Abstract
目的
筛选发生脑室内出血(IVH)早产儿血清中差异表达的环状RNA(circRNA),并探讨circRNA参与早产儿IVH发生、发展的ceRNA机制。
方法
研究对象为2019年1月~2020年1月在我院新生儿科住院,胎龄28~34周的早产儿共50例。采用circRNA芯片技术筛选在IVH早产儿血清中显著差异表达的circRNA,通过基因本体论(GO)和信号通路分析circRNA的功能,荧光定量PCR验证hsa_circ_0087893在两组的实际表达水平,构建hsa_circ_0087893的circRNA-miRNA-mRNA共表达网络。
结果
共有121条circRNA在早产IVH组显著差异表达,包括62条上调表达circRNA及59条下调表达circRNA。GO分析及信号通路分析表明,差异circRNA参与多种生物功能及信号通路,包括细胞增殖、活化及死亡、DNA损伤及修复、维生素A代谢、鞘磷脂代谢及细胞黏附等。hsa_circ_0087893在早产儿IVH组中表达显著下调(P < 0.05),41个miRNA与hsa_circ_0087893共表达,包括miR-214-3p、miR-761、miR-183-5p等。15条mRNA与hsa_circ_0087893共表达,包括AKR1B1、KRT34、PPP2CB、HPRT1等。
结论
hsa_circ_0087893可能通过ceRNA机制调控早产儿IVH发生、发展。
Keywords: 早产儿, 脑室内出血, 芯片, 竞争性内源性RNA, 机制
Abstract
Objective
To screen for differentially expressed circular RNAs (circRNAs) in the serum of preterm infants with intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) and explore the competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) mechanism of circRNAs in IVH in these infants.
Methods
Fifty preterm infants (gestational age of 28 to 34 weeks) admitted in our department between January, 2019 and January, 2020 were enrolled in this study, including 25 with a MRI diagnosis of IVH and 25 without IVH. Serum samples were collected from 3 randomly selected infants from each group for profiling differentially expressed circRNAs using circRNA array technique. Gene ontology (GO) and pathway analyses were performed to reveal the function of the identified circRNAs. The circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network was constructed to identify the co-expression network of hsa_circ_ 0087893.
Results
A total of 121 differentially expressed circRNAs were identified in the infants with IVH, including 62 up-regulated and 59 down-regulated circRNAs. GO and pathway analyses showed that these circRNAs were involved in multiple biological processes and pathways, including cell proliferation, activation and death, DNA damage and repair, retinol metabolism, sphingolipid metabolism, cell adhesion molecules. Among these circRNAs, hsa_circ_0087893 was found to have significant down-regulation in IVH group and co-express with 41 miRNAs and 15 mRNAs (such as miR-214-3p, miR-761, miR-183-5p, AKR1B1, KRT34, PPP2CB, and HPRT1).
Conclusion
