Abstract
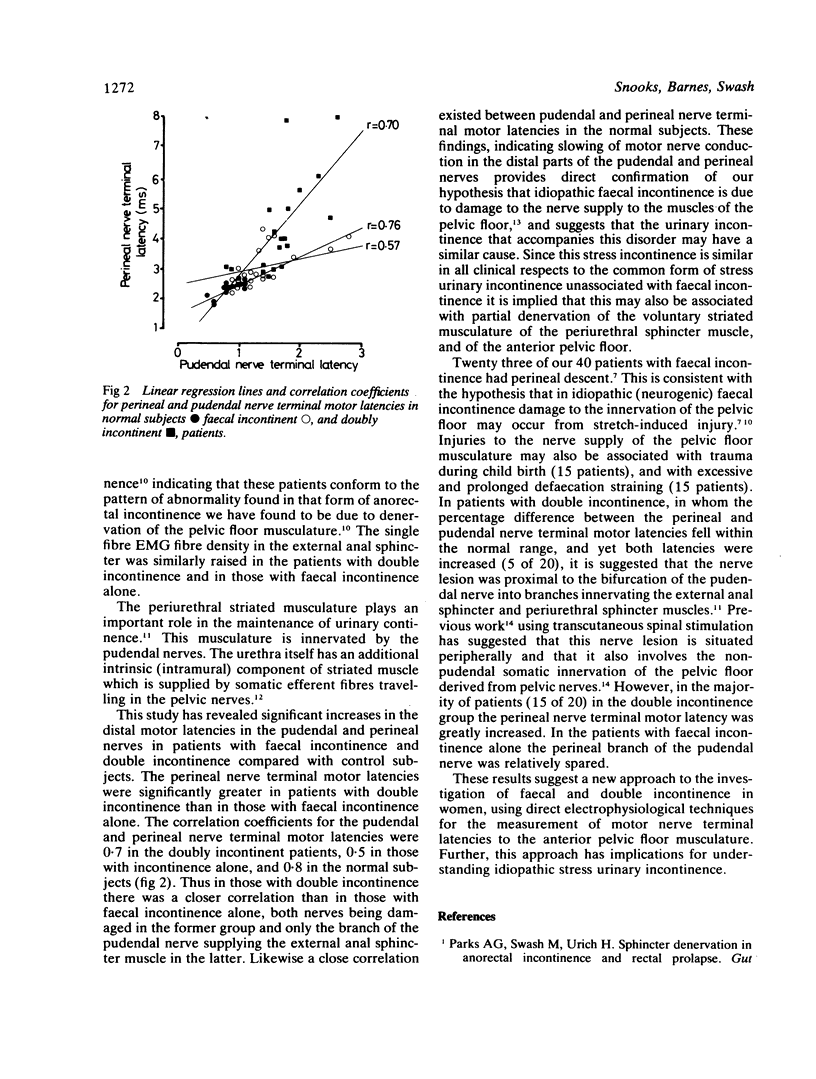
In 40 women with idiopathic (neurogenic) faecal incontinence, 20 of whom also had stress urinary incontinence, single fibre EMG studies showed an increased fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle. All these patients showed excessive descent of the pelvic floor on straining. The mean terminal motor latencies in the pudendal and perineal nerves, measured by a digitally-directed intrarectal stimulating technique, were increased when compared with 20 control subjects (p less than 0.01). The perineal nerve terminal motor latency was more markedly increased in the 20 patients with double incontinence than in those with faecal incontinence alone (p less than 0.01). These results provide direct electrophysiological evidence of damage to the innervation of the pelvic floor musculature in idiopathic faecal and double incontinence, and imply that idiopathic stress urinary incontinence may have a similar cause.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brindley G. S. Electroejaculation: its technique, neurological implications and uses. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Jan;44(1):9–18. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosling J. The structure of the bladder and urethra in relation to function. Urol Clin North Am. 1979 Feb;6(1):31–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry M. M., Parks A. G., Swash M. The pelvic floor musculature in the descending perineum syndrome. Br J Surg. 1982 Aug;69(8):470–472. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800690813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill M. E., Parks A. G., Swash M. Physiological studies of the anal sphincter musculature in faecal incontinence and rectal prolapse. Br J Surg. 1981 Aug;68(8):531–536. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800680804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill M. E., Swash M. Increased motor unit fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle in ano-rectal incontinence: a single fibre EMG study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 Apr;43(4):343–347. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.4.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percy J. P., Neill M. E., Swash M., Parks A. G. Electrophysiological study of motor nerve supply of pelvic floor. Lancet. 1981 Jan 3;1(8210):16–17. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


