Abstract
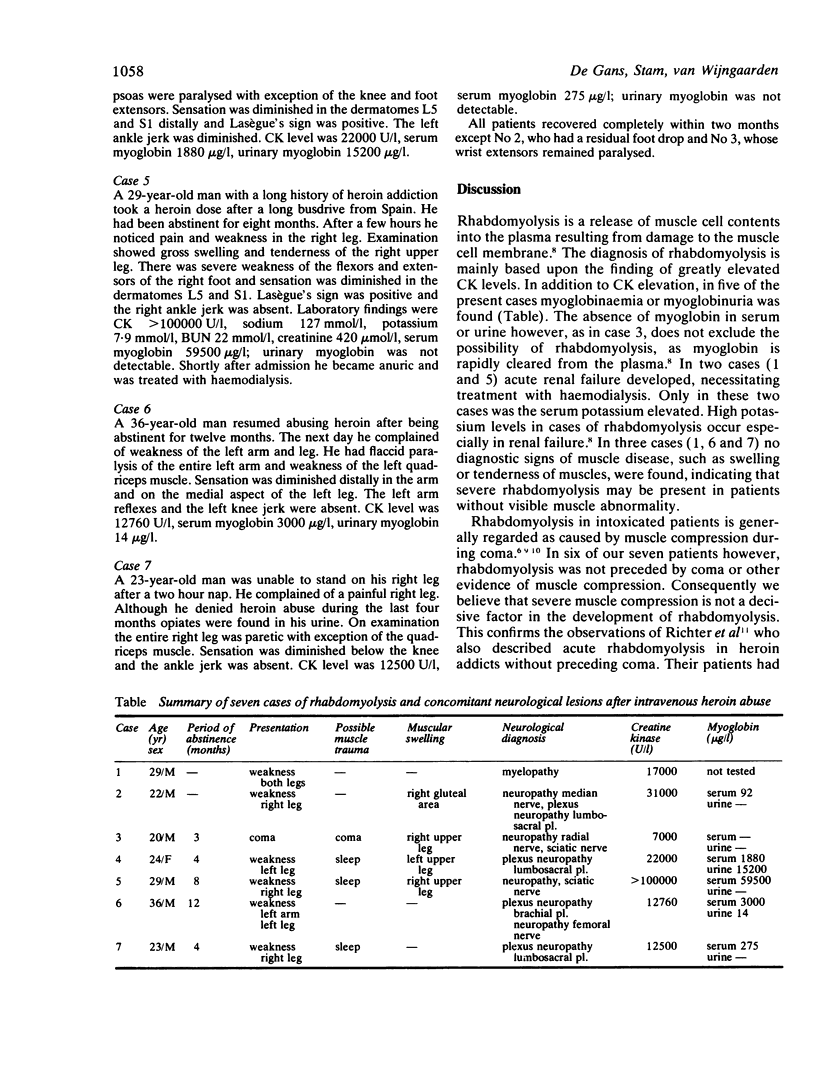
Seven cases of rhabdomyolysis in heroin addicts are presented. All patients showed concomitant neurological symptoms suggesting mononeuropathy, incomplete plexus lesions or myelopathy. In most cases rhabdomyolysis occurred without preceding trauma to the muscles (for example tissue compression or coma). Five patients had a history of recently resumed heroin abuse after prolonged abstinence. An allergic or toxic reaction to heroin or adulterants seems to be more likely than trauma in the pathogenesis of these complications. Severe rhabdomyolysis can occur without visible muscular swelling. Routine screening of creatine kinase is recommended in heroin addicts with neurological complications, as rhabdomyolysis may lead to fatal renal failure and may easily fail to be diagnosed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Challenor Y. B., Richter R. W., Bruun B., Pearson J. Nontraumatic plexitis and heroin addiction. JAMA. 1973 Aug 20;225(8):958–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ell J. J., Uttley D., Silver J. R. Acute myelopathy in association with heroin addiction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 May;44(5):448–450. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.5.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabow P. A., Kaehny W. D., Kelleher S. P. The spectrum of rhabdomyolysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1982 May;61(3):141–152. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198205000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood R. J. Lumbar plexitis and rhabdomyolysis following abuse of heroin. Postgrad Med J. 1974 Dec;50(590):772–773. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.50.590.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacome D. E. Neurogenic bladder, lumbosacral plexus neuropathy and drug-associated rhabdomyolysis. J Urol. 1982 May;127(5):994–995. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)54166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loizou L. A., Boddie H. G. Polyradiculoneuropathy associated with heroin abuse. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978 Sep;41(9):855–857. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.41.9.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louria D. B., Hensle T., Rose J. The major medical complications of heroin addiction. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Jul;67(1):1–22. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn A. S., Rowland L. P., Fraser D. W. Drugs, coma, and myoglobinuria. Arch Neurol. 1972 Apr;26(4):336–343. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490100066006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter R. W., Baden M. M. Neurological complications of heroin addiction. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1969;94:330–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter R. W., Challenor Y. B., Pearson J., Kagen L. J., Hamilton L. L., Ramsey W. H. Acute myoglobinuria associated with heroin addiction. JAMA. 1971 May 17;216(7):1172–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter R. W., Pearson J., Bruun B., Challenor Y. B., Brust J. C., Baden M. M. Neurological complications of addiction to heroin. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1973 Jan;49(1):3–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. N., Liebowitz M. R., Bernstein L. H., Srinivasan K. Limb compression and renal impairment (crush syndrome) complicating narcotic overdose. N Engl J Med. 1971 Feb 18;284(7):368–369. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197102182840708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters E. C., van Wijngaarden G. K., Stam F. C., Rengelink H., Lousberg R. J., Schipper M. E., Verbeeten B. Leucoencephalopathy after inhaling "heroin" pyrolysate. Lancet. 1982 Dec 4;2(8310):1233–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


