Abstract
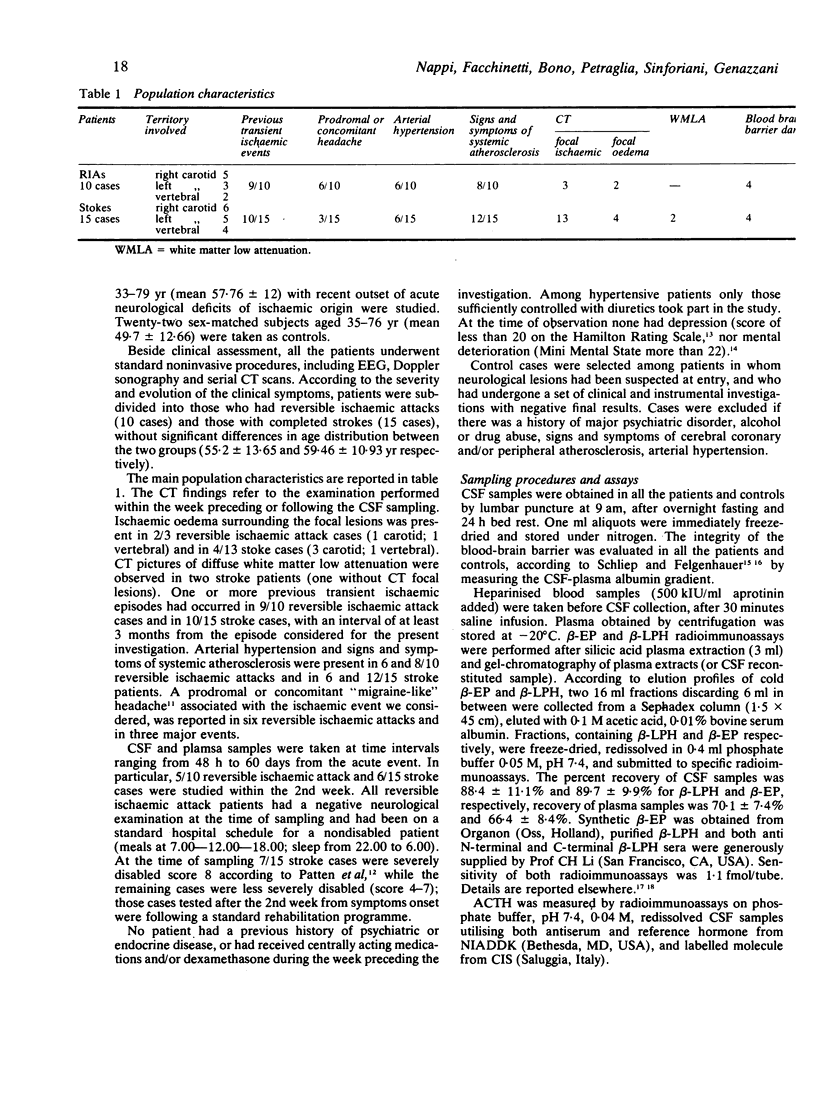
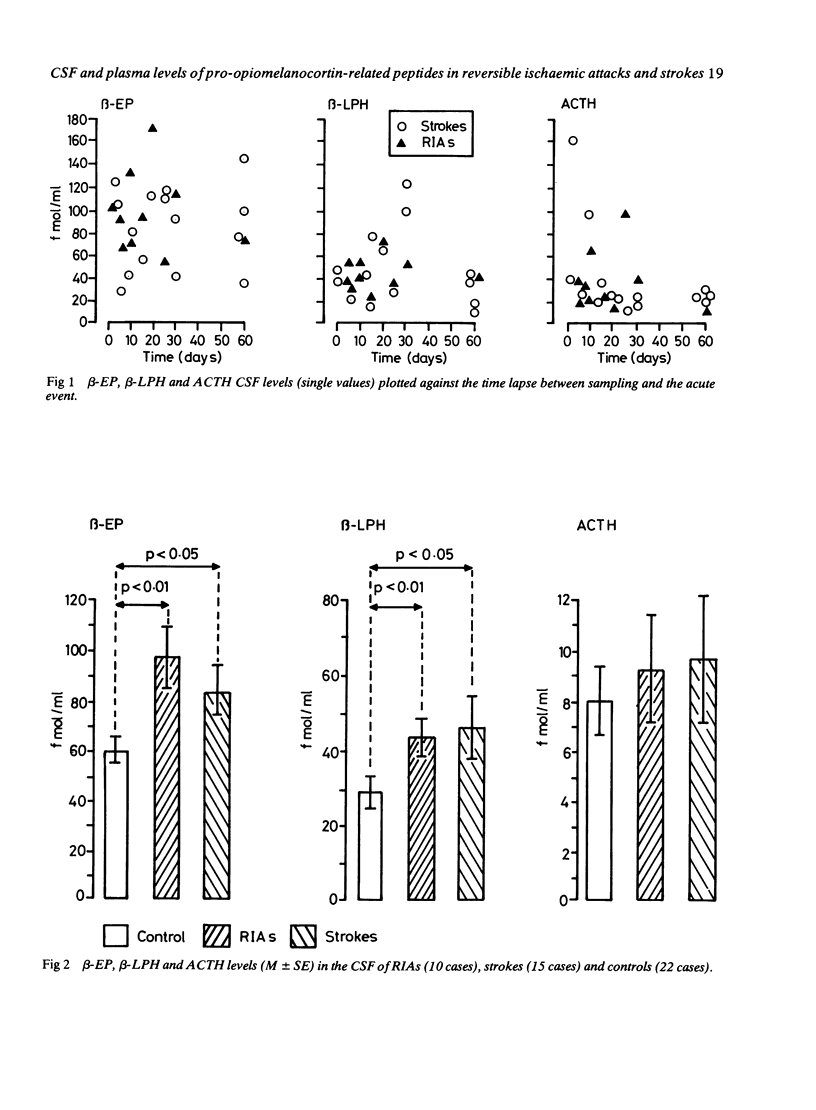
Plasma and CSF beta-endorphin (beta-EP), beta-lipotropin (beta-LPH) and ACTH levels were studied in a group of 25 patients who underwent reversible ischaemic attacks or completed strokes. CSF beta-EP and beta-LPH in ischaemic patients were higher than those of the control population, independently of both clinical reversibility of the cerebral damage, and the time lapse sampling and the acute event. The presence of a CT demonstrable lesion was related to the highest CSF beta-EP levels. These data confirm an involvement of central opioid substances in the phenomena related to brain ischaemia. ACTH levels in the CSF did not differ from the controls; this finding further supports the concept of an independent central secretion of the different pro-opiomelanocortin-related peptides. The peripheral plasma concentrations of beta-EP, beta-LPH and ACTH, were, in contrast, within the normal range, confirming that CSF and plasma contents of pro-opiomelanocortin-related peptides are differently controlled and originate from different sources.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baskin D. S., Kieck C. F., Hosobuchi Y. Naloxone reversal of ischemic neurologic deficits in baboons is not mediated by systemic effects. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 15;31(20-21):2201–2204. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90118-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. R., Bredesen D. E., Edwards R., Simon R. P. Failure of naloxone to reverse vascular neurologic deficits. Neurology. 1983 Nov;33(11):1517–1518. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.11.1517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facchinetti F., Petraglia F., Nappi G., Martignoni E., Antoni G., Parrini D., Genazzani A. R. Different patterns of central and peripheral beta EP, beta LPH and ACTH throughout life. Peptides. 1983 Jul-Aug;4(4):469–474. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(83)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden A. I., Hallenbeck J. M., Brown C. Q. Treatment of experimental stroke: comparison of naloxone and thyrotropin releasing hormone. Neurology. 1982 Oct;32(10):1083–1087. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.10.1083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden A. I. Neuropeptides and stroke: current status and potential application. Stroke. 1983 Mar-Apr;14(2):169–172. doi: 10.1161/01.str.14.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genazzani A. R., Nappi G., Facchinetti F., Mazzella G. L., Parrini D., Sinforiani E., Petraglia F., Savoldi F. Central deficiency of beta-endorphin in alcohol addicts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Sep;55(3):583–586. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-3-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON M. A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1960 Feb;23:56–62. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.23.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosobuchi Y., Baskin D. S., Woo S. K. Reversal of induced ischemic neurologic deficit in gerbils by the opiate antagonist naloxone. Science. 1982 Jan 1;215(4528):69–71. doi: 10.1126/science.6274019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R., Feustel P., Severinghaus J., Hosobuchi Y. Effect of naloxone on neurologic deficit and cortical blood flow during focal cerebral ischemia in cats. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 15;31(20-21):2205–2208. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mrsulja B. B., Mrsulja B. J., Spatz M., Klatzo I. Brain serotonin after experimental vascular occlusion. Neurology. 1976 Aug;26(8):785–787. doi: 10.1212/wnl.26.8.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donohue T. L., Dorsa D. M. The opiomelanotropinergic neuronal and endocrine systems. Peptides. 1982 May-Jun;3(3):353–395. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(82)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patten B. M., Mendell J., Bruun B., Curtin W., Carter S. Double-blind study of the effects of dexamethasone on acute stroke. Neurology. 1972 Apr;22(4):377–383. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petraglia F., Penalva A., Genazzani A. R., Müller E. E. Stimulation of beta-endorphin and beta-lipotropin release from the anterior but not the neurointermediate pituitary lobe in the rat after acute administration of serotonin-acting drugs. Life Sci. 1982 Dec 20;31(25):2809–2817. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90670-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savoldi F., Mazzella G. L., Facchinetti F., Nappi G., Petraglia F., Sinforiani E., Parrini D., Genazzani A. R. Beta-endorphin, beta-lipotropin and adrenocorticotropic hormone levels in cerebrospinal fluid, and brain damage in chronic alcoholics. Eur Neurol. 1983;22(4):265–271. doi: 10.1159/000115570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliep G., Felgenhauer K. Serum-CSF protein gradients, the blood-GSF barrier and the local immune response. J Neurol. 1978 May 18;218(2):77–96. doi: 10.1007/BF02402169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw S. L., Stark R. I., Baxi L., Frantz A. G. Plasma beta-endorphin and beta-lipotropin in the human fetus at delivery: correlation with arterial pH and pO2. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Dec;49(6):888–891. doi: 10.1210/jcem-49-6-888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch K. M., Gaudet R., Wang T. P., Chabi E. Transient cerebral ischemia and brain serotonin: relevance to migraine. Headache. 1977 Sep;17(4):145–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1977.hed1704145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


