Abstract
Aggregation of the Tar DNA-binding protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43) is a pathological hallmark of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia and likely contributes to disease by loss of nuclear function. Analysis of TDP-43 function in knockout zebrafish identified an endothelial directional migration and hypersprouting phenotype during development prior lethality. In human umbilical vein cells (HUVEC) the loss of TDP-43 leads to hyperbranching. We identified elevated expression of FIBRONECTIN 1 (FN1), the VASCULAR CELL ADHESION MOLECULE 1 (VCAM1), as well as their receptor INTEGRIN α4β1 (ITGA4B1) in HUVEC cells. Importantly, reducing the levels of ITGA4, FN1, and VCAM1 homologues in the TDP-43 loss-of-function zebrafish rescues the angiogenic defects indicating the conservation of human and zebrafish TDP-43 function during angiogenesis. Our study identifies a novel pathway regulated by TDP-43 important for angiogenesis during development.
Keywords: TDP-43, angiogenesis, neurodegeneration, zebrafish, ALS
Introduction
Aggregation of TDP-43 into stable inclusions accompanied by nuclear clearing of TDP-43 is the most prominent pathological characteristic of FTD and ALS (Neumann et al., 2006). TDP-43 delocalization and aggregation is thought to compromise TDP-43 function in the nucleus, ultimately leading to neurodegeneration. Addressing this hypothesis in vivo, loss-of-function animal models have been generated to investigate the physiological function of TDP-43 (Xu, 2012). Loss of TDP-43 is lethal in flies, zebrafish, and mice (Feiguin et al., 2009; Kraemer et al., 2010; Sephton et al., 2010; Wu et al., 2010; Schmid et al., 2013) challenging the identification of regulated pathways of TDP-43 in vivo. Conditional global knockout of TDP-43 in adult mice is lethal after 9 days of TDP-43 inactivation (Chiang et al., 2010) and cell-type specific TDP-43 knockout in motor neurons causes ALS-like motor neuron death (Wu et al., 2012; Iguchi et al., 2013), but the cause of death in these models remains unclear.
We previously generated a loss-of-function mutant for the human TDP-43 gene (TARDBP) encoding zebrafish orthologues, tardbp and tardbp-like (tardbpl) (Schmid et al., 2013). Homozygous loss of either tardbp or tardbpl does not cause any phenotype due to compensation by the other orthologous gene (Hewamadduma et al., 2013; Schmid et al., 2013). In contrast, the double homozygous mutants are affected by multiple defects, including reduced outgrowth of motor neurons, degeneration of muscle cells, as well as mis-patterning and non-perfusion of blood vessels, which together ultimately leads to early death at about 6–8 days post fertilization (dpf) (Schmid et al., 2013). The mutant vascular mis-patterning phenotype is very severe and is the first visible phenotype during development in the mutants. A growing body of evidence links vascular dysfunction to neurodegeneration (Zacchigna et al., 2008; Zlokovic, 2008), which prompted us to identify the molecular mechanism leading to the vascular phenotype in loss-of-function mutants of the ALS/FTLD gene tardbp. Given the large overlap in growth and guidance of the vasculature and neurons during development (Carmeliet and Tessier-Lavigne, 2005; Quaegebeur et al., 2011), these changes of pathways in the endothelium of TDP-43 mutants might be also essential in motor neurons and of relevance in ALS.
We therefore aimed at identifying the molecular pathways by which TDP-43 regulates angiogenic sprouting. First, we characterized a vascular mis-patterning phenotype upon loss of TDP-43 in zebrafish and human derived endothelial cells (ECs). Second, we identified de-regulated genes mediating the vascular TDP-43 deficient phenotype by conducting next-generation RNA sequencing (NGS) in TDP-43 knockdown (KD) HUVEC. Third, we rescue the zebrafish phenotypes by reducing the levels of Vcam1, Fn, and Itgα4 in TDP-43 knockout zebrafish. Lastly, we identified FN1 as a direct RNA target of TDP-43 in HUVEC by performing iCLIP experiments.
Materials and methods
Zebrafish
Zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio) were kept at 28.5°C and were staged according to Kimmel et al. (1995). The wild type line AB was used for all experiments unless stated otherwise. All experiments were performed in accordance with animal protection standards of the DZNE and were approved by the government of Upper Bavaria (Regierung von Oberbayern, Munich, Germany).
The following mutant and transgenic alleles were used: tardbp mde198−/− (Schmid et al., 2013); tardbp mde159−/− (Schmid et al., 2013); tardbpl mde222−/− (Schmid et al., 2013); Tg (fli1:EGFP)y1 (Roman et al., 2002); Tg (fli1:nlsEGFP)y7 (Roman et al., 2002); Tg (kdrl:HRAS-mCherry)s896 (Chi et al., 2008).
In situ hybridization
Whole mount in situ hybridization was performed as previously described (Schmid et al., 2013). The in situ probes used were previously described: ephrin B2a (Lawson et al., 2001), flt4 (Lawson et al., 2001), mflt1 (Bussmann et al., 2007), plxnD1 (Torres-Vazquez et al., 2004), sema3aa (Yee et al., 1999), sema3ab (Torres-Vazquez et al., 2004). A 1 Kb fragment from the sflt1 3′ UTR has been amplified by PCR from embryonic cDNA (forward primer: sflt1 3’ UTR/reverse primer: flt1-UTR) and subcloned to generate the plasmid pCS2+GW-A + sflt1-UTR for antisense probe generation.
Zebrafish immunohistochemistry
Embryos were fixed overnight (ON) at 4°C for 4 h at room temperature (RT). Next, they were rinsed 1x with PBS and washed three times for 5 min with PBST (PBS-Tween) at RT. For co-staining of 24 hpf Tg (fli1:EGFP)y1 embryos with antibodies specific for GFP and α-dystroglycan, embryos were treated with a methanol series of 30%, 60%, and 100% methanol in PBST for 5 min at RT. The samples were then stored ON or longer in 100% methanol at −20°C. Prior to the staining the embryos were rehydrated by a reverse methanol series of 60% and 30% methanol in PBST for 5 min at RT. Afterwards, the samples were washed three times for 5 min in PBST at RT. The embryos were blocked for 1 h in 10% NCST (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, United States). Incubation with primary antibodies was conducted at 4°C ON. On the next day, samples were rinsed with PBST and washed four times for 30 min in PBST at RT. Then they were blocked two times for 30 min in NCST. Secondary antibodies were used at a dilution of 1:500 in NCST and incubated at 4°C ON. The secondary antibodies were removed and the samples rinsed once with PBST followed by at least three washing steps for 15 min in PBST. The stained embryos were kept at 4°C in PBST or PBS until imaging with the spinning disk or confocal microscopes (Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
Morpholino injections
All morpholinos (MO) were purchased from Gene Tools (Philomath, OR, United States). Approximately 2 nL of MO were microinjected into fertilized zebrafish eggs at the 1 cell stage into the yolk.
| Name | Sequence | Concentration |
|---|---|---|
| tardbp-5′UTR | CAATAAACAACTGCTCGGGTCCAGT | 0.5 mM |
| tardbp-ATG | CTCGAATGTACATCTCGGCCATCTT | 0.5 mM |
| tardbp-e3i3 | TTTTACCTGCACCATGATGACTTCC | 0.5 mM |
| tardbpl-ATG | ATAGCACTCCGTCATGATTACACCG | 0.5 mM |
| tardbpl-e2i2 | CTAACCTGCACCATGATCACCTCTC | 0.5 mM |
| vcam1-e1i1 | CTAACAGATGAAACTTACCTGCAAC | 0.75 mM |
| itga4 -e2i2 | GTAATGGAGGGAAAACCTACCAACA | 0.5 mM |
| itgaV -ATG | CGGACGAAGTGTTTGCCCATGTTTT | 1 mM |
| was previously described (Liu et al., 2012) | ||
| fn1a mo1 [162] | TTTTTTCACAGGTGCGATTGAACAC | 0.75 mM |
| was previously described (Trinh and Stainier, 2004) | ||
| itga5-5′UTR [165] | TAACCGATVTATCAAAATCCACTGC | 0.5 mM |
| fn1b mo1 [165] | TACTGACTCACGGGTCATTTTCACC | 0.5 mM |
| fn1b mo2 [165] | GCTTCTGGCTTTGACTGTATTTCGG | 0.5 mM |
itga5-5′UTR and fn1b morpholinos were previously described (Julich et al., 2005).
Primer for KD validation of successful itgα4 and vcam1 KD.
KS A53 dr-itga4-Ex17-18 F AGGTTTCTGCTCGTTTGGTT
KS A54 dr-itga4-3UTR R CTTTCATGCTTGGGCACATA
KS A55 dr-vcam1-ex1-2 F GCTTTCTTGCTGACTTTGCT
KS A56 dr-vcam1-ex1-2 R GCATCTCAGCTCATTCCTGTC
Cell transplantation
The transplantation experiments were conducted as previously described (Kemp et al., 2009). Coinjection of 3% dextran cascade blue (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, United States) was used to label donor derived cells. In 3 independent transplantation experiments a total of 96 donors and recipients survived. n = 4 wild type and n = 4 mutant donors with EC labeling transplanted in wild type recipients were scored.
