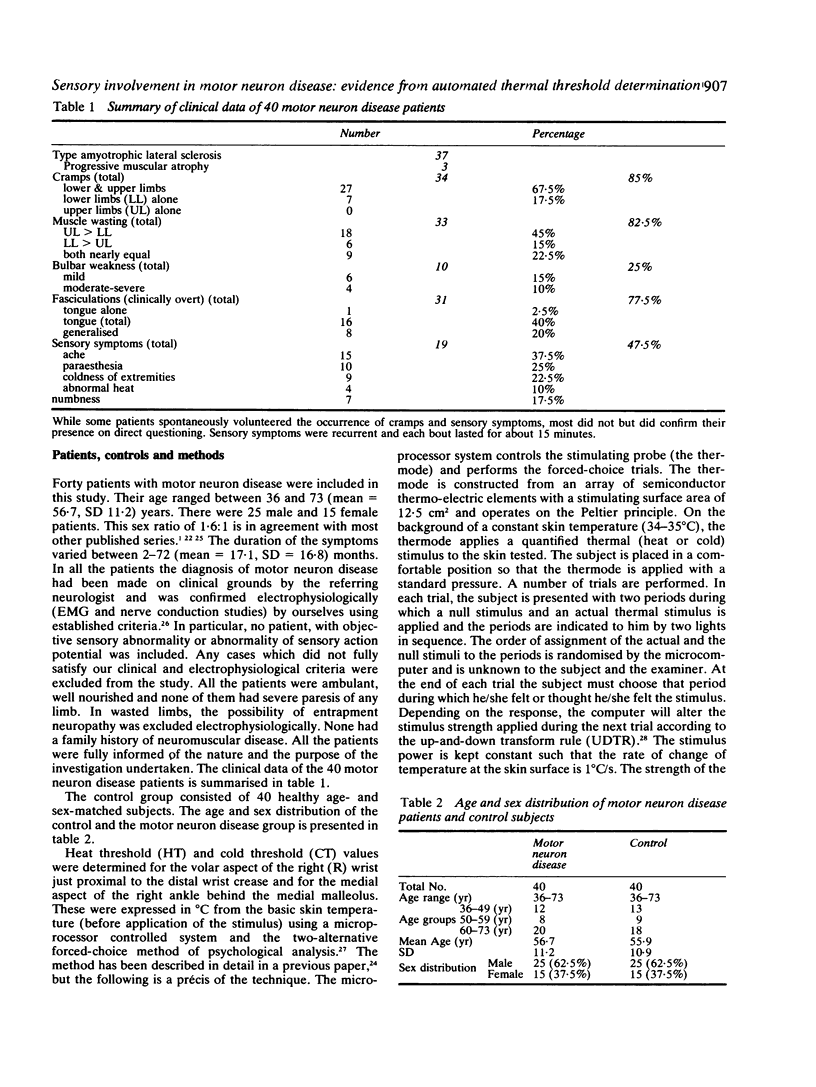
Abstract
Thermal thresholds were determined in 40 patients with motor neuron disease and in 40 age- and sex-matched healthy subjects. The thermal thresholds were estimated on the skin of wrist and ankle using an automated microprocessor controlled system and the "two alternative forced-choice method" of psycholphysical analysis. Abnormalities of thermal thresholds (greater than or equal to 99th percentile) were seen in 80% of the motor neuron disease patients. The results are in agreement with reports of sensory pathway involvement in the literature. Thermal threshold abnormalities are common in motor neuron disease and indicate the involvement of the small fibre afferent pathways.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brownell B., Oppenheimer D. R., Hughes J. T. The central nervous system in motor neurone disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Jun;33(3):338–357. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.3.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayan A. D., Graveson G. S., Illis L. S., Robinson P. K. Schwann cell damage in motoneuron disease. Neurology. 1969 Mar;19(3):242–246. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.3.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake M. E., Jr Chronic pain syndrome in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1983 Jul;40(7):453–454. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1983.04050070083025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck P. J., Stevens J. C., Mulder D. W., Espinosa R. E. Frequency of nerve fiber degeneration of peripheral motor and sensory neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Morphometry of deep and superficial peroneal nerves. Neurology. 1975 Aug;25(8):781–785. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.8.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGEL W. K., KURLAND L. T., KLATZO I. An inherited disease similar to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with a pattern of posterior column involvement. An intermediate form? Brain. 1959 Jun;82:203–220. doi: 10.1093/brain/82.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINCHAM R. W., VANALLEN M. W. SENSORY NERVE CONDUCTION IN AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS. Neurology. 1964 Jan;14:31–33. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN A. P., FREEDMAN D. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1950 Jan;111(1):1–18. doi: 10.1097/00005053-195011110-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson A. J. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and its association with dementia, parkinsonism and other neurological disorders: a review. Brain. 1981 Jun;104(2):217–247. doi: 10.1093/brain/104.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. T., Jerrome D. Ultrastructure of anterior horn motor neurones in the Hirano-Kurland-Sayre type of combined neurological system degeneration. J Neurol Sci. 1971 Aug;13(4):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(71)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura Y., Dyck P. J., Shimono M., Okazaki H., Tateishi J., Doi H. Morphometric comparison of the vulnerability of peripheral motor and sensory neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 Nov;40(6):667–675. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198111000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWYER T., Jr, NETSKY M. G. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1953 Feb;69(2):171–192. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1953.02320260029002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLER R. Progressive motor neuron disease in adults; a clinical study with special reference to the course of the disease. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand. 1952;27(1-2):137–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1952.tb04647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder D. W., Bushek W., Spring E., Karnes J., Dyck P. J. Motor neuron disease (ALS): evaluation of detection thresholds of cutaneous sensation. Neurology. 1983 Dec;33(12):1625–1627. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.12.1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekuler R., Nash D., Armstrong R. Sensitive, objective procedure for evaluating response to light touch. Neurology. 1973 Dec;23(12):1282–1291. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.12.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLISON R. G. Electrodiagnosis in motor neurone disease. Proc R Soc Med. 1962 Dec;55:1024–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