The circRNA hsa_circ_0087893 may function as a ceRNA and play an important role in the occurrence and progression of IVH in preterm infants.
Keywords: preterm infants, intraventricular hemorrhage, microarray, competitive endogenous RNA, mechanism
早产儿脑室内出血(IVH)是影响早产儿神经系统发育的一个严重问题,部分早产儿甚至可能发展为脑瘫,为早产儿及其家庭带来沉重负担[1, 2]。但早产儿IVH发生的分子机制目前尚不清楚,前期有研究表明,许多蛋白编码基因及非编码RNA参与其中[3]。
环状RNA(circRNA)是一种特殊的非编码RNA,它是一种连接3'和5'末端的共价键的闭环结构[4],具有稳定性强、表达丰富、高度保守性的特点[5, 6]。大量证据表明,circRNA在人类疾病中发挥着至关重要的作用,如肿瘤[7, 8]、动脉粥样硬化性血管疾病[9]及神经系统疾病等[10-12]。有学者提出,circRNA可以作为miRNA海绵,通过miRNA结合位点竞争性地与miRNA结合,从而阻止miRNA对靶mRNA的调控作用,进而调控基因表达[13-15],被称为竞争性内源性RNA(ceRNA)机制。这种ceRNA机制在各类神经疾病中得到了广泛报道,如急性缺血性脑卒中[16]、颅内出血[17]、阿尔茨海默病[18]及神经胶质瘤[19]等,但在早产儿IVH中报道较少。近期,有学者应用生物信息学方法整合前期不同研究中已上传的mRNA、miRNA、circRNA数据集后提出,ceRNA机制可能参与早产儿神经损伤[20],但因整合的数据不具有同源性,因此意义有限。
本研究应用circRNA芯片技术筛选在IVH早产儿血清中显著差异表达的circRNA,选择hsa_circ_0087893这一差异表达倍数高、功能丰富的circRNA进一步验证表达水平,并构建circRNA-miRNA-mRNA共表达网络,以探索circRNA是否通过ceRNA机制参与早产儿IVH发生、发展,为阐明早产儿IVH发生机制提供新思路。
1. 资料和方法
1.1. 临床资料
1.1.1. 研究对象
收集2019年1月~2020年1月在宁夏医科大学总医院新生儿科住院,经头颅超声或头颅MRI诊断为IVH的28~34周的早产儿25例为实验组,同时收集头颅超声或头颅MRI正常的28~34周的早产儿25例作为对照。实验组纳入标准:临床资料完整,家属知情同意;胎龄28~34周,头颅超声或MRI诊断为IVH。排除标准:死亡、中途放弃治疗或中途转科;出生后未行头颅超声检查,或经后龄(PMA)40~44周未行头颅MRI检查或NBNA评分;伴有其他系统严重合并症,包括多发畸形、青紫型先天性心脏病、新生儿坏死性小肠结肠炎、胆红素脑病、染色体异常或遗传代谢病。
两组早产儿胎龄、出生体质量差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,表 1),IVH组NBNA评分低于正常组(30.8±1.9 vs 33.9±1.74,P < 0.05)。
表 1.
芯片实验6例早产儿基本信息
Characteristics of the 6 preterm infants
| Group | Gestational age | Weight (g) | Cranial ultrasound | Cranial MRI | NBNA score | |
| Control | C1 | 32 weeks, 2 days | 2040 | Normal | Norma | 35 (40 weeks, 2 days PMA) |
| C2 | 32 weeks, 0 days | 2090 | Norma | Norma | 35 (40 weeks, 1 days PMA) | |
| C3 | 33 weeks, 2 days | 2120 | Norma | Norma | 36 (40 weeks, 5 days PMA) | |
| IVH | T1 | 32 weeks, 0 days | 2050 | Grade III IVH | Focal PVL | 29 (40 weeks, 0 days PMA) |
| T2 | 32weeks, 3 days | 2120 | Grade II IVH | Bilateral lateral ventricle dilatation | 29 (40 weeks, 4 days PMA) | |
| T3 | 33 weeks, 5 days | 2130 | Grade II IVH | Focal PVL | 30 (42 weeks, 1 days PMA) |
1.1.2. 标本处理
所有早产儿在生后24 h内抽取2 mL静脉血,分离血清后储存于-80 ℃备用。每组采用简单随机抽样法选取3例早产儿血清进行circRNA芯片检测。本研究经宁夏医科大学总医院伦理委员会同意并批准(编号:2020-107)。
1.2. 总RNA提取及质控
用TRIzol提取每例血清样本总RNA,紫外分光光度计检测总RNA浓度及A260/A280,琼脂糖凝胶电泳判断RNA完整性,分析样本总RNA质量(表 2)。
表 2.