Antibodies
β-tubulin, T6199 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, United States), WB: 1:10,000
AKT, 9272 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States), WB: 1:1,000
Alexa Fluor 405 anti-mouse, A-31553 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States), IF 1:500
Alexa Fluor 405 anti-rabbit, A-31556 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States), IF 1:500
Alexa Fluor 488 anti-mouse, A-11029 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States), IF 1:500
Alexa Fluor 488 anti-rabbit, A-11034 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States), IF 1:500
Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated Isolectin-B4, I21411 (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, United States), IF: 1:300
Alexa Fluor 568 anti-rabbit, A-11011 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States), IF 1:500
Alexa Fluor 622 anti-rabbit, A-21070 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States), IF 1:500
anti-rabbit-HRP, W401B (Promega, Madison, WI, United States), WB 1: 10,000
anti-mouse-HRP, W402B (Promega, Madison, WI, United States), WB 1:5,000
α-dystroglycan, NCL-b-DG (Leica Biosystems, Nußloch, Germany), IF: 1:50
Calnexin, SPA-860 (Stressgen, Victoria, BC, Canada), WB: 1:10,000
ERK1/2, 9102 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States), WB: 1:2000
Fibronectin, HPA027066 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, United States), WB: 1:500
GFP, 632375 (Clontech, Danvers, MA, United States), IF: 1:500
GFP, 632592 (Clontech, Danvers, MA, United States), IF: 1:500
Integrin α4, 8440 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States), WB: 1:1,000
Integrin β1, 610467 (BD, Franklin Lakes, NJ, United States), WB: 1:2000
Tardbp, 4A12-111 (Helmholtz Center, Munich, Germany), WB: 1:1 (Schmid et al., 2013)
TDP-43 N-term, SAB4200006 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, United States), WB: 1:10,000–1:50,000
p38, 9212 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States), WB: 1:1,000
pAKT, 9271 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States), WB: 1:500
pERK1/2, 9101 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States), WB: 1:2000
PLCG1, sc-426 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, United States), WB: 1:200
p-p38, 9211 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States), WB: 1:1,000
pPLCG1, SAB4300082 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, United States), WB: 1:500
pPI3K, 4228 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States), WB: 1:1,000
pVEGFR2, 2478 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States), WB: 1:1,000
VEGFR2, 9698 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, United States), WB: 1:1,000
Western blot analysis
Zebrafish embryos were lysed in 10–15 μL Laemmli buffer per embryo, homogenized, and heated at 95°C for 5 min. Lysates were centrifuged at 13,000 rpm and supernatant was loaded on a 12% SDS-PAGE gels (7% gels for VEGFR2 and PLCG1) and transferred to a PVDF membrane (Merck Millipore, Burlington, MA, United States) for 70 min at 400 mA. Membranes were blocked in 3% milk powder (Carl Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany), membranes for phosphorylated epitopes were blocked in 0.2% I-Block (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, United States), and membranes for FN1 were blocked in 5% BSA (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, United States) for 60 min at RT. Incubation of primary antibody was performed ON at 4°C followed by 4 PBST washes and incubation in secondary antibody for 1 h at RT. After 6 washes with PBST membranes were developed with ECL Plus (Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States). The intensity of the bands was quantified using ImageJ. Each protein of interest was normalized to calnexin and significant changes between shCtr and shTARDBP determined by paired t-test analysis (n = 3).
shRNAS
| shCtr sense | gatccccCGTACGCGGAATACTTCGAttcaagaga |
| TCGAAGTATTCCGCGTACGtttttggaaa | |
| shCtr antisense | tttccaaaaaCGTACGCGGAATACTTCGAtctcttgaa |
| TCGAAGTATTCCGCGTACGggggatc | |
| shTARDBP #1 sense | gatccccGGAGAGGACTTGATCATTAttcaagaga |
| TAATGATCAAGTCCTCTCCtttttggaaa | |
| shTARDBP #1 antisense | tttccaaaaaGGAGAGGACTTGATCATTAtctcttgaa |
| TAATGATCAAGTCCTCTCCggggatc | |
| shTARDBP #2 sense | gatccccGGGTATGATGGGCATGTTAttcaagaga |
| TAACATGCCCATCATACCCtttttggaaa | |
| shTARDBP #2 antisense | gggCCCATACTACCCGTACAATaagttctct |
| ATTGTACGGGTAGTATGGGaaaaaccttttcga |
Chemical treatment of zebrafish
The treatment with chemical inhibitors was performed prior to outgrowth of ISA and it was hence not possible to differentiate tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− embryos from their wild type siblings at this stage, tardbp−/−;Tardbpl KD and their control MO injected tardbp −/− siblings were used for testing the rescue potential of the applied chemical inhibitors. The VEGFR2 inhibitor DMH4 (Tocris Bioscience, Bristol, United Kingdom, 4,471) was applied at the 16- to 17-somite stage in different concentrations: 0.1, 0.5, and 2.5 μM. 1% DMSO served as a negative control. Embryos were kept till they reached the required developmental stage that was determined by status of ISA growth according to (Isogai et al., 2003). Next, they were fixed in 4% PFA ON at 4°C and imaged by confocal or spinning disk microscopes (Zeiss, Jena, Germany) at ×25 magnification.
Reverse transcription and quantitative PCR
Total RNA was extracted using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) or TRIzol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States) according to the manufacturer’s protocol and reverse transcribed with random hexanucleotide primers using the M-MLV Reverse Transcription kit (Invitrogen) with RiboLock RNase inhibitor (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States). The complementary DNA was amplified using qPCR SsoFast Evagreen Supermix (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, United States) and analyzed in the C1000 Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad). Each reaction was conducted as technical triplicates with at least 3 biological replicates. The relative expression of each gene was calculated using the ΔΔCT-method and the normalized fold expression was calculated by normalization to the reference genes rpl13a and elf1a2.
The following primers were used for qPCR.
| oA03 β-actin F | TGTTTTCCCCTCCATTGTTGG |
| oA04 β -actin R | TTCTCCTTGATGTCACGGAC |
| KS A1 sema3ab_I1_F | AACGTACCCCGGCTTAAACT |
| KS A2 sema3ab_I1_R | GCAGAGCTGTTAGCCAATCC |
| KS A3 sema3aa_I1_R | TCCATCAGGAACGTGTCGTA |
| KS A4 sema3aa_I3_F | CTTCCAAACGCGATGAATG |
| KS A5 Vegfr2_I11_F | TCCTCTTCCCATTGAAAACG |
| KS A6 Vegfr2_I11_R | CTGTTTTCACCACCAGGGTA |
| KS A7 mflt_I24_F | TGGTCATATGGAGTCCTGCTC |
| KS A8 mflt_I24_R | AGGAGAACACATCCGAGTGC |
| KS A9 sflt_E10-11c_F | GTCCCACCACCTCAAATCC |
| KS A10 sflt_E10-11c_R | GGCCCACAACTCCACTCTC |
| KS A11 Rpl13a_E3-4a_F | ATTGTGGTGGTGAGGTGTGA |
| KS A12 Rpl13a_E3-4a_R | CATTCTCTTGCGGAGGAAAG |
| KS A13 elf1a2 F | AGCAGCAGCTGAGGAGTGAT |
| KS A14 elf1a2 R | GTGGTGGACTTTCCGGAGT |
| KS A43 dr-vcam1 ex9-10 F | CAAACGACCTGGGTTACGAA |
| KS A44 dr-vcam1-ex9-10 R | CAGCAGAACCTCCCAAGAAA |
| KS A45 dr-itga4-ex2-3 F | TGCAGTATGTTGAACAGCCAG |
| KS A46 dr-itga4-ex2-3 R | CAAACTCACACCCAGCCAC |
| KS A47 dr-fn1a-ex3-4 F | TGTACTTGCATTGGCTCTGC |
| KS A48 dr-fn1a-ex3-4 R | GTCTCTGCCATGTGTCTCCA |
| KS A49 dr-fn1b-ex39-40 F | CATTGCCCTTCTGAATAACCA |
| KS A50 dr-fn1b-ex39-40 R | ATGACTGGGCAGGCTAGGTA |
HUVEC
HUVEC were purchased from PromoCell (Heidelberg, Germany) and cultured in 50% Endothelial Cell Basal Medium (PromoCell, Heidelberg, Germany) and 50% Medium 199 (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, United States) with 20% FCS. VEGF-A stimulation was performed 5 days post transduction with 25 ng/μL VEGF-A for 0, 5, 15, or 30 min at 37°C and 5% CO2 respectively. The cells were subsequently washed twice with ice cold PBS and further processed with RIPA with 1x phosphatase and protease inhibitor for SDS-PAGE or TRIZOL for RNA analysis.
For virus transduction, cells were grown to 80% confluence and detached with Trypsin/EDTA. They were seeded and transduced with virus containing either the sequence coding for shCtr, shTARDBP #1, or shTARDBP #2 on the following day with 25 μL virus mix (described below) per 10 mL culture volume in a 10 cm dish.
The Tube formation assay was performed on the artificial extracellular matrix Geltrex (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States) according to the manufacturer’s protocol “Endothelial Tube formation assay (in vitro Angiogenesis)”.
