Abstract
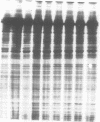
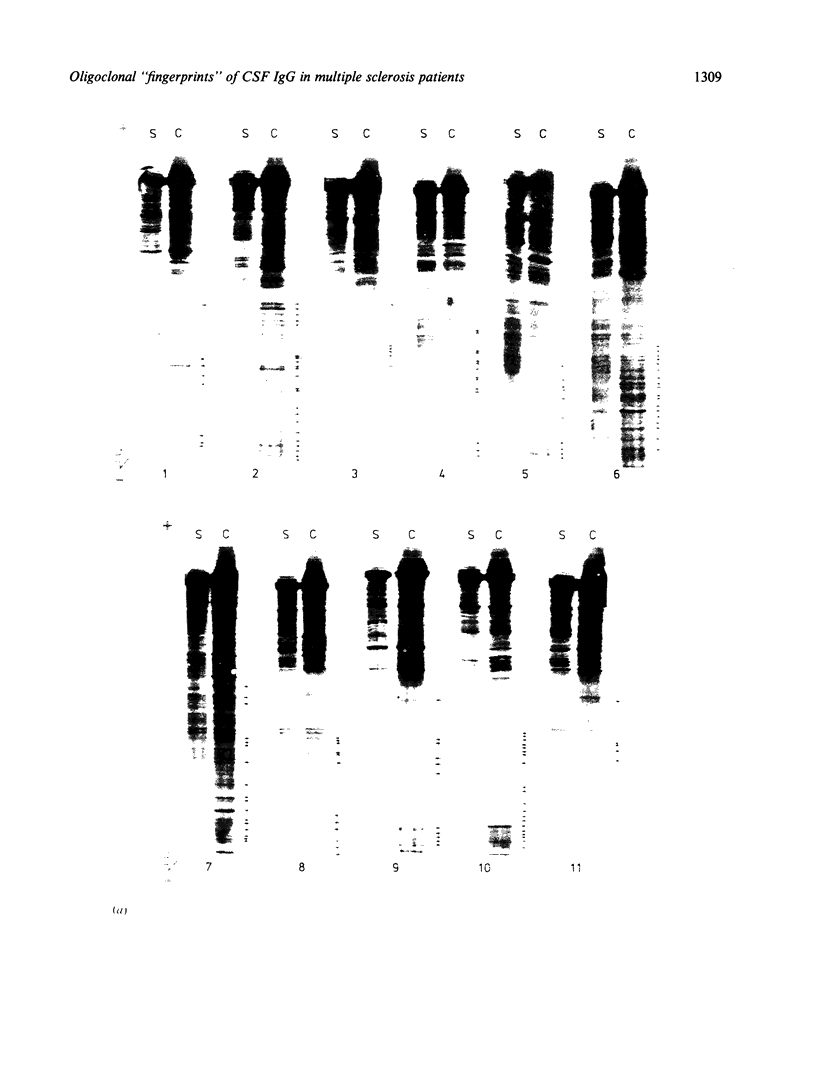
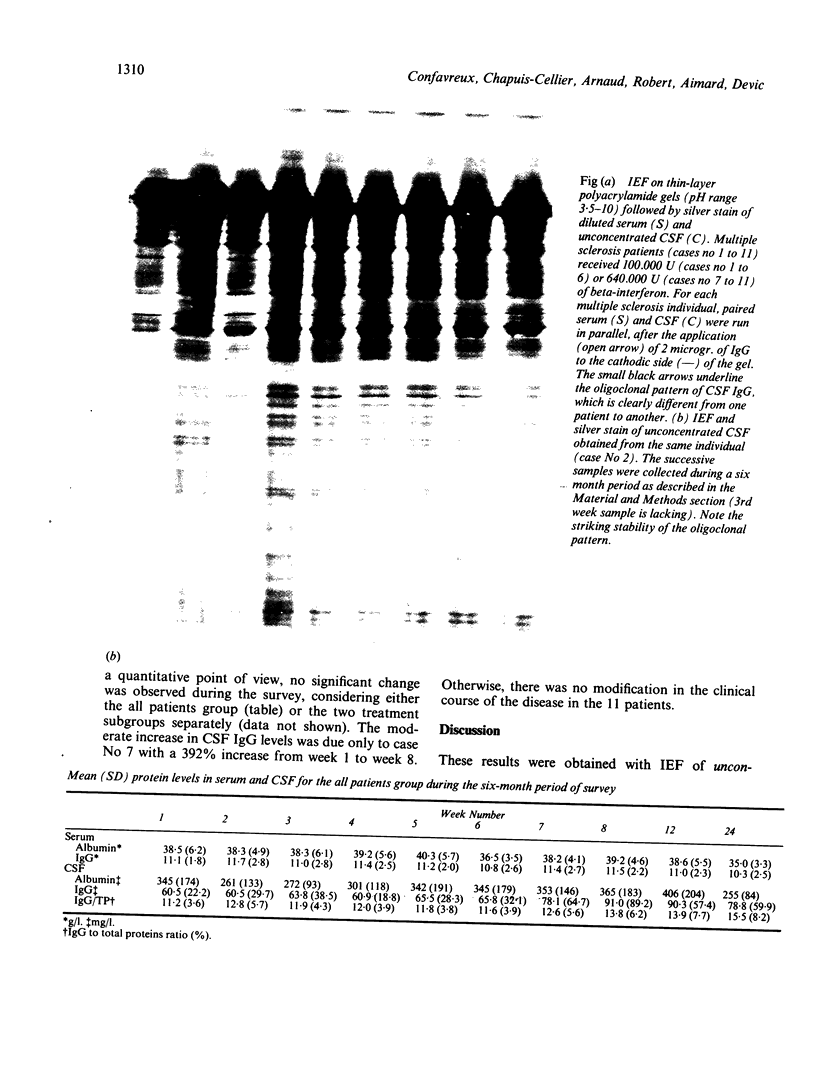
The IgG pattern in CSF was studied in 11 patients with multiple sclerosis who exhibited an oligoclonal banding upon thin-layer polyacrylamide gel isoelectric focusing followed by silver stain of unconcentrated CSF. Each patient received beta-interferon intrathecally during a 2 month period. No modification was observed over a 6 month period. In addition, the oligoclonal pattern was remarkably unique for each individual representing a typical "fingerprint" which allowed the identification of any single CSF.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Confavreux C., Aimard G., Devic M. Course and prognosis of multiple sclerosis assessed by the computerized data processing of 349 patients. Brain. 1980 Jun;103(2):281–300. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmotte P., Gonsette R. Biochemical findings in multiple sclerosis IV. Isoelectric focusing of the CSF gamma globulins in multiple sclerosis (262 cases) and other neurological diseases (272 cases). J Neurol. 1977 Apr 28;215(1):27–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00312547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell M. A., Kaufmann J. C., Gilbert J. J., Noseworthy J. H., Armstrong H. A., Ebers G. C. Oligoclonal bands in multiple sclerosis: clinical-pathologic correlation. Neurology. 1985 Feb;35(2):212–218. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.2.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey L. A., Trotter J. L. The use and abuse of the cerebrospinal fluid IgG profile in the adult: a practical evaluation. Ann Neurol. 1980 Oct;8(4):426–434. doi: 10.1002/ana.410080415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holness R. O., Shlossberg A. H., Heffernan L. P. Cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea caused by bromocriptine therapy of prolactinoma. Neurology. 1984 Jan;34(1):111–113. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.1.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. M., Litman N., Miller M. H. Sinusitis: induced subdural empyema. Neurology. 1983 Feb;33(2):123–132. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.2.