Abstract
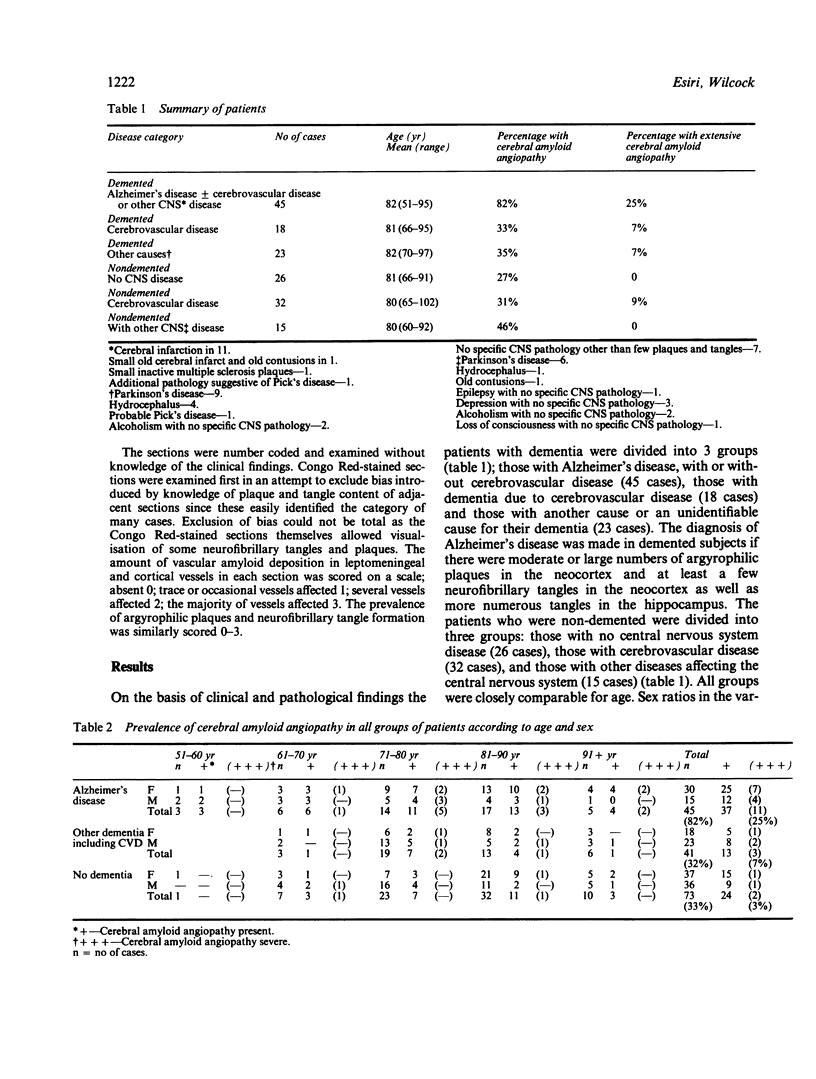
A necropsy study of 159 elderly patients drawn mainly from a prospectively assessed geriatric hospital population was carried out to investigate the relationship of cerebral amyloid angiopathy to Alzheimer's disease, other CNS disease and ageing. About half the patients were demented and the majority of these had Alzheimer's disease. In Alzheimer's disease there was an incidence of cerebral amyloid angiopathy of 82%. Among the other groups of patients, both demented and non-demented, the incidence of cerebral amyloid angiopathy was a little over 30%, and remained constant between 60 and 102 years of age.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chapel H. M., Esiri M. M., Wilcock G. K. Immunoglobulin and other proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer's disease. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jun;37(6):697–699. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.6.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. H., Feiner H., Jensson O., Frangione B. Amyloid fibril in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis (HCHWA) is related to the gastroentero-pancreatic neuroendocrine protein, gamma trace. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):623–628. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove G. R., Leblanc R., Meagher-Villemure K., Ethier R. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology. 1985 May;35(5):625–631. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.5.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. B. Demonstration of neurofibrillary tangles in paraffin sections: a quick and simple method using a modification of Palmgren's method. Med Lab Sci. 1982 Jan;39(1):67–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. J., Vinters H. V. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: incidence and complications in the aging brain. I. Cerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 1983 Nov-Dec;14(6):915–923. doi: 10.1161/01.str.14.6.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. A., Mortimer T. F., Oppenheimer D. R., Spalding J. M. Congophilic angiopathy of the brain: a clinical and pathological report on two siblings. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 May;45(5):396–408. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.5.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb A., Jensson O., Gudmundsson G., Arnason A., Löfberg H., Malm J. Abnormal metabolism of gamma-trace alkaline microprotein. The basic defect in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Dec 13;311(24):1547–1549. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198412133112406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudmundsson G., Hallgrímsson J., Jónasson T. A., Bjarnason O. Hereditary cerebral haemorrhage with amyloidosis. Brain. 1972;95(2):387–404. doi: 10.1093/brain/95.2.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hare M. Clinical check list for diagnosis of dementia. Br Med J. 1978 Jul 22;2(6132):266–267. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6132.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodkinson H. M. Evaluation of a mental test score for assessment of mental impairment in the elderly. Age Ageing. 1972 Nov;1(4):233–238. doi: 10.1093/ageing/1.4.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii N., Nishihara Y., Horie A. Amyloid angiopathy and lobar cerebral haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Nov;47(11):1203–1210. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.11.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinger K. Cerebrovascular amyloidosis with cerebral hemorrhage. J Neurol. 1977 Feb 17;214(3):195–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00316150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalyan-Raman U. P., Kalyan-Raman K. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy causing intracranial hemorrhage. Ann Neurol. 1984 Sep;16(3):321–329. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. S., Stemmermann G. N. Congophilic angiopathy and cerebral hemorrhage. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1978 Jun;102(6):317–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandybur T. I., Bates S. R. Fatal massive intracerebral hemorrhage complicating cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Arch Neurol. 1978 Apr;35(4):246–248. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1978.00500280064014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandybur T. I. The incidence of cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1975 Feb;25(2):120–126. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.2.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimatsu M., Hirai S., Muramatsu A., Yoshikawa M. Senile degenerative brain lesions and dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1975 Sep;23(9):390–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1975.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountjoy C. Q., Tomlinson B. E., Gibson P. H. Amyloid and senile plaques and cerebral blood vessels. A semi-quantitative investigation of a possible relationship. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Nov-Dec;57(1):89–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki H., Reagan T. J., Campbell R. J. Clinicopathologic studies of primary cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Mayo Clin Proc. 1979 Jan;54(1):22–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers J. M., Schlaepfer W. W., Willingham M. C., Hall B. J. An immunoperoxidase study of senile cerebral amyloidosis with pathogenetic considerations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 Nov;40(6):592–612. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198111000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torack R. M. Congophilic angiopathy complicated by surgery and massive hemorrhage. A light and electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1975 Nov;81(2):349–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinters H. V., Gilbert J. J. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: incidence and complications in the aging brain. II. The distribution of amyloid vascular changes. Stroke. 1983 Nov-Dec;14(6):924–928. doi: 10.1161/01.str.14.6.924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcock G. K., Esiri M. M., Bowen D. M., Smith C. C. The nucleus basalis in Alzheimer's disease: cell counts and cortical biochemistry. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1983 May-Jun;9(3):175–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1983.tb00105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcock G. K., Esiri M. M. Plaques, tangles and dementia. A quantitative study. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Nov;56(2-3):343–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