Virus production
For virus production, HEK 293-FT cells were used as packaging cells at low passage number and only grown to 60%–70% confluence in 10 cm dishes. One day after the last passaging, cells were transfected with three different constructs, two that code for the lentiviral particles (pVSVg and pSPAX) and with the construct of interest. Before transfection, medium was replaced by 5 mL pre-warmed Optimem (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States) with 10% FCS. Then, per three 10 cm dishes to be transfected, 108 μL Lipofectamin 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States) was mixed with 4,500 μL Optimem (L2K) and incubated for 5 min. The transfection mix contains 18.6 μg of the construct of interest, 11.0 μg pSPAX2, and 6.4 μg pVSVg with 4,500 μL Optimem. This mix was combined with the L2K and incubated for 20 min at RT. Finally, 3 mL per mix was added to one 10 cm dish. Next day, media were replaced by 10 mL high packaging media (1% penicillin/streptomycin, 1% NEAA and 10% FCS in DMEM Glutamax (all from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States). On the second day after transfection, the supernatant of three 10 cm dishes containing virus with the same sequence of interest was pooled in 50 mL tubes and centrifuged for 5 min at 2000 rpm to remove debris. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.45 μm PES membrane filter (Whatman, Little Chalfont, Buckinghamshire, United Kingdom) into 28SW ultracentrifuge tubes. The virus particles were ultracentrifuged for 2.5 h at 22,000 rpm. Supernatant was discarded and the virus particles resuspended over night at −4°C in 120 μL NB medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States).
RNA-sequencing analysis
RNA-sequencing resulted in ∼25–31 million reads (Supplementary Table S1). Quality assessment was based on the raw reads using the FASTQC quality control tool (v0.10.1). The sequence reads (single-end 50 bp) were aligned to the human reference genome (hg38) with Bowtie2 (v2.0.2) using RSEM (v1.2.29) with default parameters. First, the human reference genome was indexed using the Ensembl annotations (v84.38) with rsem-prepare-reference from RSEM software. Next, rsem-calculate-expression was used to align the reads and quantify the gene abundance. Differential expression analysis was carried out using gene read counts with DESeq2 package (v1.12.4). Genes with less than 5 reads (baseMean) were filtered out. Genes with an adjusted p-value ≤0.01 and log2 fold change > |0.5| were considered to be differentially expressed.
Gene ontology enrichment analysis
Gene ontology (GO) analysis was conducted using WebGestalt. An adjusted p-value ≤0.01 using the Benjamini–Hochberg method for controlling the false discovery rate was set as significant for GO terms in biological processes. EnrichmentMap (v2.1.0) plugin was used in Cytoscape (v3.4.0) for enrichment visualization of top 20 terms (Supplementary Figure S5). The overlap between the gene sets (biological process) was calculated using overlap coefficient implemented in the plugin, i.e, [size of (A intersect B)]/[size of (minimum (A, B))].
ICLIP analysis
The iCLIP protocol was performed as described previously (Tollervey et al., 2011), with the following modifications. Early passage HUVECs were irradiated once with 155 mJ/cm2 in a Stratlinker 2,400 at 254 nm. TDP-43 was immunoprecipitated with protein A Dynabeads (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States) conjugated to rabbit-anti TDP-43 (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, United States, SAB4200006). The region corresponding to 55–100 kDa complexes was excised from the membrane to isolate the RNA. High-throughput sequencing using Illumina HiSeq was done. Analysis of reproducibility of crosslink sites, identification of the significant iCLIP crosslink clusters and z-score analysis of enriched pentamers was done as described previously (Tollervey et al., 2011) and data was processed by iCount webserver (http://icount.biolab.si).
Results
TDP-43 loss-of-function causes increased and ectopic angiogenic sprouting and impaired directional migration of endothelial cells (ECs) in zebrafish
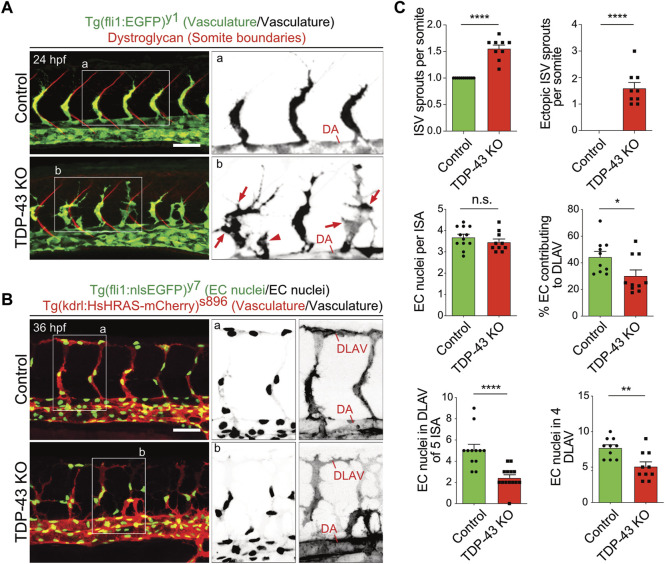
The initial characterization of tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− double homozygous loss-of-function zebrafish mutants uncovered hyperbranching and mis-patterning of EC during development (Schmid et al., 2013). In zebrafish, the intersegmental arteries (SA) grow dorsally from the dorsal aorta (DA) in the zebrafish trunk at 24 h post fertilization (hpf) in a very stereotypic manner (Isogai et al., 2001; Hogan and Schulte-Merker, 2017). In wild type embryos only one sprout per somite is formed at every somite boundary. The main lamellipodium of the sprouting SA is directed dorsally towards the physiological target region of the growing sprout (Figure 1A). In contrast, in the tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants, more sprouts are formed also at ectopic positions between somite boundaries. Moreover, growing sprouts extend lateral lamellipodia that frequently connect with neighboring sprouts (Figures 1A, B). The direction of lamellipodia extension defines the directionality of cell migration (Petrie et al., 2009). The extension of lateral lamellipodia and migration of EC at ectopic positions along the DA hence indicates a defect in directed migration. In wild type embryos, directed migration of EC to the dorsal roof of the neural tube is followed by formation of lateral connections between EC of neighboring SA to form the dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel (DLAV) at 32 hpf (Isogai et al., 2001). To provide further evidence for impaired directed migration of EC in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants, we quantified EC nuclei contributing to the DLAV at 32 hpf. EC nuclei in the DLAV of the analyzed 5 somites are drastically reduced in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants (Figures 1B, C). We further excluded a delay in cell migration, since EC nuclei contributing to the DLAV in the analyzed 4 somites are still significantly decreased at 2.5 dpf (Figure 1C). EC nuclei number per SA is not different in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants compared to wild type siblings in line with impaired migration of EC during angiogenesis in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants.
FIGURE 1.
Loss of TDP-43 leads to increased vascular sprouting and defective migration. (A) More and ectopic SA sprouts in zebrafish tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants. Immunofluorescence of a sibling and a tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutant embryo at 24 hpf. The Tg (fli1a:EGFP) y1 highlights the vasculature in green, the somite boundaries are stained in red. Scale bar 50 μm, anterior to the left. The insets a and b highlight the vasculature only. DA = dorsal aorta (B) Impaired directed migration in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants. Less mutant EC nuclei have reached the DLAV at 32 hpf. Embryos are transgenic for Tg (fli1:nlsEGFP) y7 with nuclear EGFP expression (green) and Tg (kdrl:HsHRAS-mCherry) s896, highlighting the vasculature (red). Scale bar 50 μm, anterior to the left. The insets a and b highlight the EC nuclei (left) and the vasculature (right). (C) Quantifications of the vascular defects in the tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants as indicated. Kruskal–Wallis test and Dunn’s multiple comparison post test, n ≥ 9, sprouts between boundaries of six somites dorsal to the end of the yolk sack extension were quantified. D’Agostino-Pearson omnibus normality test and unpaired t-test, n = 10 for "% EC contributing to DLAV” and “number of EC in DLAV of 4 segments at 2.5 dpf”.
We next established a TDP-43 KD model for the subsequent experiments to obtain higher numbers of phenotypic embryos compared to the 25% of double homozygous mutant embryos obtained from a tardbp−/−; tardbpl+/- incross. The KD specificity was carefully evaluated by comparison to the tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutant phenotypes. The KD of Tardbpl protein in the tardbp−/− background (tardbp−/−; Tardbpl KD) can fully phenocopy the tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutant EC phenotype demonstrating the specificity and efficiency of the morpholino (MO) (Supplementary Figures S1A–C).