6例样本总RNA质控结果
RNA quality control of the 6 samples
| Sample | A260/A280 | Concentration (ng/μL) | Total RNA (ng) | Quality |
| T1 | 1.86 | 121.47 | 1822.05 | Pass |
| T2 | 2.09 | 357.5 | 5362.5 | Pass |
| T3 | 1.87 | 361.6 | 5424 | Pass |
| C1 | 1.80 | 346.75 | 5201.25 | Pass |
| C2 | 2.07 | 362.15 | 5432.25 | Pass |
| C3 | 1.93 | 97.87 | 1468.05 | Pass |
1.3. 芯片实验
总RNA经RNA酶(Epicentre, Inc.)消化后收集circRNA,再应用随机引物法转录为荧光标记cRNA (Arraystar Super RNA Labeling Kit; Arraystar)后,与芯片进行杂交(Arraystar Human circRNA Array, 8 X 15K)。杂交的芯片进行清洗、固定并扫描(Agilent Scanner G2505C)。
应用Agilent Feature Extraction软件分析芯片图像,应用R software对数据标准化。将P≤0.05且差异倍数(FC)≥1.5的circRNA认定为具有显著差异的circRNA。用箱型图表示各样本标准化后的数据,用散点图表示差异circRNA的分布。应用Cytoscape software构建circRNA-miRNA-mRNA网络图,应用miRNA target prediction software(Arraystar)预测与circRNA结合的miRNA,即miRNA-recognition elements(MREs)。以上芯片实验及生物信息学分析由上海康成公司完成。
1.4. 差异circRNA的功能分析
应用基因本体论(GO)(http://www.geneontology.org)分析差异基因的功能,包括生物学过程、分子功能及细胞成分分析,应用KEGG数据库(http://www.genome.jp/kegg/)分析差异基因参与的信号通路。
1.5. qRT-PCR验证
选择hsa_circ_0087893应用qRT-PCR进一步验证它在两组早产儿血液中的实际表达水平。应用Super-ScriptTM III逆转录酶(Invitrogen, USA)将总RNA逆转录为cDNA,以cDNA为模板,按照说明书配制反应体系,以人β-actin为内参,结果以Ct值表示,采用2-△△Ct法比较circRNA在两组的表达水平。β-actin引物序列为:F: 5'GTGGCCGAGGACTTTGATTG3';R: 5'CCTG-TAACAACGCATCTCATATT3'。hsa_circ_0087893引物序列为:F: 5'ATTCAGTTCCCACGCCAAA3';R: 5'CCATTCTCGTCCATACTGATACAC3'。
1.6. 统计学分析
采用SPSS 23.0统计软件对数据进行统计学分析,计量资料以均数±标准差表示,采用独立样本t检验比较胎龄、出生体质量、NBNA评分及circRNA在两组样本中的表达差异,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1. 两组差异表达circRNA筛选结果
6例样本数据标准化程度好(图 1A),散点图显示差异circRNA的分布(图 1B)。芯片检测结果显示IVH组与对照组患儿血清中cirRNA表达有较大差异。共有121条circRNA在IVH组显著差异表达(FC≥1.5,P < 0.05),包括62条上调表达circRNA及59条下调表达circRNA。上调circRNA包含56个exonic circRNA (90%),3个intronic circRNA(5%)和3个sense overlapping circRNA(5%)(图 1C),下调circRNA包含50个exonic circRNA(85%),5个sense overlapping circRNA(9%),2个intronic circRNA(3%)和2个antisense circRNA(3%)(图 1D)。差异表达倍数最高的前10条circRNA及其共表达的miRNA见表 3。
图 1.

两组差异表达circRNA基本情况
Basic information of the differentially expressed circRNAs in preterm infants with intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH). A: Box plot showing normalization of the 6 samples. B: Scatter plot showing differentially expressed circRNAs between the two groups. The blocks above the top and below the bottom green lines represent circRNAs with fold change ≥1.5 and P < 0.05 in the IVH group. C: Classification of up-regulated circRNAs. D: Classification of down-regulated circRNAs.
表 3.
两组差异表达倍数最高的前10条circRNA
Top 10 differentially expressed circRNAs between the two groups
| CircRNA | Fold change | Regulation | Classification | Strand | Top 3 miRNA-recognition elements |
| hsa_circ_0001790 | 6.6752243 | up | exonic | + | hsa-miR-494-5p; hsa-miR-410-5p; hsa-miR-370-3p |
| hsa_circ_0007145 | 5.8230765 | down | exonic | + | hsa-miR-139-3p; hsa-miR-339-5p; hsa-miR-612 |
| hsa_circ_0004954 | 5.574101 | up | exonic | - | hsa-miR-193b-3p; hsa-miR-193a-3p; hsa-miR-3922-3p |
| hsa_circ_0079948 | 5.182954 | up | exonic | - | hsa-miR-3620-5p; hsa-miR-4446-3p; hsa-miR-6796-5p |
| hsa_circ_0068189 | 5.1715179 | down | exonic | + | hsa-miR-423-5p; hsa-miR-202-3p; hsa-miR-181b-5p |
| hsa_circ_0009057 | 4.482602 | up | exonic | + | hsa-miR-27a-5p; hsa-miR-769-3p; hsa-miR-215-3p |
| hsa_circ_0055002 | 4.4151094 | up | exonic | + | hsa-miR-494-5p; hsa-miR-758-3p; hsa-miR-660-3p |
| hsa_circ_0087893 | 4.29315 | down | exonic | - | hsa-miR-567; hsa-miR-183-5p; hsa-miR-653-3p |
| hsa_circ_0003991 | 4.0928545 | down | exonic | + | hsa-miR-3928-3p; hsa-miR-664a-3p; hsa-miR-545-5p |
| hsa_circ_406541 | 3.9861519 | down | exonic | - | hsa-miR-367-5p; hsa-miR-4739; hsa-miR-1270 |
2.2. 差异表达cirRNA的功能分析
GO分析显示,差异circRNA参与多种生物功能,包括ATP转运、组蛋白H4乙酰化、细胞增殖、活化及死亡、DNA损伤及修复等(图 2A)。信号通路分析显示,差异circRNA参与的信号通路包括造血细胞系、维生素A代谢、鞘磷脂代谢及细胞黏附等(图 2B)。
图 2.