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H. Immunoglobulin G and low molecular weight proteins in human cerebrospinal fluid. Chemical and immunological characterisation with special reference to multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1967;43(Suppl):1–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livrea P., Trojano M., Simone I. L., Zimatore G. B., Lamontanara G., Leante R. Intrathecal IgG synthesis in multiple sclerosis: comparison between isoelectric focusing and quantitative estimation of cerebrospinal fluid IgG. J Neurol. 1981;224(3):159–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00313278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson D. H., Roos R. P., Arnason B. G. Comparison of agar gel electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing in multiple sclerosis and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Ann Neurol. 1981 Jan;9(1):34–41. doi: 10.1002/ana.410090107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J. E., Link H. Immunoglobulin abnormalities in multiple sclerosis. Relation to clinical parameters: exacerbations and remissions. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jun;28(6):392–399. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490240052009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg-Wollheim M. Optic neuritis: studies on the cerebrospinal fluid in relation to clinical course in 61 patients. Acta Neurol Scand. 1975 Sep;52(3):167–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1975.tb05771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoulson I., Fahn S. Huntington disease: clinical care and evaluation. Neurology. 1979 Jan;29(1):1–3. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidén A., Kjellin K. G. CSF protein examinations with thin-layer isoelectric focusing in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Nov;39(1):131–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. J., Kaufmann P., Rudge P. Sequential changes in oligoclonal patterns during the course of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Jun;46(6):547–550. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.6.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. J. Laboratory diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: immunological and biochemical aspects. Br Med Bull. 1977 Jan;33(1):28–33. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]