Abstract
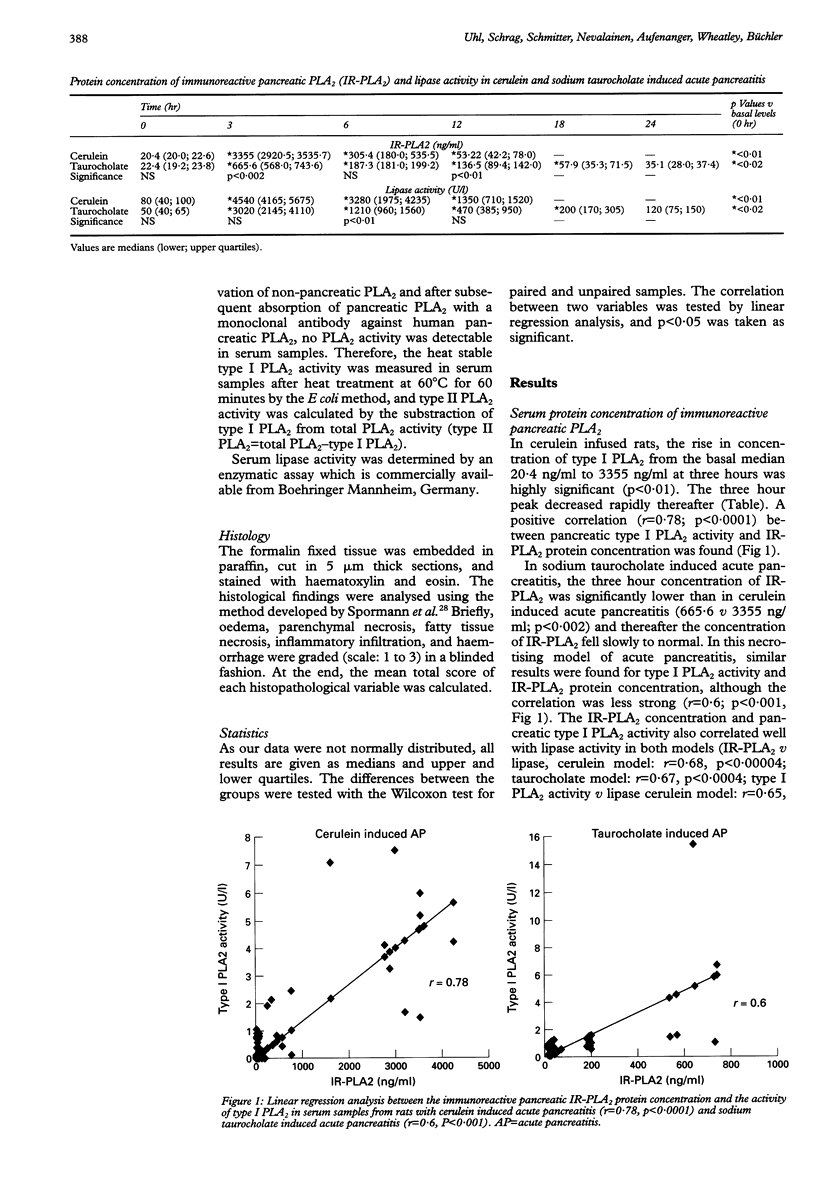
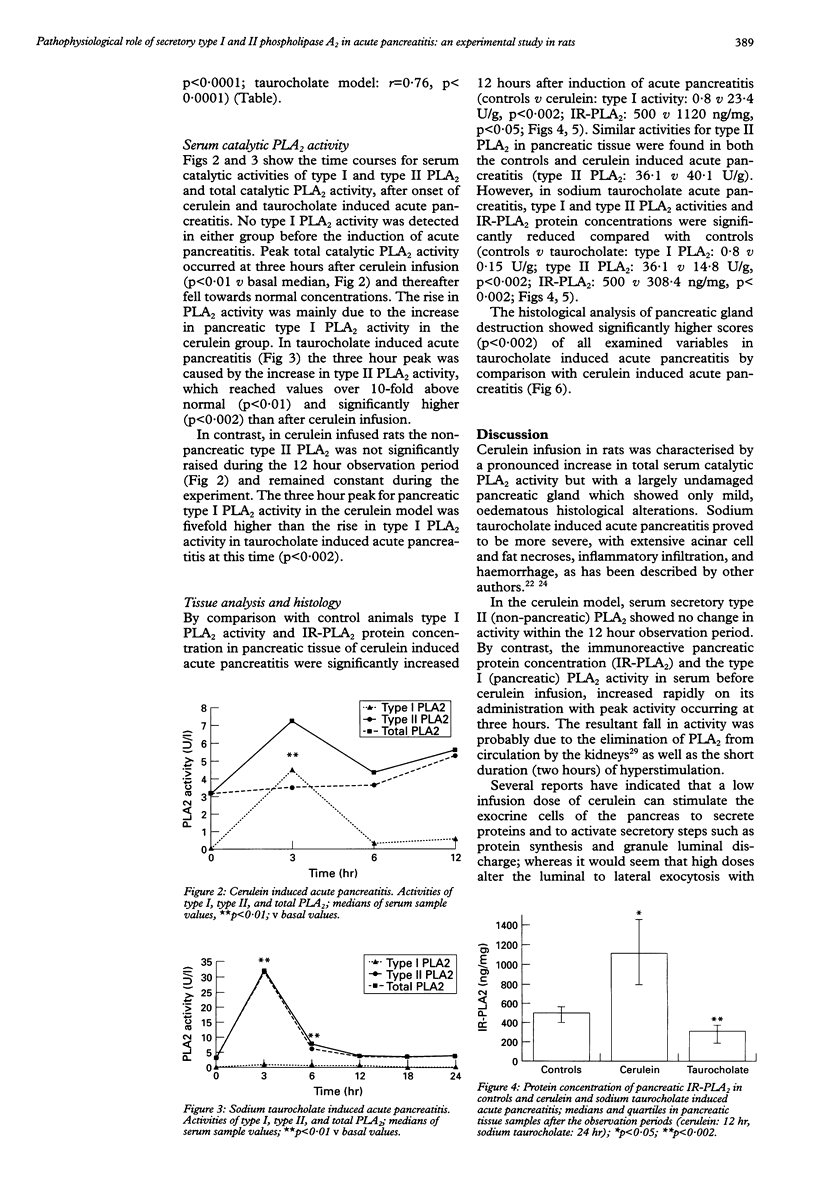
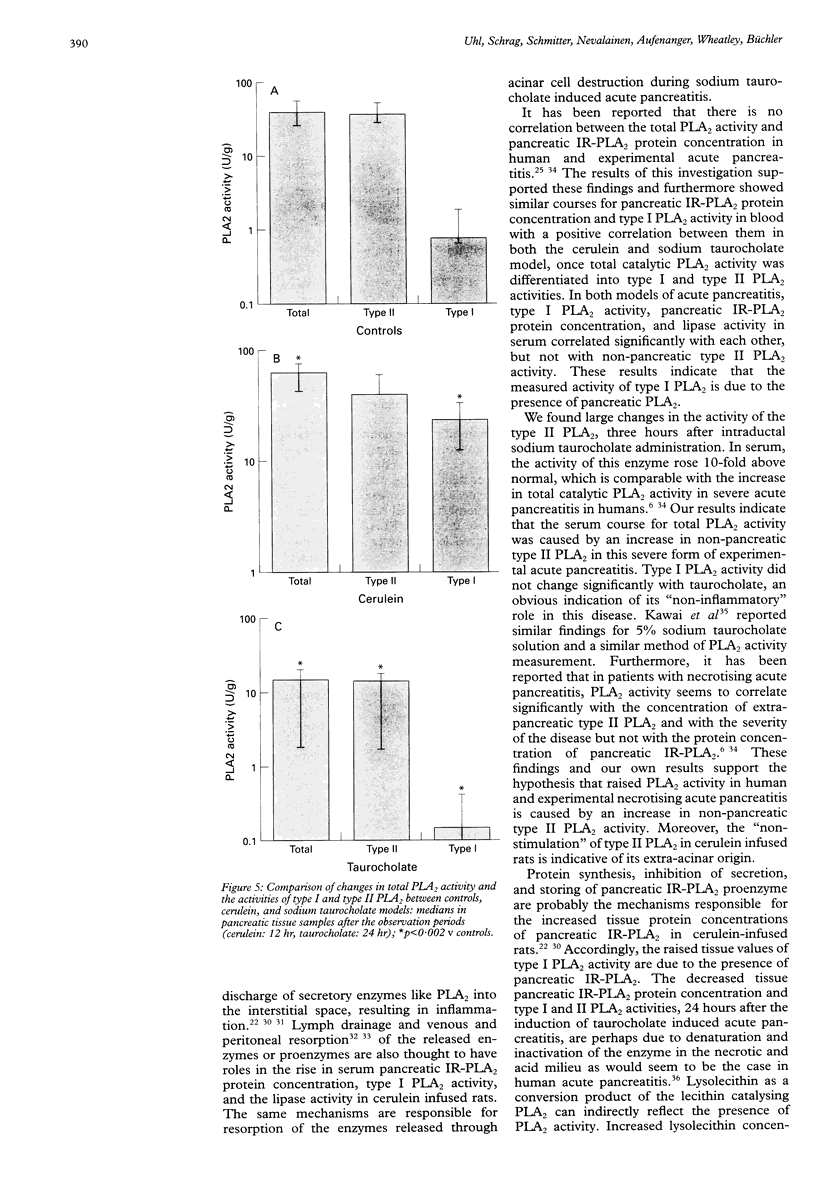
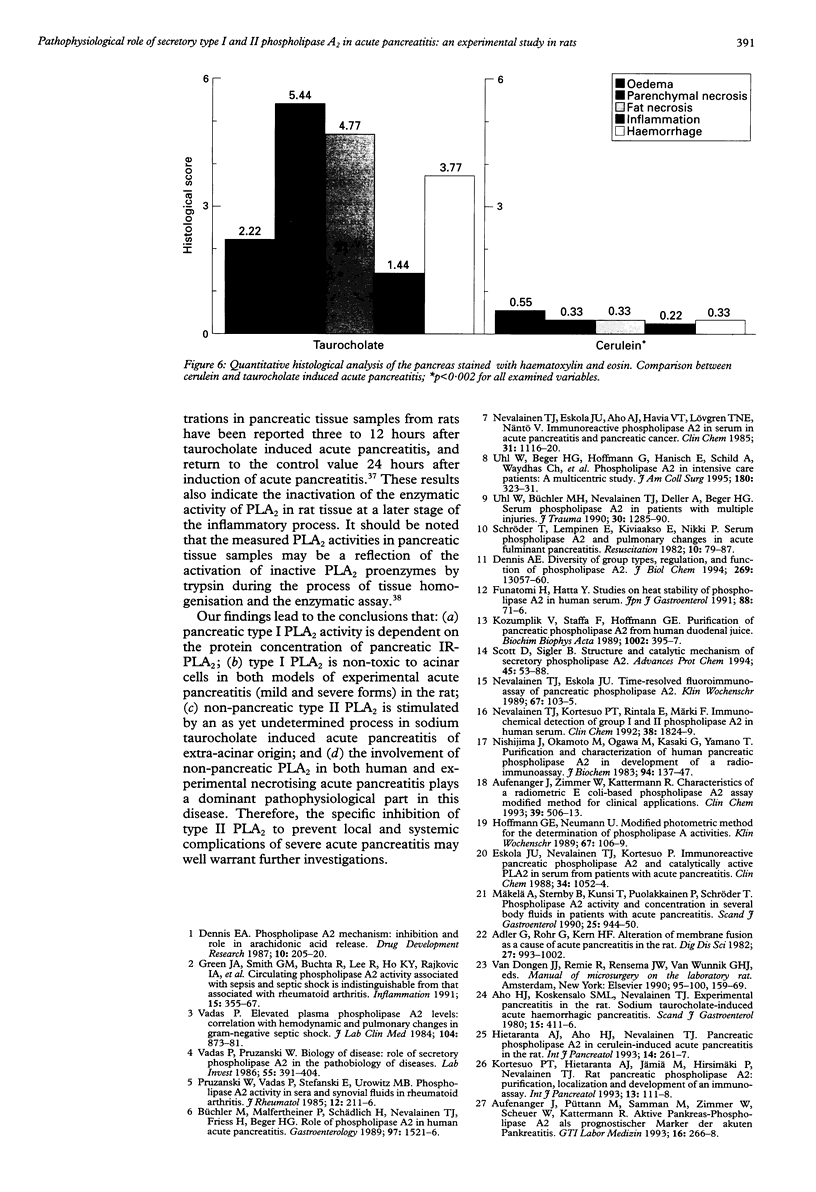
BACKGROUND: In human acute pancreatitis two different types of secretory phospholipase A2 (PLA2) have been found. AIM: To analyse the specific pattern of distribution of these PLA2 activities and their pathophysiological role in experimental acute pancreatitis. SUBJECTS AND METHODS: Catalytic activities of secretory type I (pancreatic) and type II (non-pancreatic) PLA2 and the protein concentration of immunoreactive pancreatic PLA2 (IR-PLA2) in serum and pancreatic tissue of rats with cerulein (mild form) and sodium taurocholate (severe form) induced acute pancreatitis were determined. RESULTS: Cerulein infusion caused a significant increase in type I PLA2 activity (p < 0.01) and IR-PLA2 protein concentration (p < 0.01) in serum and pancreas, whereas type II PLA2 activity remained unchanged during the 12 hour observation period. Histology showed no significant tissue destruction. In sodium taurocholate induced acute pancreatitis type II PLA2 activity significantly increased, reaching values over 10-fold higher than controls (p < 0.01), whereas IR-PLA2 protein concentration and type I PLA2 activity were only marginally increased. In this severe model of acute pancreatitis significantly lower values were detected than in the control pancreas (p < 0.002) for PLA2 activity and IR-PLA2 protein concentration. Histology showed parenchymal and fat necroses with haemorrhage, oedema, and inflammatory cell infiltration. CONCLUSIONS: Type I PLA2 activity is dependent on the IR-PLA2 protein concentration in serum and pancreatic tissue. The type II PLA2 activity is not stimulated by cerulein, which indicates an extra-acinar origin of this enzyme. Type II PLA2 activity is significantly increased in sodium taurocholate induced acute pancreatitis indicating its role in the local necrotising process and involvement in the systemic effects in severe acute pancreatitis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abita J. P., Lazdunski M., Bonsen P. P., Pieterson W. A., de Haas G. H. Zymogen-enzyme transformations. On the mechanism of activation of prophospholipase A. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct 17;30(1):37–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler G., Rohr G., Kern H. F. Alteration of membrane fusion as a cause of acute pancreatitis in the rat. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Nov;27(11):993–1002. doi: 10.1007/BF01391745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aho H. J., Koskensalo S. M., Nevalainen T. J. Experimental pancreatitis in the rat. Sodium taurocholate-induced acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(4):411–416. doi: 10.3109/00365528009181493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aho H. J., Nevalainen T. J., Lindberg R. L., Aho A. J. Experimental pancreatitis in the rat. The role of phospholipase A in sodium taurocholate-induced acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(8):1027–1031. doi: 10.3109/00365528009181808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchler M., Malfertheiner P., Schädlich H., Nevalainen T. J., Friess H., Beger H. G. Role of phospholipase A2 in human acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 1989 Dec;97(6):1521–1526. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90398-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. A. Diversity of group types, regulation, and function of phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13057–13060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskola J. U., Nevalainen T. J., Kortesuo P. Immunoreactive pancreatic phospholipase A2 and catalytically active phospholipases A2 in serum from patients with acute pancreatitis. Clin Chem. 1988 Jun;34(6):1052–1054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatomi H., Hatta Y. [Studies on heat stability of phospholipase A2 in human serum]. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1991 Jan;88(1):71–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. A., Smith G. M., Buchta R., Lee R., Ho K. Y., Rajkovic I. A., Scott K. F. Circulating phospholipase A2 activity associated with sepsis and septic shock is indistinguishable from that associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation. 