TDP-43 deficient endothelial phenotypes are not mediated by Vegfr and Notch signaling
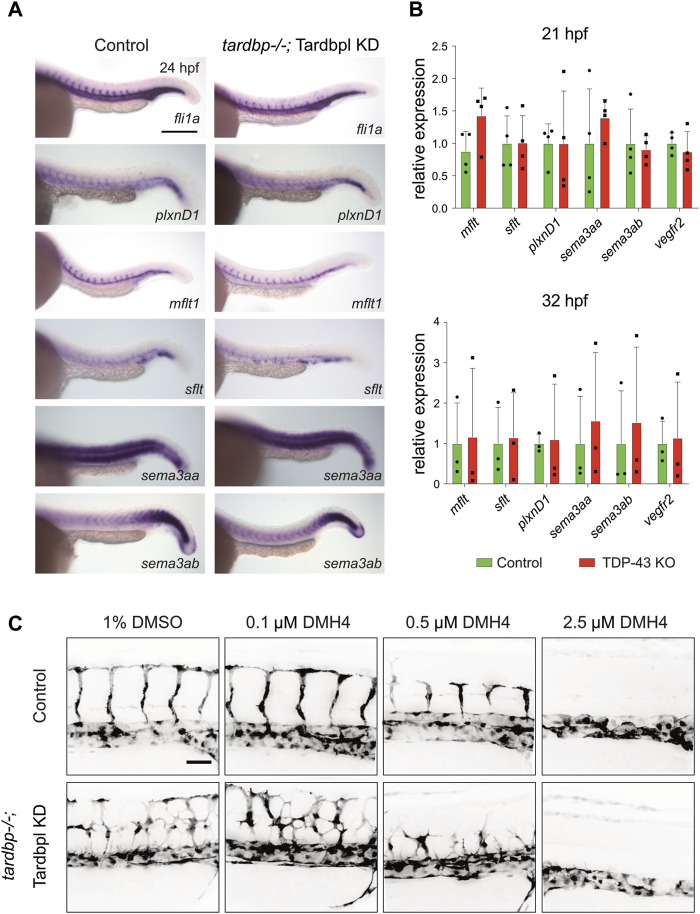
Numerous guidance cues and growth factors are known to regulate angiogenic sprouting of SA in the zebrafish embryo. The similarity of the PlxnD1 loss-of-function mutant out of bounds (obd) to the tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutant phenotype indicated a possible impairment of this signaling pathway in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− EC (Childs et al., 2002; Torres-Vazquez et al., 2004; Zygmunt et al., 2011). The zebrafish homologue of VEGFR1, flt1 (fms-related tyrosine kinase), is alternatively spliced into a soluble decoy receptor, sflt1, and a membrane bound version, mflt1. In obd mutants, the ratio of the soluble sflt1 and membrane bound mflt1 is shifted towards increased expression of the mflt1 splice variant, leading to an increased availability of Vegf for its pro-angiogenic receptor Kdrl (Zygmunt et al., 2011), the zebrafish orthologue of VEGFR2. However, no alterations in expression patterns of sflt1, mflt1, plxnD1 and its receptor sema3aa and sema3ab were detectable in TDP-43 deficient embryos by in situ hybridization (Figure 2A). The expression levels of sflt1, mflt1, plxnD1, sema3aa, sema3ab, and kdrl, were also not altered as determined by RT-PCR (Figure 2B). Thus, although phenotypically similar, the tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− phenotype is not caused by the same alteration of guidance cues upstream of Kdrl signaling as in obd mutants.
FIGURE 2.
Selected candidate genes and the VEGF pathway are not affected in TDP-43 KO zebrafish (A) WISH with antisense probes specific for the candidate genes fli1a, plxnD1, sflt1, mflt1, sema3aa, and sema3ab in tardbp−/− ctr MO injected embryos (Control) and their tardbp−/−; Tardbpl KD siblings at 24 hpf (Magnification: ×10 anterior to the left). Depicted are representative images of embryos from one clutch. Experiment was performed with embryos of three independent clutches. (B) Relative mRNA expression of mflt1, sflt1, plxnD1, sema3aa, sema3ab, and kdrl in tardbp−/−; Tardbpl KD embryos compared to their ctr MO injected tardbp−/− siblings (Control) at 21 and 32 hpf. N = 3 (32 hpf) or n = 4 (21 hpf) pools of embryos of independent clutches, unpaired t-test, all p-values >0,5. Results were reproduced three times using the same cDNA. (C) Representative images of ctr MO injected siblings (Control) and tardbp−/−; Tardbpl KD embryos treated with 1% DMSO (solvent) as control or 0.1 μM, 0.5 μM, and 2.5 μM DMH4 inhibitor. Scale bar 50 μm, anterior to the left.
Notch is another important regulator of angiogenic sprouting and could thus contribute to increased sprouting of SA in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants. Besides the different location and timing of additional sprouting in Notch deficient embryos and tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants, the increased EC number in sprouting SA in embryos with Notch deficiency is not present in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants (Figure 1C and (Siekmann and Lawson, 2007)). Further, Notch is an important player in EC fate determination. However, the Notch determined cell fate markers ephrin-B2a and flt4 are not altered in tardbp−/−; Tardbpl KD embryos (Supplementary Figure S2), demonstrating that arterial-venous cell differentiation is normal. Taken together, there is no evidence for Notch-related phenotypes in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants based on EC numbers and expression of marker genes.
VEGFR2 signaling influences a multitude of EC behaviors and vascular patterning (Simons et al., 2016) and is the mediator of various signaling molecules. Increased VEGFR2 signaling stimulates angiogenesis and could potentially explain excessive angiogenic sprouting as seen in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants. If increased Kdrl signaling is indeed responsible for the sprouting phenotype, then slight reduction of Kdrl signaling with low concentrations of VEGFR2 inhibitor should be able to rescue the phenotype. To test this hypothesis, the selective VEGFR2 inhibitor DMH4 was used to slightly reduce Kdrl signaling to intermediate levels and assayed for rescue of the mutant phenotype (Cannon et al., 2010; Hao et al., 2010; van Rooijen et al., 2010). DMH4 was carefully titrated until sprouting was strongly impaired or completely absent in control (ctr) MO injected siblings. Then, the inhibitory effects of the intermediate concentrations (0.1 and 0.5 μM DMH4) that do not fully block sprouting were compared between TDP-43 deficient embryos and their ctr MO injected morphologically wild type siblings (Figure 2C). Even if sprouting is impaired in tardbp−/−; Tardbpl KD embryos at these intermediate concentrations, EC still show increased and ectopic sprouting indicating that Kdrl signaling is impaired but the hypersprouting phenotype is not rescued. Furthermore, titration of the DMH4 inhibitor to a 2.5 μM concentration that is just sufficient to block SA sprouting in tardbp−/− ctr MO siblings is equally sufficient to block angiogenic sprouting in tardbp−/−; Tardbpl KD embryos (Figure 2C) suggesting that Kdrl signaling is not increased in tardbp−/−; Tardbpl KD embryos.
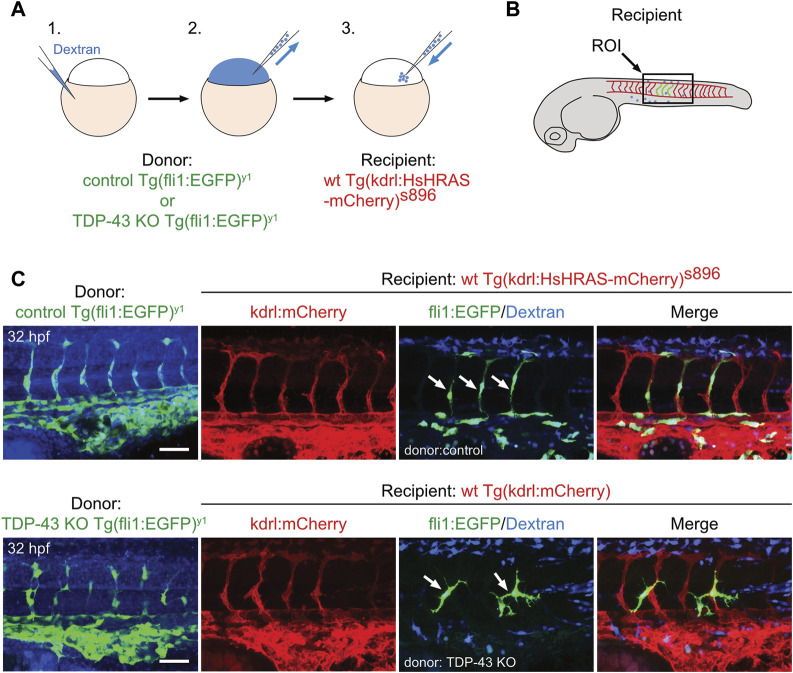
The TDP-43 KO vascular phenotype persists in a wild type environment
To test if a wildtype environment can rescue the mutant EC phenotype, we performed cell transplantation experiments of mutant EC into a wild type recipient embryo. Transplantation of donor cells from Tg (fli1:EGFP)y1 expressing eGFP in Tg (kdrl:mCherry)s896 recipients expressing mCherry in the endothelium does neither alter donor derived nor recipient EC morphology, showing that the transplantation procedure per se does not affect EC morphology (Figures 3A–C upper panel). When tardbp−/−; Tardbpl KD Tg (fli:GFP)y1 or tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− Tg (fli:GFP)y1 embryos are used as donors, the transplanted cells differentiating into EC within the Tg (kdrl:mCherry)s896 recipient embryos show the mutant phenotype with supernumerous sprouts at ectopic positions (Figure 3C lower panel) consistent with a cell autonomous function of TDP-43. All donor cells were labeled with fluorescent dextran and only EC without co-transplanted dextran positive cells in the vicinity were scored.
FIGURE 3.
The tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutant vascular phenotype is cell autonomous. (A) Scheme of the transplantation of control Tg (fli1:EGFP)y1 or TDP-43 KO; Tg (fli1:EGFP)y1 donor EC cells (EC in green, injected tracer label in blue) into Tg (kdrl:HsHRAS-mCherry)s896 hosts (EC in red). (B) The region of interest (ROI) imaged in the transplanted donor larvae is the area dorsal to the end of the yolk sack extension for all images (box). (C) Tg (fli1:EGFP)y1 donor (EC in green, injected tracer label in blue) transplanted into Tg (kdrl:HsHRAS-mCherry)s896 recipients (EC in red) had a wild type morphology. TDP-43 KO; Tg (fli1:EGFP)y1 mutant donor into Tg (kdrl:HsHRAS-mCherry)s896 recipient showed the TDP-43 deficient phenotype (n = 4). Scale bar 50 μm, anterior to the left. Displayed is the area dorsal to the end of the yolk sack extension for all images.
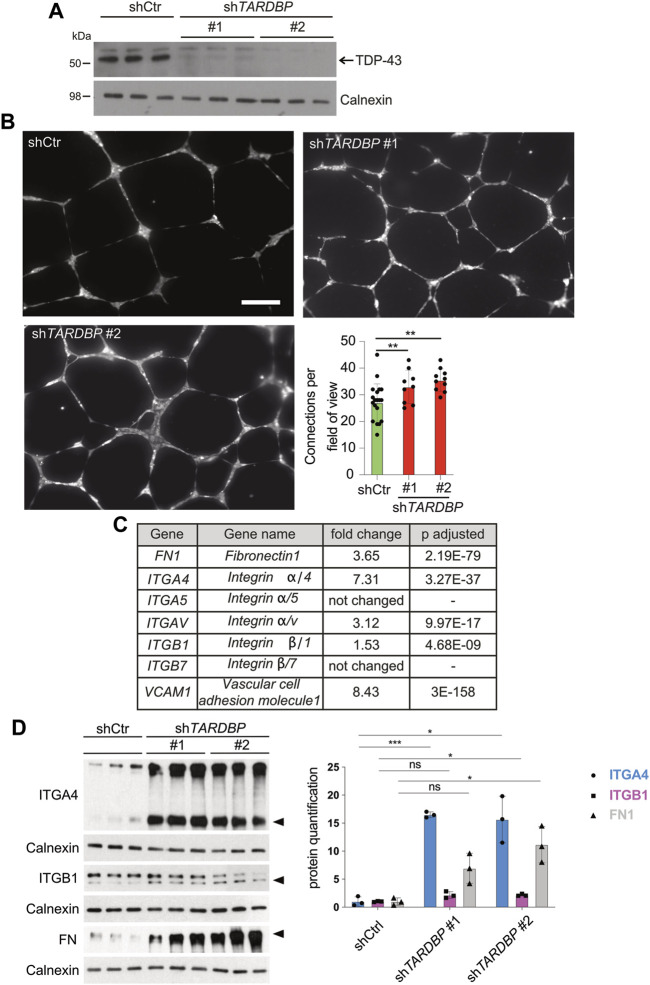
TDP-43 regulates branching of human ECs in vitro independent of VEGFR2 activation
We reasoned that the signaling pathways mediating the angiogenic phenotype are conserved in the human system and that identification of the molecular pathway is facilitated in a primary cell culture model. We used two independent TARDBP targeting shRNAs, shTARDBP#1 and #2 (Figure 4A) to KD TDP-43 in HUVEC. A tube formation assay was performed to analyze collective migration on an artificial extracellular matrix (ECM) (Friedl and Gilmour, 2009), which is routinely used as an in vitro tube formation assay (Montañez et al., 2002; Friedl and Gilmour, 2009). Strikingly, network complexity (as reflected by the number of connections between branch points) is increased upon TDP-43 KD with both TARDBP targeting shRNAs (Figure 4B). This phenotype is not mediated by hyperproliferation, since TDP-43 KD does not affect proliferation, but rather leads to increased cell death (Supplementary Figure S3A). Thus, the TDP-43 loss-of-function affects branching and tube formation in zebrafish and human, suggesting an evolutionary conserved requirement of TDP-43 for EC patterning.
FIGURE 4.
Increased in vitro angiogenesis upon TDP-43 KD in HUVEC and identification of mis-regulated pathways by NGS. (A) KD of TDP-43 in HUVEC with two different shRNAs, shTARDBP #1 and #2 reduces TDP-43 protein levels. shCtr transduced HUVEC serve as control, each lane represents a biological replicate, Calnexin serves as loading control. (B) Images show tubular network formation of representative fields of view of shCtr, shTARDBP #1, and shTARDBP #2 transduced HUVEC (magnification: ×10). Bar graph displays the quantified connections per field of view in TDP-43 KD with shTARDBP#1 and shTARDBP#2 compared to shCtr. D’Agostino-Pearson omnibus normality test and one-way ANOVA, n ≥ 8 in three independent experiments. (C) Selection of NGS hits of HUVEC upon TDP-43 KD with fold change and adjusted p-value. (D) Immunoblot validation of FN1, ITGA4, and ITGB1 upon KD of TDP-43 with shTARDBP #1 and shTARDBP #2 in comparison to shCtr transduced cells. Each lane represents one biological replicate. The band intensities of the indicated bands (arrowhead) have been quantified using ImageJ, t-test n = 3.
Next, we analyzed VEGFR2 signaling pathway activity and its responsiveness to a VEGF-A stimulus upon TDP-43 deficiency in HUVEC. Baseline activation after deprivation of growth factors was assessed as well as the time dependent increase in phosphorylation, and therefore kinase activity, upon VEGF stimulation. However, neither expression levels of the kinases nor the activation of VEGFR2 and the downstream kinases AKT, p38, PLCG and ERK1/2 were altered upon TDP-43 KD at any time point investigated (Supplementary Figure S3B and Supplementary Figure S4B). Thus, VEGFR2 signaling and responsiveness to VEGF, as well as kinetics of activation of kinases following a VEGF stimulus are not altered upon TDP-43 KD. Taken together, our data exclude involvement of impaired VEGFR2 signaling in the vascular phenotype observed in both, tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− zebrafish and TDP-43 loss-of-function HUVEC.
TDP-43 KD activates the FN1/VCAM1/ITGA4B1 pathway in HUVECs
After excluding prominent candidate pathways mediating the EC phenotype in TDP-43 KO we turned to RNA next-generation sequencing (NGS) as an unbiased approach to identify differentially expressed genes upon KD of TDP-43 in HUVECs. We identified 2,129 genes with differential expression and adjusted p-value smaller or equal to 0.01 and a minimum coverage of 5 reads (see Supplementary Table S1). Pathway analysis of the differentially expressed genes identifies migration, extracellular structure organization, chemotaxis and morphogenesis defects as the most prominent hits (Supplementary Figure S5 and Supplementary Table S2). Strikingly, VCAM1 and ITGA4, two of the top 10 upregulated genes functionally interact, suggesting upregulation of a whole pathway. This pathway is one of the most prominently affected pathways in this analysis. VCAM1 is a ligand of the heterodimeric receptor ITGA4/B1, whose subunits ITGA4 and ITGB1 are upregulated 7.31 fold and 1.5 fold, respectively. Moreover, the other ligand of ITGA4/B1, the ECM component FN1, is also upregulated 3.65 fold (Figure 4C). FN1 can also bind to the Integrin α4β7 receptor (White and Muro, 2011), however ITGB7 is not upregulated in our dataset, arguing for ITGA4/B1 as the relevant heterodimeric receptor. Ligand mediated local activation of the α4β1 Integrin heterodimeric receptor promotes directional migration of different cell types (Goldfinger et al., 2003; Nishiya et al., 2005) and therefore represented a promising candidate for inducing the vascular phenotypes caused by loss of TDP-43.
Next, we tested whether the increased mRNA expression of ITGA4, ITGB1, FN1, and VCAM1 leads to increased protein expression. Protein expression of ITGA4 and FN1 is strongly increased upon TDP-43 KD compared to controls (Figure 4D and Supplementary Figure S4A), while ITGB1 expression is moderately increased. Unfortunately, we could not detect endogenous VCAM1 expression by immunoblot. Thus, TDP-43 is required to attenuate expression of FN1 and VCAM1 and their receptor ITGA4B1 in HUVECs.