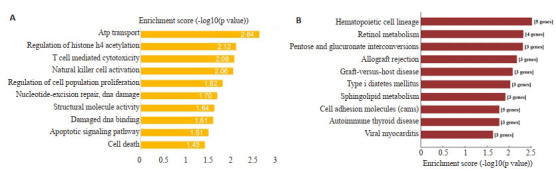
差异circRNA的GO分析及pathway分析
GO and pathway analysis of the differentially expressed circRNAs. A: Significantly enriched GOs between the two groups. B: Significantly enriched pathways between the two groups.
2.3. qRT-PCR验证hsa_circ_0087893在两组的表达水平
RT-PCR实验结果显示,hsa_circ_0087893在IVH组中表达显著下调(P < 0.05),与芯片结果一致(图 3)。
图 3.
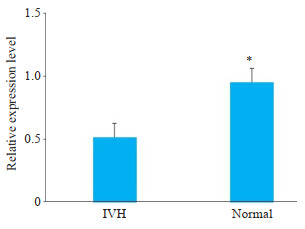
hsa_circ_0087893在早产儿IVH组显著下调
hsa_circ_0087893 was significantly down-regulated in IVH group. *P < 0.05.
2.4. hsa_circ_0087893共表达网络
对hsa_circ_0087893构建circRNA- miRNA-mRNA共表达网络,41个miRNA与hsa_circ_0087893共表达,包括miR-214-3p、miR-761、miR-183-5p、miR-651-3p等。还有共15条mRNA与hsa_circ_0087893共表达,包括AKR1B1、KRT34、PPP2CB、HPRT1等(图 4)。GO分析及pathway分析显示,这些mRNA及miRNA参与众多重要功能(表 4)。
图 4.

hsa_circ_0087893的circRNA-miRNA-mRNA共表达网络图
Co-expression network of hsa_circ_0087893. Red circle represents miRNA, and blue circle represents mRNA.
表 4.
与hsa_circ_0087893共表达的miRNA及mRNA
miRNAs and mRNAs co-expressed with hsa_circ_0087893
| mRNAs | Co-expressed miRNAs | GO/pathway analysis |
| AKR1B1 | miR-214-3p, miR-376a-2-5p, miR-761, miR-31-5p, miR-15a-3p, miR-588, miR-888-3p, miR-506-5p | positive regulation of cell population proliferation, response to stimulus, cell death |
| KRT34 | miR-651-3p, miR-520a-5p, miR-525-5p, miR-484, miR-421, miR-31-5p, miR-198 | programmed cell death, structural molecule activity |
| PPP2CB | miR-183-5p, miR-651-3p, miR-214-3p, miR-143-3p, miR-761, miR-455-3p | apoptotic mitochondrial changes, response to stimulus, cell death |
| IQCJ-SCHIP1 | miR-183-5p, miR-653-3p, miR-338-5p, miR-196b-5p, miR-196a-5p, miR-125b-2-3p | response to stimulus, positive regulation of biological process, negative regulation of organelle organization |