1991 Oct;15(5):355–367. doi: 10.1007/BF00917352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hietaranta A. J., Aho H. J., Grönroos J. M., Hua Z. Y., Nevalainen T. J. Pancreatic phospholipase A2 in proximal tubules of rat kidney in experimental acute pancreatitis and after intravenous injection of the enzyme. Pancreas. 1992;7(3):326–333. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199205000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hietaranta A. J., Aho H. J., Nevalainen T. J. Pancreatic phospholipase A2 in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in the rat. Int J Pancreatol. 1993 Dec;14(3):261–267. doi: 10.1007/BF02784935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann G. E., Neumann U. Modified photometric method for the determination of phospholipase A activities. Klin Wochenschr. 1989 Feb 1;67(3):106–109. doi: 10.1007/BF01711332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortesuo P. T., Hietaranta A. J., Jämiä M., Hirsimäki P., Nevalainen T. J. Rat pancreatic phospholipase A2. Purification, localization, and development of an enzyme immunoassay. Int J Pancreatol. 1993 Apr;13(2):111–118. doi: 10.1007/BF02786079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozumplik V., Staffa F., Hoffmann G. E. Purification of pancreatic phospholipase A2 from human duodenal juice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Apr 26;1002(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampel M., Kern H. F. Acute interstitial pancreatitis in the rat induced by excessive doses of a pancreatic secretagogue. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1977 Mar 11;373(2):97–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00432156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange J. F., Beyaert P. J., van Vugt H., Tytgat G. N., van Gool J. Pathways of enzyme transfer in sodium taurocholate-induced acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis. Digestion. 1986;35(4):229–236. doi: 10.1159/000199373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer A. D., Airey M., Hodgson J., McMahon M. J. Enzyme transfer from pancreas to plasma during acute pancreatitis. The contribution of ascitic fluid and lymphatic drainage of the pancreas. Gut. 1985 Sep;26(9):876–881. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.9.