TDP-43 is known to bind to RNA with the ability to regulate RNA stability and splicing (Polymenidou et al., 2011; Tollervey et al., 2011). However, we did not identify altered splicing of FN1, ITGA4B1or VCAM1 RNA in HUVEC upon TDP-43 KD (data not shown). We next asked if TDP-43 protein binds to FN1, ITGA4B1or VCAM1 RNA in HUVEC and thereby increases their expression upon TDP-43 KD. Consistent with previous reports we identified TDP-43 binding in coding and non-coding RNAs, introns, exons and UTRs (Supplementary Figure S6) by individual-nucleotide resolution cross-linking immunoprecipitation-high-throughput sequencing (iCLIP) with a binding preference for the sequence motif GTGTG (Supplementary Figure S6B). Despite FN1 being among the top 30 bound transcripts (Supplementary Table S3) and binding of TDP-43 at the exon/intron boundaries of FN1 (Supplementary Figure S6C), TDP-43 KD does not alter its splicing. Prominent binding of TDP-43 to the 3′and 5′UTR of FN1 (Supplementary Figure S6C) suggests regulation of transcript stability or translation (Glisovic et al., 2008; Costessi et al., 2014).
fn1b is increased in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants
We next analyzed whether the increase in expression of ITGA4, FN1, and VCAM1 identified in HUVEC is also present in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutant zebrafish. itgb1 levels were not analyzed, because first, zebrafish express six different paralogues of the human ITGB1 and second, it was only mildly upregulated in HUVEC. Since zebrafish have two FN1 orthologues, fn1a and fn1b, mRNA expression of both were analyzed. fn1b mRNA levels are increased in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− whole animal samples compared to their wild type siblings, whereas fn1a, itgα4 and vcam1 levels are not (Figure 5). Potentially, increased levels of fn1a, itgα4 and vcam1 in the EC could be masked by unaltered levels in more abundant cell types.
FIGURE 5.
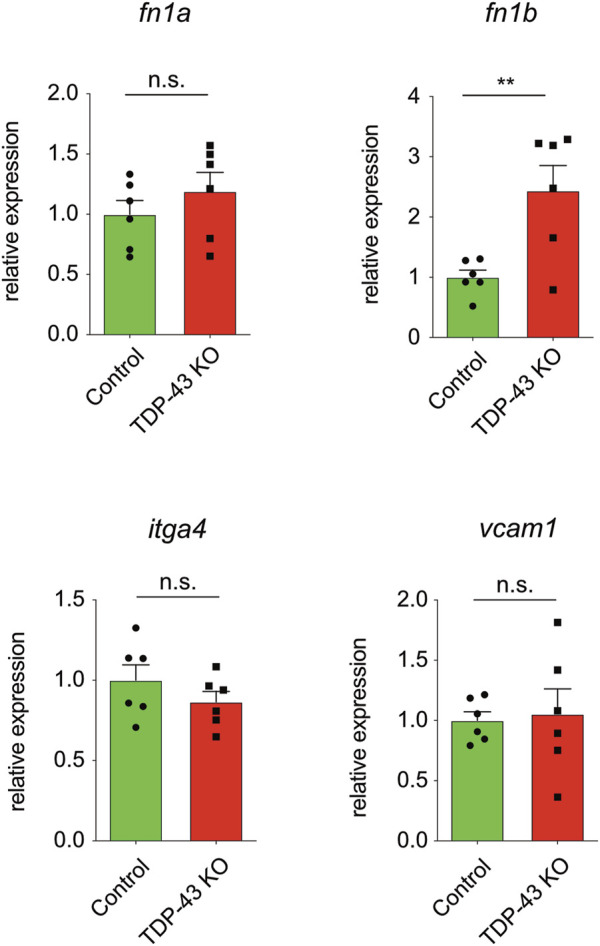
fn1b is increased in zebrafish. Relative mRNA expression of fn1b, but not fn1a, itgα4, or vcam1 is increased in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants compared to their wild type siblings. n = 6 pools of embryos of independent clutches at 24 hpf, unpaired t-test. Results by qPCR were reproduced twice using the same cDNA.
Lowering of fn1b, itgα4, and vcam1 levels rescues hypersprouting of SA in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants
If increased levels of fn1b, itgα4 and vcam1 in ECs is causative for the angiogenic defect in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− zebrafish embryos, then reducing their expression to approximately wild type levels should rescue the angiogenic phenotype. The developmental stage at which SA sprouts reach the horizontal myoseptum was chosen for quantification of angiogenic sprouting. To exclude off-site target effects of MO in general and to reduce impact of lowered expression of targeted genes in other tissues than the vasculature, low MO concentrations were chosen that do not impact SA growth in control MO injected embryos at 24 hpf (Figure 6A). However, as evaluated by the desired alterations in splicing patterns, successful partial KD of itgα4 and vcam1 is still detectable on RNA level (Supplementary Figure S7). Importantly, partial KD of fn1b but also itgα4, or vcam1 rescued the hypersprouting phenotype of (Figures 6A, B). In contrast, KD of fn1a did not rescue this phenotype, consistent with the lack of upregulation in TDP-43 mutants (Figure 5, Figures 6A, B). The ability to rescue the mutant phenotype demonstrates that fn1b, itgα4, and vcam1 upregulation is causative for the vascular phenotype in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− zebrafish.
FIGURE 6.
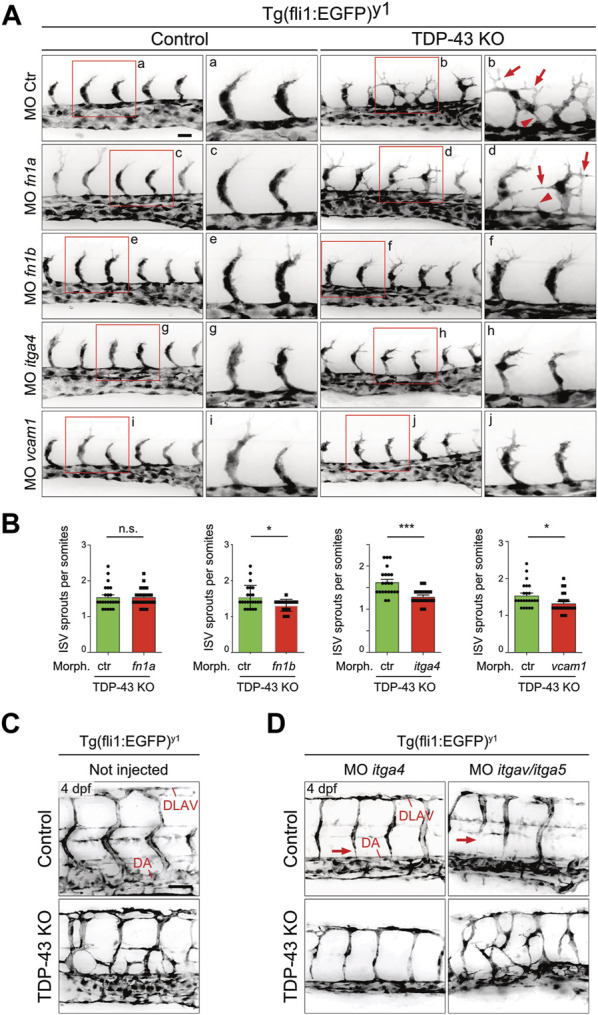
Mild KD of fn1b, itgα4, or vcam1, but not fn1a rescues increased SA sprouting in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants. (A) Mild KD of fn1a, fn1b, itgα4, or vcam1 does not affect SA growth in wild type embryos compared to ctr MO injected siblings. Images showing rescue results with normal SA sprout number in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants injected with 0.33 mM fn1b, 0.5 mM itgα4, or 0.75 mM vcam1 MO. Note the morphological difference compared to ctr MO injected tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants and the similarity to 0.75 mM ctr MO injected wild type sibglings. fn1a KD tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants (0.75 mM MO) are not rescued. (B) Statistical analysis demonstrating that mild KD of fn1b, itgα4, or vcam1 can statistically significantly rescue increased sprouting of SA from the DA at 24 hpf in tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants compared to ctr MO injected tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants. One of three (fn1a, fn1b, itgα4 KD) or two (vcam1 KD) independent experiments with two clutches per experiment are shown, normality test and unpaired t-test, n ≥ 23. (C) Mutant tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− and control embryos carry the Tg (fli1:EGFP)y1 transgene, SA of the trunk dorsal of the yolk sack extension are shown. (D) Representative image of 1 mM itgα4 MO and itgα5/itgαv MO injected sibling and tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutant embryos (right panel). Note the normal number of SA of the itgα4 MO injected tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutant. Arrows point to SA defects in wild type siblings injected with 0.5 mM itgα5 and 1 mM itgαv MO indicating lack of rescue activity. Scale bar 50 μm, anterior to the left.
The FN1 receptor Integrin α5β1 was previously implicated in angiogenesis in vivo (Astrof and Hynes, 2009). ITGAV is known to compensate the FN fibril assembly defect of ITGA5 knockout embryonic cells (Yang and Hynes, 1996). To circumvent a compensation of itgα5 KD by itgαv, itgα5 and itgαv MO were coinjected together and tested for rescue ability. Whereas combined KD of itgα5 and itgαv did not rescue the vascular mis-patterning in any tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutant, itgα4 MO injection into tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants could strongly ameliorate the vascular phenotype (Figures 6A–C). tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− embryos with itgα4 KD have SA with nearly wild type morphology dorsal of the yolk sack extension. These findings underscore that the relevant integrin receptor α subunit of Fn1b causing the angiogenic defect of tardbp−/−; tardbpl−/− mutants is Itgα4.