| HPRT1 | miR-653-3p, miR-103a-2-5p, miR-577, miR-186-3p, miR-588, miR-888-3p | T cell mediated cytotoxicity, cell killing, positive regulation of biological process, cell population proliferation |
3. 讨论
本研究通过circRNA芯片筛选出在IVH早产儿血液中差异表达的circRNA。芯片结果显示,与对照组相比,早产儿IVH组中差异表达的circRNA有121个,其中上调表达的62个,下调表达的59个,说明IVH早产儿血清中的circRNA表达谱发生了明显的变化。GO分析和pathway分析表明,这些差异表达的circRNA参与了许多功能和通路,如细胞周期、代谢、DNA损伤和修复等,提示这些circRNA可能在早产儿IVH中发挥重要作用。
在众多差异表达的circRNA中,我们选择hsa_circ_0087893做进一步生物信息学分析。芯片结果提示,hsa_circ_0087893在早产儿IVH组中表达显著下调,下调倍数为4.2倍,扩大样本量进行qRT-PCR实验证实hsa_circ_0087893在IVH早产儿血清中表达明显下调,与芯片结果一致。且通过对芯片原始数据进行分析,我们发现hsa_circ_0087893在组内样本之间的信号强度较为均一,提示该circRNA表达较为稳定,因此选择它作为进一步研究对象。
为探讨早产儿IVH发生、发展中的ceRNA机制,本研究构建了hsa_circ_0087893的circRNA- miRNA-mRNA共表达网络。结果表明,与hsa_circ_0087893共表达的miRNA共有41个,包括miR-214-3p、miR-761、miR-183-5p、miR-651-3p等,它们在神经系统中的潜在作用已被较多研究证实。其中miR-214-3p是一条被报道较多的miRNA,广泛参与肿瘤、心血管系统疾病、神经系统疾病等病理过程[21-23]。研究发现,miR-214-3p是一种新的潜在的神经保护因子,它可通过抑制硫氧还蛋白结合蛋白的表达减轻新生小鼠缺氧缺血性脑损伤[24];还有研究报道,miR-214-3p可通过抑制自噬和减轻海马神经元凋亡来缓解阿尔茨海默病[25]。有研究显示,miR-761可作为细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶抑制因子2B基因的海绵,通过与某些长链非编码RNA相互作用,调控大鼠周围神经损伤后轴突再生和功能恢复[26]。有学者研究发现,miRNA-183-5p可以控制出血性中风后的炎症和氧化损伤,是一种有前景的治疗靶标[27]。
另外,本研究还发现了15个与hsa_circ_0087893共表达的mRNA,如AKR1B1、IQCJ-SCHIP1、KRT34、PPP2CB、HPRT1等,它们在神经系统疾病中的作用也得到了证实。GO分析和信号通路分析表明,这些mRNA参与多种生理、病理过程。如细胞增殖和死亡、生物过程、对刺激的反应等。有研究报道,上调AKR1B1可调节脊髓损伤的大鼠体内能量代谢,促进神经炎症发展和星形胶质细胞增殖[28]。有研究发现,IQCJ-SCHIP1突变可导致脑发育畸形综合征[29]。以上结果均表明,hsa_circ_0087893可能通过与这些miRNA和mRNA相互作用,发挥ceRNA机制,调控早产儿IVH发生、发展。但本研究未能验证环状RNA表达的变化与早产儿IVH严重程度的相关性,这是本研究的局限性之一。本研究为初步的生物信息学分析,将为早产IVH发病机制提供新的思路,但还需进一步体内和体外实验验证。
Funding Statement
宁夏自然科学基金(2020AAC03373)
Contributor Information
陈 茹娟 (Rujuan CHEN), Email: 648974977@qq.com.
武 伟 (Wei WU), Email: 184093452@qq.com.