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myren J. Acute pancreatitis. Pathogenetic factors as a basis for treatment. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(5):513–517. doi: 10.3109/00365527709181327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä A., Sternby B., Kuusi T., Puolakkainen P., Schröder T. Phospholipase A2 activity and concentration in several body fluids in patients with acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1990 Sep;25(9):944–950. doi: 10.3109/00365529008997616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevalainen T. J., Eskola J. U., Aho A. J., Havia V. T., Lövgren T. N., Näntö V. Immunoreactive phospholipase A2 in serum in acute pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Clin Chem. 1985 Jul;31(7):1116–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevalainen T. J., Eskola J. U., Aho A. J., Havia V. T., Lövgren T. N., Näntö V. Immunoreactive phospholipase A2 in serum in acute pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Clin Chem. 1985 Jul;31(7):1116–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevalainen T. J., Eskola J. U. Time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay of pancreatic phospholipase A2. Klin Wochenschr. 1989 Feb 1;67(3):103–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01711331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevalainen T. J., Grönroos J. M., Kortesuo P. T. Pancreatic and synovial type phospholipases A2 in serum samples from patients with severe acute pancreatitis. Gut. 1993 Aug;34(8):1133–1136. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.8.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevalainen T. J., Kortesuo P. T., Rintala E., Märki F. Immunochemical detection of group I and group II phospholipases A2 in human serum. Clin Chem. 1992 Sep;38(9):1824–1829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishijima J., Okamoto M., Ogawa M., Kosaki G., Yamano T. Purification and characterization of human pancreatic phospholipase A2 and development of a radioimmunoassay. J Biochem. 1983 Jul;94(1):137–147. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordback I., Teerenhovi O., Auvinen O., Koivula T., Thuren T., Kinnunen P., Eskola J., Näntö V. Human pancreatic phospholipase A2 in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Digestion. 