship of bicycle exercise performance to clinical and hemodynamic characterization. Am J Med. 1979 Sep;67(3):460–466. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90794-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUCKABEE W. E., JUDSON W. E. The role of anaerobic metabolism in the performance of mild muscular work. I. Relationship to oxygen consumption and cardiac output, and the effect of congestive heart failure. J Clin Invest. 1958 Nov;37(11):1577–1592. doi: 10.1172/JCI103751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg J. M., Hickson R. C., Ehsani A. A., Holloszy J. O. Faster adjustment to and recovery from submaximal exercise in the trained state. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Feb;48(2):218–224. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.48.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashida W., Kumada T., Kohno F., Noda M., Ishikawa N., Kambayashi M., Kawai C. Post-exercise oxygen uptake kinetics in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. Int J Cardiol. 1993 Jan;38(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0167-5273(93)90205-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Sahlin K. Regulation of lactic acid production during exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Aug;65(2):509–518. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.2.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin D. P., Perrins J., Poole-Wilson P. A. Respiratory gas exchange in the assessment of patients with impaired ventricular function. Br Heart J. 1985 Sep;54(3):321–328. doi: 10.1136/hrt.54.3.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massie B., Conway M., Yonge R., Frostick S., Ledingham J., Sleight P., Radda G., Rajagopalan B. Skeletal muscle metabolism in patients with congestive heart failure: relation to clinical severity and blood flow. Circulation. 1987 Nov;76(5):1009–1019. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.76.5.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakins J., Long C. N. OXYGEN CONSUMPTION, OXYGEN DEBT AND LACTIC ACID IN CIRCULATORY FAILURE. J Clin Invest. 1927 Jun;4(2):273–293. doi: 10.1172/JCI100123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nery L. E., Wasserman K., Andrews J. D., Huntsman D. J., Hansen J. E., Whipp B. J. Ventilatory and gas exchange kinetics during exercise in chronic airways obstruction. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Dec;53(6):1594–1602. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.6.1594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson J. A., Naughton J., Pietras R. J., Gunnar R. M. Treadmill exercise in assessment of the functional capacity of patients with cardiac disease. Am J Cardiol. 1972 Nov;30(7):757–762. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(72)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen E. S., Whipp B. J., Davis J. A., Huntsman D. J., Brown H. V., Wasserman K. Effects of beta-adrenergic blockade on ventilation and gas exchange during exercise in humans. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 May;54(5):1306–1313. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.5.1306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole D. C., Schaffartzik W., Knight D. R., Derion T., Kennedy B., Guy H. J., Prediletto R., Wagner P. D. Contribution of exercising legs to the slow component of oxygen uptake kinetics in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Oct;71(4):1245–1260. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.71.4.1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poortmans J. R., Delescaille-Vanden Bossche J., Leclercq R. Lactate uptake by inactive forearm during progressive leg exercise. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Dec;45(6):835–839. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.45.6.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON H. J. Energy-speed relation and optimal speed during level walking. Int Z Angew Physiol. 1958;17(4):277–283. doi: 10.1007/BF00698754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M., Elborn J. S., McKane W. R., Bell N., Stanford C. F., Nicholls D. P. Resting energy expenditure in chronic cardiac failure. Clin Sci (Lond) 1991 Jun;80(6):633–639. doi: 10.1042/cs0800633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M., Northridge D. B., Henderson E., Stanford C. F., Nicholls D. P., Dargie H. J. The use of an exponential protocol for bicycle and treadmill exercise testing in patients with chronic cardiac failure. Eur Heart J. 1992 Oct;13(10):1363–1367. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a060067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M., Sullivan M., Froelicher V. F., Genter F., Myers J. Predicting oxygen uptake from treadmill testing in normal subjects and coronary artery disease patients. Am Heart J. 1984 Dec;108(6):1454–1460. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90692-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roston W. L., Whipp B. J., Davis J. A., Cunningham D. A., Effros R. M., Wasserman K. Oxygen uptake kinetics and lactate concentration during exercise in humans. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 May;135(5):1080–1084. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.5.1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sietsema K. E. Oxygen uptake kinetics in response to exercise in patients with pulmonary vascular disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 May;145(5):1052–1057. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.5.1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solal A. C., Chabernaud J. M., Gourgon R. Comparison of oxygen uptake during bicycle exercise in patients with chronic heart failure and in normal subjects. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990 Jul;16(1):80–85. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(90)90460-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan M. J., Higginbotham M. B., Cobb F. R. Increased exercise ventilation in patients with chronic heart failure: intact ventilatory control despite hemodynamic and pulmonary abnormalities. Circulation. 1988 Mar;77(3):552–559. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.77.3.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K. T., Kinasewitz G. T., Janicki J. S., Fishman A. P. Oxygen utilization and ventilation during exercise in patients with chronic cardiac failure. Circulation. 1982 Jun;65(6):1213–1223. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.6.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp B. J., Ward S. A. Cardiopulmonary coupling during exercise. J Exp Biol. 1982 Oct;100:175–193. doi: 10.1242/jeb.100.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. R., Martin J. L., Schwartz D., Ferraro N. Exercise intolerance in patients with chronic heart failure: role of impaired nutritive flow to skeletal muscle. Circulation. 1984 Jun;69(6):1079–1087. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.69.6.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. Y., Johnson M. C., 2nd, Chow N., Wasserman K. The role of fitness on VO2 and VCO2 kinetics in response to proportional step increases in work rate. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1991;63(2):94–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00235176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. Y., Wasserman K., Sietsema K. E., Ben-Dov I., Barstow T. J., Mizumoto G., Sullivan C. S. O2 uptake kinetics in response to exercise. A measure of tissue anaerobiosis in heart failure. Chest. 1993 Mar;103(3):735–741. doi: 10.1378/chest.103.3.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