References
- 1.Leijser LM, de Vries LS. Preterm brain injury: Germinalmatrix-intraventricular hemorrhage and post-hemorrhagic ventricular dilatation. Handb Clin Neurol. 2019;162:173–99. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-64029-1.00008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gilard V, Tebani A, Bekri S, et al. Intraventricular hemorrhage in very preterm infants: a comprehensive review. J Clin Med. 2020;9(8):2447–60. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fejes Z, Erdei J, Pócsi M, et al. Elevated pro-inflammatory cell-free microRNA levels in cerebrospinal fluid of premature infants after intraventricular hemorrhage. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(18):6870–85. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chen LL, Yang L. Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2015;12(4):381–8. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1020271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhu GM, Chang XY, Kang YC, et al. CircRNA: a novel potential strategy to treat thyroid cancer (Review) Int J Mol Med. 2021;48(5):201–13. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhang P, Dai MQ. CircRNA: a rising star in plant biology. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2022;49(12):1081–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2022.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cheng ZA, Yu CT, Cui SH, et al. circTP63 functions as a ceRNA to promote lung squamous cell carcinoma progression by upregulating FOXM1. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3200–12. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11162-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.张 思, 袁 凡恩, 陈 谦学. circRNA在胶质母细胞瘤中的研究进展. 中国临床神经外科杂志. 2023;28(1):57–9. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Holdt LM, Stahringer A, Sass K, et al. Circular non-coding RNA ANRIL modulates ribosomal RNA maturation and atherosclerosis in humans. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12429–37. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lukiw WJ. Circular RNA (circRNA) in alzheimer's disease (AD) Front Genet. 2013;4:307–21. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ravanidis S, Bougea A, Karampatsi D, et al. Differentially expressed circular RNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2021;36(5):1170–9. doi: 10.1002/mds.28467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lu D, Ho ES, Mai HC, et al. Identification of blood circular RNAs as potential biomarkers for acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:81–92. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495(7441):384–8. doi: 10.1038/nature11993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mahmoudi E, Cairns MJ. Circular RNAs are temporospatially regulated throughout development and ageing in the rat. Sci Rep. 2019;9:2564–72. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38860-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhang XJ, Hamblin MH, Yin KJ. Noncoding RNAs and stroke. Neuroscientist. 2019;25(1):22–6. doi: 10.1177/1073858418769556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.郑 继青, 龙 耀斌, 刘 云. circRNA作用于急性缺血性脑卒中的研究进展. 天津医药. 2022;50(12):1335–9. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liu Z, Wu XR, Yu ZH, et al. Reconstruction of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA associated ceRNA networks reveal functional circRNAs in intracerebral hemorrhage. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):11584–90. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91059-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wang Z, Xu PP, Chen BY, et al. Identifying circRNA-associated-ceRNA networks in the hippocampus of Aβ1-42-induced Alzheimer's disease-like rats using microarray analysis. Aging (Albany NY) 2018;10(4):775–88. doi: 10.18632/aging.101427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Haibin Xia. circRNA 0002109 promotes glioma malignant progression via modulating the miR-129-5P/EMP2 axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022;27:1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.11.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Huang J, Liang XJ, Cai ZY. A potential ceRNA network for neurological damage in preterm infants. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:2628824–33. doi: 10.1155/2021/2628824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang YH, Chen YW, Xiao WL, et al. miR-214-3p prevents the development of perioperative neurocognitive disorders in elderly rats. Curr Med Sci. 2022;42(4):871–84. doi: 10.1007/s11596-022-2572-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.He GN, Bao NR, Wang S, et al. Ketamine induces ferroptosis of liver cancer cells by targeting lncRNA PVT1/miR-214-3p/GPX4. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2021;15:3965–78. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S332847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.蔡 子纯, 蒋 元桢, 张 春生, et al. 环状RNA在心血管疾病中的研究进展及应用前景. 中国临床药理学与治疗学. 2022;27(4):397–404. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhang MY, Zhou HY, He RN, et al. Up-regulating microRNA-214-3p relieves hypoxic- ischemic brain damage through inhibiting TXNIP expression. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023;478(3):597–608. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04530-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yueqi, Zhang miR-214-3p attenuates cognition defects via the inhibition of autophagy in SAMP8 mouse model of sporadic Alzheimer's disease. NeuroToxicology. 2016;56:139–49. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2016.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Do ng, Wa ng. The long noncoding RNA Arrl1 inhibits neurite outgrowth by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA during neuronal regeneration in rats. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(25):8374–86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang Y, Song YJ, Pang YX, et al. miR-183-5p alleviates early injury after intracerebral hemorrhage by inhibiting heme oxygenase-1 expression. Aging (Albany NY) 2020;12(13):12869–95. doi: 10.18632/aging.103343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chen XQ, Chen C, Hao J, et al. AKR1B1 upregulation contributes to neuroinflammation and astrocytes proliferation by regulating the energy metabolism in rat spinal cord injury. Neurochem Res. 2018;43(8):1491–9. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Elsaid MF, Chalhoub N, Ben-Omran T, et al. Homozygous nonsense mutation in SCHIP1/IQCJ- SCHIP1 causes a neurodevelopmental brain malformation syndrome. Clin Genet. 2018;93(2):387–91. doi: 10.1111/cge.13122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