1989;42(3):128–134. doi: 10.1159/000199837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Vadas P., Stefanski E., Urowitz M. B. Phospholipase A2 activity in sera and synovial fluids in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Its possible role as a proinflammatory enzyme. J Rheumatol. 1985 Apr;12(2):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder T., Lempinen M., Kivilaakso E., Nikki P. Serum phospholipase A2 and pulmonary changes in acute fulminant pancreatitis. Resuscitation. 1982 Jun;10(2):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0300-9572(82)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., Sigler P. B. Structure and catalytic mechanism of secretory phospholipases A2. Adv Protein Chem. 1994;45:53–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60638-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spormann H., Sokolowski A., Letko G. Effect of temporary ischemia upon development and histological patterns of acute pancreatitis in the rat. Pathol Res Pract. 1989 May;184(5):507–513. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(89)80143-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl W., Beger H. G., Hoffmann G., Hanisch E., Schild A., Waydhas C., Entholzner E., Müller K., Kellermann W., Vogeser M. A multicenter study of phospholipase A2 in patients in intensive care units. J Am Coll Surg. 1995 Mar;180(3):323–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl W., Büchler M., Nevalainen T. J., Deller A., Beger H. G. Serum phospholipase A2 in patients with multiple injuries. J Trauma. 1990 Oct;30(10):1285–1290. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199010000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P. Elevated plasma phospholipase A2 levels: correlation with the hemodynamic and pulmonary changes in gram-negative septic shock. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Dec;104(6):873–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Pruzanski W. Role of secretory phospholipases A2 in the pathobiology of disease. Lab Invest. 1986 Oct;55(4):391–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