Discussion
One of the major problems identifying the physiological functions of TDP-43 in vivo has been the early embryonic lethality of the KO mouse (Kraemer et al., 2010; Sephton et al., 2010; Wu et al., 2010) and the large number of RNA targets it can bind and modulate (Polymenidou et al., 2011; Tollervey et al., 2011). We identified an essential function of TDP-43 in zebrafish and human cell culture in EC patterning. In zebrafish, KO of both TDP-43 orthologues is also embryonic lethal, however, due to the extra-corporal embryonic development of fish we uncovered an early embryonic severe EC phenotype (Schmid et al., 2013). In the SA of TDP-43 mutant zebrafish, EC sprout and extend lamellipodia into the somite area instead of being restricted to the somite boundaries and fail to migrate along their normal paths. In human EC branching is similarly increased. In an unbiased transcriptomics analysis, we identified FN1, VCAM1, and ITGα4/β1 as upregulated genes upon loss of TDP-43 in HUVEC. In a previous study, VCAM1 was also found to be 1.7 fold upregulated in adult mouse brain upon TDP-43 depletion (Polymenidou et al., 2011) supporting our findings. Additionally, in TDP-43 KO embryonic stem cells FN1 was among other focal adhesion KEGG pathway members strongly mis-regulated (Chiang et al., 2010). In zebrafish we found fn1b RNA to be 2 fold upregulated, however the levels of vcam1, and itgα4/β1 were not altered in whole embryo extracts. The zebrafish RNA sequencing was performed on whole embryos and gene expression changes in EC might be masked by lack of expression changes in other abundant cell types. Alternatively, basal EC expression of itgα4 and vcam1 might be very low keeping a potential increase in expression still below the detection limit. However, the rescue of the angiogenic defect with not only fn1b, but also vcam1 and itgα4/β1 MO supports the involvement of elevated vcam1 and itgα4/β1 also in zebrafish vascular mis-patterning. Importantly, FN1/VCAM1/ITGα4/β1 signaling can induce the vascular mis-patterning distinct from the known key players in angiogenesis: the VEGFR2-pathway, NOTCH, ITGA5, and ITGAV. How loss of TDP-43 leads to fn1b, vcam1, and itgα4/β1 upregulation remains unclear. Interestingly, FN1 mRNA is a direct target of TDP-43 in HUVEC. We hypothesize that TDP-43 binding destabilizes the FN1 mRNA since FN1 levels are elevated upon loss of TDP-43. VCAM1 and ITGA4/Β1 levels most likely are regulated indirectly potentially by a feedback regulatory loop through increase of FN1 or by changes in microRNA expression.
Our data shows that Fn1 and Vcam1 binding to and activation of ItgA4/Β1 induces defects in directed migration of EC upon TDP-43 loss. Activation of ITGA4 has been previously shown to be required for directional migration of several cell types in vivo (Kil et al., 1998; Sengbusch et al., 2002; Grazioli et al., 2006; Lim et al., 2008) consistent with the zebrafish phenotype. Moreover, activation of ITGA4/Β1 induces and maintains polarity during directed migration (Goldfinger et al., 2003; Nishiya et al., 2005). Additionally, a prominent instructive role for directed cell migration of Fn has previously been demonstrated in myocardial precursors in zebrafish (Trinh and Stainier, 2004; Jessen, 2015) and directed migration of EC in mouse retinal angiogenesis (Stenzel et al., 2011) in line with our findings.
TDP-43 is the major pathological hallmark of ALS and our findings of its physiological function in angiogenesis is of potential disease relevance. Upon aggregation in the cytoplasm in disease state, TDP-43 is cleared from its normal nuclear localization and mis-regulated pathways through loss of TDP-43 contribute to disease. Several features of TDP-43 loss-of-function, such as splice alterations of STATHMIN2 (Melamed et al., 2019; Prudencio et al., 2020), UNC13A (Brown et al., 2022; Ma et al., 2022) and cryptic proteins have been isolated from the ALS patient’s cerebral spinal fluid (Irwin et al., 2023; Seddighi et al., 2023) underscoring the clinical relevance of loss of TDP-43 consequences for ALS.
Misregulation of FN1 in motor neurons from sporadic ALS patients has been previously reported and might contribute directly to toxicity by altering the ECM-interaction of motor neurons and thereby affecting their vulnerability (Rabin et al., 2010; Prudencio et al., 2015). Alternatively, a TDP-43 driven vasculopathy could indirectly lead to motor neuron death in ALS. Evidence from TDP-43 inclusions in patient’s brain endothelial cells (Ferrer et al., 2021) and blood brain—and blood spinal cord barrier leakage in a conditional TDP-43 knockout mouse (Sasaki, 2015) support a direct TDP-43 dependent effect of vascular alterations to ALS pathology. Interestingly, a number of pro-inflammatory cytokines (CXCL6, CXCL10, CXCL12) have been identified to be highly upregulated by RNA sequencing in HUVEC upon TDP-43 KD (Supplementary Table S1), which might also contribute to disease progression in ALS by modulating the inflammatory response.
In summary, our study identified FN1/VCAM1-ITGA4B1 as a novel, important and evolutionary conserved molecular pathway regulated by TDP-43 with a potential mechanistic link to the pathophysiology of ALS.
Acknowledgments
We thank Roberto Rojas Rojas and Sabine Schlink for fish care support. Vincenzo Capece for analyzing RNA sequencing data.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the Helmholtz cross-program topic “Metabolic Dysfunction” and “AMPro”, the Thierry Latran foundation, the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) within the framework of the Munich Cluster for Systems Neurology (EXC 1010 SyNergy), the Hans und Ilse Breuer foundation, and IMPRS. SAL is supported by the Swedish FTD initiative, Olle Engkvist Byggmästare Foundation and Åhlén Foundation (mA2/h17). EM is supportd by the DFG grant MO2562/1-2. and by the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities (PID 2019-108902 GB-I00).
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found as follows: The analysis as presented in Supplementary Figure S6 was processed by the iCount software (https://github.com/tomazc/iCount). Original iCLIP data is deposited at: https://imaps.goodwright.com/collections/993546811444/, https://imaps.goodwright.com/collections/285935488641/. The RNA sequencing data is deposited at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE233588.
Ethics statement
The animal study was reviewed and approved by Regierung von Oberbayern.
Author contributions
KH, BP, AH, FvB, MM, VB, and EM conducted experiments, KH and BS wrote the paper with contribution from AH, FvB, EM, BP, SB,VB, MM, UP, CH, and SL, DO, DE, and CH provided reagents.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2023.1169962/full#supplementary-material
Tardbpl Morpholino KD in tardbp −/− mutants fully phenocopies the tardbp/tardbpl KO. (A) Western blot indicating successful KD of Tardbpl_tv1protein levels in the wild type and in tardbp −/− mutant background in single embryos (note the high levels of Tardbpl_tv1 in tardbp -/- mutants in lane c compared to wild type in lane a compensating for the loss of Tardbp). Lane e are double homozygous tardbp −/− ; tardbp −/− mutants and in lane f are the corresponding pooled siblings with the genotype tardbp +/- and tardbp +/+; tardbpl −/− loaded. Tubulin serves as a loading control. (B) Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 highlights the vasculature shown in black. KD of Tardbpl in the tardbp-/- is phenotypically indistinguishable from the tardbp-/-; tardbpl-/- mutants (compare d with e). Scale bar 50 μm, anterior to the left. (C) There is no statistically significant difference between tardbp-/-; tardbpl-/- and tardbp-/- Tardbpl KD embryos in the average SA sprout number per somite and the ectopic sprout number per somite. Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’s multiple comparison post test, n ≥ 9, sprouts between boundaries of six somites dorsal to the end of the yolk sack extension were quantified.
Arterial-venous differentiation and Notch target gene expression patterns are unaffected by TDP-43 KD. WISH with antisense probes specific for the Notch target and the arterial-venous differentiation markers ephrin-B2a and flt4 in tardbp-/- ctr MO injected embryos (Control) and their tardbp-/-; Tardbpl KD siblings at 24 hpf (Magnification: ×10 anterior to the left). Depicted are representative images of embryos from one clutch. Experiment was performed with embryos of three independent clutches.
TDP-43 KD in HUVEC does not increase proliferation and shows no activation of the VEGFR2 signaling pathway. (A) Protein content as a measure of cellular survival is statistically significantly decreased upon TDP-43 KD with two TDP-43 targeting shRNAs. One-way ANOVA, n = 30 in three independent experiments. Cell death due to apoptosis and necrosis determined by quantification of LDH release is statistically significantly increased upon TDP-43 KD with two TDP-43 targeting shRNAs. One-way ANOVA, n = 30 in three independent experiments. KD of TDP-43 in HUVEC does not alter proliferation as shown by quantification of percentage of Ki67 positive cells. Unpaired t test, n = 9 in three independent experiments, p-value 0,5519. (B) Expression as well as phosphorylation levels of VEGFR2 signaling pathway components upon VEGF stimulation is not altered upon TDP-43 KD in HUVEC. Immunoblot of TDP-43 demonstrates successful KD upon transduction with shTARDBP#1 (KD) compared to shCtr transduced HUVEC (shCtr). VEGFR2, AKT, p38, PLCG, and ERK1/2 levels are not altered upon TDP-43 KD or upon stimulation with VEGF after 5/15/30 min. Also, phosphorylation levels of VEGFR2, AKT, p38, PLCG, and ERK1/2 are not altered upon TDP-43 KD or upon stimulation with VEGF after 5/15/30 min (pVEGFR2, pp38, pPLCG, pERK1/2). Time point 0 represents baseline levels after deprivation of growth factors before cells were stimulated with VEGF. Calnexin served as a loading control. Depicted is one representative experiment out of three independent experiments.
