Abstract
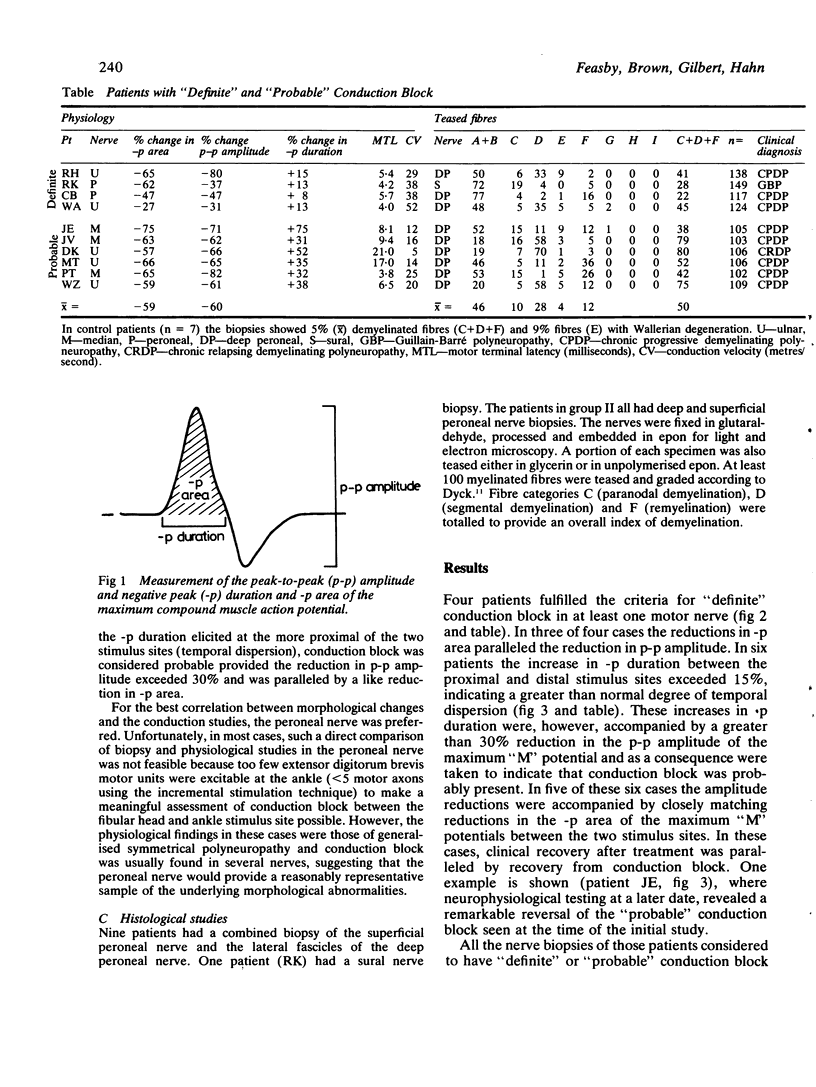
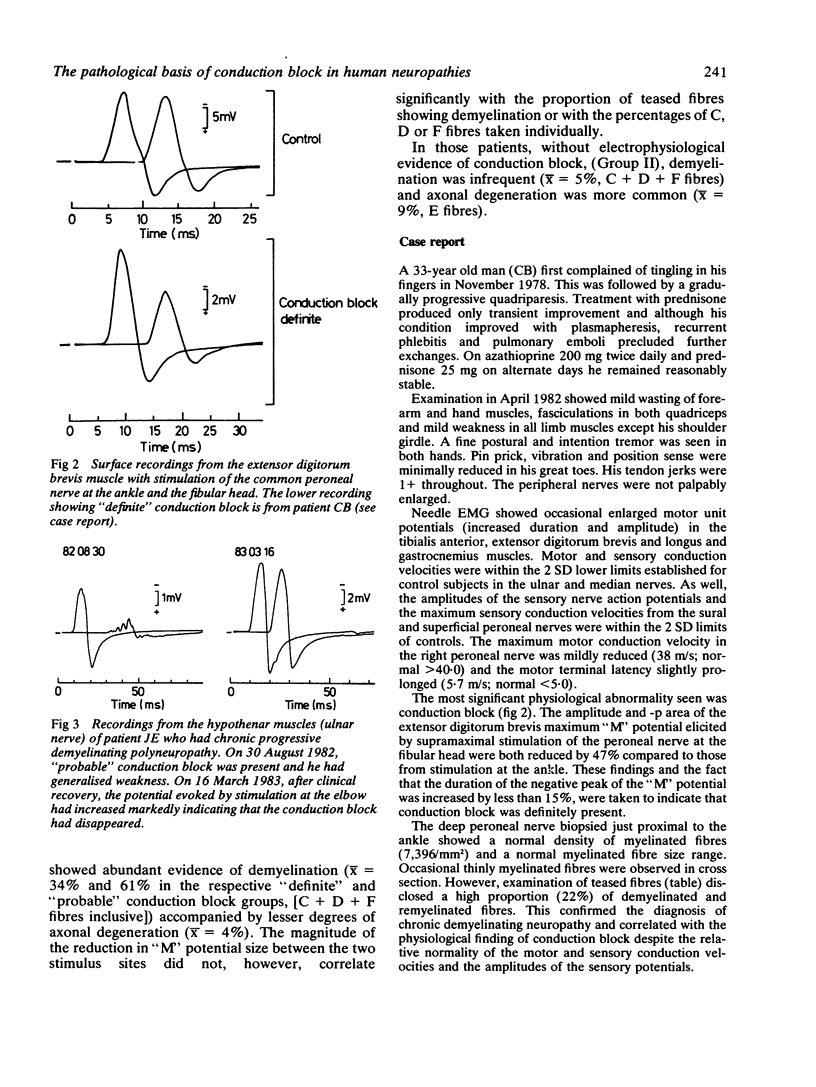
Conduction block was detected in patients with neuropathy by measuring a decrease in the size of the compound muscle action potential of more than 20% on proximal versus distal stimulation of the peroneal, median or ulnar nerve in the absence of excess temporal dispersion of the potential. The teased fibre analyses of nerve biopsies from four patients with "definite" and six patients with "probable" conduction block and from seven patients with neuropathy but without conduction block were compared. All patients with conduction block had significant demyelination (X% demyelinated and remyelinated fibres = 50%) while those without conduction block did not (X = 5.0%). Demyelination is the pathological basis of conduction block in human neuropathies.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUSTIN J. H. Recurrent polyneuropathies and their corticosteroid treatment; with five-year observations of a placebo-controlled case treated with corticotrophin, cortisone, and prednisone. Brain. 1958 Jun;81(2):157–192. doi: 10.1093/brain/81.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton C. F., McFarlane R. M. Human pneumatic tourniquet paralysis. Neurology. 1978 Aug;28(8):787–793. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.8.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock H., Sears T. A. The internodal axon membrane: electrical excitability and continuous conduction in segmental demyelination. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:273–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. F., Feasby T. E. Conduction block and denervation in Guillain-Barré polyneuropathy. Brain. 1984 Mar;107(Pt 1):219–239. doi: 10.1093/brain/107.1.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. F., Ferguson G. G., Jones M. W., Yates S. K. The location of conduction abnormalities in human entrapment neuropathies. Can J Neurol Sci. 1976 May;3(2):111–122. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100025865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAGG B. G., THOMAS P. K. CHANGES IN NERVE CONDUCTION IN EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC NEURITIS. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1964 Apr;27:106–115. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.27.2.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck P. J., Lambert E. H. Lower motor and primary sensory neuron diseases with peroneal muscular atrophy. I. Neurologic, genetic, and electrophysiologic findings in hereditary polyneuropathies. Arch Neurol. 1968 Jun;18(6):603–618. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470360025002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLIATT R. W., WILLISON R. G. Peripheral nerve conduction in diabetic neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1962 Feb;25:11–18. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.25.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. J. Pressure palsy of the ulnar nerve with prolonged conduction block. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Jan;39(1):96–99. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongell A., Mattsson H. S. Neurographic studies before, after, and during operation for median nerve compression in the carpal tunnel. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1971;5(2):103–109. doi: 10.3109/02844317109042948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. J., Jr The electrodiagnostic findings in peripheral neuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Sep;6(7):504–509. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koles Z. J., Rasminsky M. A computer simulation of conduction in demyelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):351–364. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafontaine S., Rasminsky M., Saida T., Sumner A. J. Conduction block in rat myelinated fibres following acute exposure to anti-galactocerebroside serum. J Physiol. 1982 Feb;323:287–306. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Sumner A. J., Brown M. J., Asbury A. K. Multifocal demyelinating neuropathy with persistent conduction block. Neurology. 1982 Sep;32(9):958–964. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.9.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Sumner A. J. The electrodiagnostic distinctions between chronic familial and acquired demyelinative neuropathies. Neurology. 1982 Jun;32(6):592–596. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.6.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDONALD W. I. THE EFFECTS OF EXPERIMENTAL DEMYELINATION ON CONDUCTION IN PERIPHERAL NERVE: A HISTOLOGICAL AND ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL STUDY. II. ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS. Brain. 1963 Sep;86:501–524. doi: 10.1093/brain/86.3.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. G., Olney R. K. Persistent conduction block in compression neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 1982;5(9S):S154–S156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. W., Joyner R. W., Brill M. H., Waxman S. D., Najar-Joa M. Simulations of conduction in uniform myelinated fibers. Relative sensitivity to changes in nodal and internodal parameters. Biophys J. 1978 Feb;21(2):147–160. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85515-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa J., Fowler T. J., Gilliatt R. W. Anatomical changes in peripheral nerves compressed by a pneumatic tourniquet. J Anat. 1972 Dec;113(Pt 3):433–455. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudge P. Tourniquet paralysis with prolonged conduction block. An electro-physiological study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1974 Nov;56-B(4):716–720. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.56B4.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I. New measurements of the capacity and the resistance of the myelin sheath and the nodal membrane of the isolated frog nerve fiber. Am J Physiol. 1955 Jun;181(3):639–650. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.181.3.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojaborg W. Prolonged conduction block with axonal degeneration. An electrophysiological study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Jan;40(1):50–57. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman S. G., Brill M. H. Conduction through demyelinated plaques in multiple sclerosis: computer simulations of facilitation by short internodes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978 May;41(5):408–416. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.41.5.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


