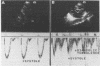
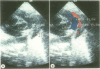
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Drayton M. R., Skidmore R. Ductus arteriosus blood flow during first 48 hours of life. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Oct;62(10):1030–1034. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.10.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans N. J., Archer L. N. Postnatal circulatory adaptation in healthy term and preterm neonates. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Jan;65(1 Spec No):24–26. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.1_spec_no.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans N., Moorcraft J. Effect of patency of the ductus arteriosus on blood pressure in very preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Oct;67(10 Spec No):1169–1173. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.10_spec_no.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentile R., Stevenson G., Dooley T., Franklin D., Kawabori I., Pearlman A. Pulsed Doppler echocardiographic determination of time of ductal closure in normal newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1981 Mar;98(3):443–448. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80719-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gersony W. M., Peckham G. J., Ellison R. C., Miettinen O. S., Nadas A. S. Effects of indomethacin in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus: results of a national collaborative study. J Pediatr. 1983 Jun;102(6):895–906. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerman C., Strates E., Valaitis S. The silent ductus: its precursors and its aftermath. Pediatr Cardiol. 1986;7(3):121–127. doi: 10.1007/BF02424985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. B., Rausch J., Friedman W. F., Hirschklau M. J., Kirkpatrick S. E., Goergen T. G., Reinke R. T. Patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants with idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome. Radiographic and echocardiographic evaluation. Radiology. 1977 Jul;124(1):189–195. doi: 10.1148/124.1.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata T., Wolfe S. B., Popp R. L., Helmen C. H., Feigenbaum H. Estimation of left atrial size using ultrasound. Am Heart J. 1969 Jul;78(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(69)90257-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschklau M. J., DiSessa T. G., Higgins C. B., Friedman W. F. Echocardiographic diagnosis: pitfalls in the premature infant with a large patent ductus arteriosus. J Pediatr. 1978 Mar;92(3):474–477. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80452-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhta J. C., Cohen M., Gutgesell H. P. Patency of the ductus arteriosus in normal neonates: two-dimensional echocardiography versus Doppler assessment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1984 Sep;4(3):561–564. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(84)80102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarmakani M. M., Graham T. P., Jr, Canent R. V., Jr, Spach M. S., Capp M. P. Effect of site of shunt on left heart-volume characteristics in children with ventricular septal defect and patent ductus arteriosus. Circulation. 1969 Sep;40(3):411–418. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.40.3.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. L., Breart G. L., Gewitz M. H., Brenner J. I., Lang P., Dooley K. J., Ellison R. C. Echocardiographic characteristics of premature infants with patient ductus arteriosus. Pediatrics. 1983 Dec;72(6):864–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupferschmid C., Lang D., Pohlandt F. Sensitivity, specificity and predictive value of clinical findings, m-mode echocardiography and continuous-wave Doppler sonography in the diagnosis of symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Apr;147(3):279–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00442695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelbaum-Isken V. H., Linderkamp O. Cardiac output by pulsed Doppler in neonates using the apical window. Pediatr Cardiol. 1991 Jan;12(1):13–16. doi: 10.1007/BF02238491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellander M., Larsson L. E., Ekström-Jodal B., Sabel K. G. Prediction of symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants using Doppler and M-mode echocardiography. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1987 Jul;76(4):553–559. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1987.tb10520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellander M., Sabel K. G., Caidahl K., Solymar L., Eriksson B. Doppler determination of cardiac output in infants and children: comparison with simultaneous thermodilution. Pediatr Cardiol. 1987;8(4):241–246. doi: 10.1007/BF02427536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner I., Perelmuter B., Toews W., Whitfield J. Association of low systolic and diastolic blood pressure with significant patent ductus arteriosus in the very low birth weight infant. Crit Care Med. 1985 Jun;13(6):497–500. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198506000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller M. D., Ziegler M. L., Rice M. J., Solin R. C., McDonald R. W. Duration of ductal shunting in healthy preterm infants: an echocardiographic color flow Doppler study. J Pediatr. 1988 Mar;112(3):441–446. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahn D. J., Vaucher Y., Williams D. E., Allen H. D., Goldberg S. J., Friedman W. F. Echocardiographic detection of large left to right shunts and cardiomyopathies in infants and children. Am J Cardiol. 1976 Jul;38(1):73–79. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(76)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serwer G. A., Armstrong B. E., Anderson P. A. Continuous wave Doppler ultrasonographic quantitation of patent ductus arteriosus flow. J Pediatr. 1982 Feb;100(2):297–299. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80658-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman N. H., Lewis A. B., Heymann M. A., Rudolph A. M. Echocardiographic assessment of ductus arteriosus shunt in premature infants. Circulation. 1974 Oct;50(4):821–825. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.50.4.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson J. G., Kawabori I., Guntheroth W. G. Pulsed Doppler echocardiographic diagnosis of patent ductus arteriosus: sensitivity, specificity, limitations, and technical features. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1980;6(3):255–263. doi: 10.1002/ccd.1810060306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdes-Cruz L. M., Dudell G. G. Specificity and accuracy of echocardiographic and clinical criteria for diagnosis of patent ductus arteriosus in fluid-restricted infants. J Pediatr. 1981 Feb;98(2):298–305. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80665-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vick G. W., 3rd, Huhta J. C., Gutgesell H. P. Assessment of the ductus arteriosus in preterm infants utilizing suprasternal two-dimensional/Doppler echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985 Apr;5(4):973–977. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(85)80442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther F. J., Kim D. H., Ebrahimi M., Siassi B. Pulsed Doppler measurement of left ventricular output as early predictor of symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus in very preterm infants. Biol Neonate. 1989;56(3):121–128. doi: 10.1159/000243112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou T. F., Guntheroth W. G. Valve-incompetent foramen ovale in premature infants with ductus arteriosus: a Doppler echocardiographic study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987 Jul;10(1):193–199. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(87)80179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]