Full Western blots. (A) Full Western blots for Fig. 4D. (B) Full Western blot for Fig. S3. Boxes contain corresponding membranes used as loading control and for quantification.
Pathways analysis of NGS hits using Webgestalt.
Individual-nucleotide resolution cross-linking immunoprecipitation (iCPLIP), sequence preference of TDP-43 binding in HUVEC and binding sites of TDP-43 to FN1. (A) Autoradiograph of 32P-labelled RNAs in the presence or absence of UV crosslinking and anti-TDP-43 antibody. High and low concentrations of RNase were used to confirm the presence of RNA bound to TDP-43. The asterisk marks the position in the gel corresponding to the size of a TDP-43 monomer. (B) Z-scores of pentamer occurrences surrounding (−30 nt to +30 nt) all TDP-43 cross-linked sites in HUVEC as determined by iCLIP. The sequences of the two most enriched pentamers are depicted. (C) Pie chart depicting the regional distribution of TDP-43 binding sites identified by TDP-43 iCLIP in HUVEC. TDP-43 cross-linked sites in the FN1 transcript as indicated by the TDP-43 iCLIP experiment in HUVEC cells (n = 2).
itgα4 and vcam1KD strategy and MO validation. (A) Scheme illustrating the first three exons and two introns of zebrafish itgα4. Binding of the itgα4 MO (indicated in red) leads to skipping of exon2, as verified by sequence analysis of the resulting lower band at about 100 bp shown in (B). Primers used for amplification are indicated by black arrows. B) PCR products of cDNA from ctr MO injected (-) or itgα4 MO injected (+) siblings of the embryos used in the rescue experiment shown in Figure 6. Injection of itgα4 MO leads to appearance of a second, lower migrating band representing itgα4 RNA lacking exon2. The upper band represents the normally spliced itgα4 RNA with exon1, 2, and 3. Bands were sequencing confirmed, revealing a frame shift resulting from exon skipping leading to a premature stop codon. (C) Scheme illustrating the first two exons and first intron of vcam1. Binding of the vcam1 MO (indicated in red) leads to partial inclusion of intron1 resulting in two RNAs with different length (see D). This was verified by sequence analysis. Primers used for amplification are indicated by black arrows. (D) PCR products of cDNA from ctr MO injected (-) or vcam1 MO injected (+) siblings of the embryos used in the rescue experiment shown in Figure 6. Injection of vcam1 MO leads to appearance of a second and third, higher migrating band representing vcam1 RNA with partial intron1 inclusion. The lowest band represents the normally spliced vcam1 RNA with exon1 and 2. Bands were sequence confirmed, revealing a frame shift resulting from partial exon inclusion leading to a premature stop codon.
References
- Astrof S., Hynes R. O. (2009). Fibronectins in vascular morphogenesis. Angiogenesis 12, 165–175. 10.1007/s10456-009-9136-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. L., Wilkins O. G., Keuss M. J., Hill S. E., Zanovello M., Lee W. C., et al. (2022). TDP-43 loss and ALS-risk SNPs drive mis-splicing and depletion of UNC13A. Nature 603, 131–137. 10.1038/s41586-022-04436-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussmann J., Bakkers J., Schulte-Merker S. (2007). Early endocardial morphogenesis requires Scl/Tal1. PLoS Genet. 3, e140. 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030140 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. E., Upton P. D., Smith J. C., Morrell N. W. (2010). Intersegmental vessel formation in zebrafish: Requirement for VEGF but not BMP signalling revealed by selective and non-selective BMP antagonists. Br. J. Pharmacol. 161, 140–149. 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00871.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet P., Tessier-Lavigne M. (2005). Common mechanisms of nerve and blood vessel wiring. Nature 436, 193–200. 10.1038/nature03875 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi N. C., Shaw R. M., De Val S., Kang G., Jan L. Y., Black B. L., et al. (2008). Foxn4 directly regulates tbx2b expression and atrioventricular canal formation. Genes Dev. 22, 734–739. 10.1101/gad.1629408 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang P. M., Ling J., Jeong Y. H., Price D. L., Aja S. M., Wong P. C. (2010). Deletion of TDP-43 down-regulates Tbc1d1, a gene linked to obesity, and alters body fat metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107, 16320–16324. 10.1073/pnas.1002176107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs S., Chen J. N., Garrity D. M., Fishman M. C. (2002). Patterning of angiogenesis in the zebrafish embryo. Development 129, 973–982. 10.1242/dev.129.4.973 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costessi L., Porro F., Iaconcig A., Muro A. F. (2014). TDP-43 regulates beta-adducin (Add2) transcript stability. RNA Biol. 11, 1280–1290. 10.1080/15476286.2014.996081 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiguin F., Godena V. K., Romano G., D'Ambrogio A., Klima R., Baralle F. E. (2009). Depletion of TDP-43 affects Drosophila motoneurons terminal synapsis and locomotive behavior. FEBS Lett. 583, 1586–1592. 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.04.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer I., Andres-Benito P., Carmona M., Assialioui A., Povedano M. (2021). TDP-43 vasculopathy in the spinal cord in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (sALS) and frontal cortex in sALS/FTLD-TDP. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 80, 229–239. 10.1093/jnen/nlaa162 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedl P., Gilmour D. (2009). Collective cell migration in morphogenesis, regeneration and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 445–457. 10.1038/nrm2720 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisovic T., Bachorik J. L., Yong J., Dreyfuss G. (2008). RNA-binding proteins and post-transcriptional gene regulation. FEBS Lett. 582, 1977–1986. 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.03.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfinger L. E., Han J., Kiosses W. B., Howe A. K., Ginsberg M. H. (2003). Spatial restriction of alpha4 integrin phosphorylation regulates lamellipodial stability and alpha4beta1-dependent cell migration. J. Cell Biol. 162, 731–741. 10.1083/jcb.200304031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grazioli A., Alves C. S., Konstantopoulos K., Yang J. T. (2006). Defective blood vessel development and pericyte/pvSMC distribution in alpha 4 integrin-deficient mouse embryos. Dev. Biol. 293, 165–177. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.01.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hao J., Ho J. N., Lewis J. A., Karim K. A., Daniels R. N., Gentry P. R., et al. (2010). In vivo structure-activity relationship study of dorsomorphin analogues identifies selective VEGF and BMP inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 5, 245–253. 10.1021/cb9002865 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewamadduma C. A., Grierson A. J., Ma T. P., Pan L., Moens C. B., Ingham P. W., et al. (2013). Tardbpl splicing rescues motor neuron and axonal development in a mutant tardbp zebrafish. Hum. Mol. Genet. 22, 2376–2386. 10.1093/hmg/ddt082 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan B. M., Schulte-Merker S. (2017). How to plumb a pisces: Understanding vascular development and disease using zebrafish embryos. Dev. Cell 42, 567–583. 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.08.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi Y., Katsuno M., Niwa J.-I., Takagi S., Ishigaki S., Ikenaka K., et al. (2013). Loss of TDP-43 causes age-dependent progressive motor neuron degeneration. Brain 136, 1371–1382. 10.1093/brain/awt029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin K. E., Jasin P., Braunstein K. E., Sinha I., Bowden K. D., Moghekar A., et al. (2023). A fluid biomarker reveals loss of TDP-43 splicing repression in pre-symptomatic ALS. bioRxiv. 10.1101/2023.01.23.525202 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isogai S., Horiguchi M., Weinstein B. M. (2001). The vascular anatomy of the developing zebrafish: An atlas of embryonic and early larval development. Dev. Biol. 230, 278–301. 10.1006/dbio.2000.9995 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isogai S., Lawson N. D., Torrealday S., Horiguchi M., Weinstein B. M. (2003). Angiogenic network formation in the developing vertebrate trunk. Development 130, 5281–5290. 10.1242/dev.00733 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessen J. R. (2015). Recent advances in the study of zebrafish extracellular matrix proteins. Dev. Biol. 401, 110–121. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.12.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julich D., Geisler R., Holley S. A., Tubingen Screen C. (2005). Integrinalpha5 and delta/notch signaling have complementary spatiotemporal requirements during zebrafish somitogenesis. Dev. Cell 8, 575–586. 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.01.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp H. A., Carmany-Rampey A., Moens C. (2009). Generating chimeric zebrafish embryos by transplantation. J. Vis. Exp., 1394. 10.3791/1394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kil S. H., Krull C. E., Cann G., Clegg D., Bronner-Fraser M. (1998). The alpha4 subunit of integrin is important for neural crest cell migration. Dev. Biol. 202, 29–42. 10.1006/dbio.1998.8985 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel C. B., Ballard W. W., Kimmel S. R., Ullmann B., Schilling T. F. (1995). Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. official Publ. Am. Assoc. Anatomists 203, 253–310. 10.1002/aja.1002030302 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer B. C., Schuck T., Wheeler J. M., Robinson L. C., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M., et al. (2010). Loss of murine TDP-43 disrupts motor function and plays an essential role in embryogenesis. Acta Neuropathol. 119, 409–419. 10.1007/s00401-010-0659-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson N. D., Scheer N., Pham V. N., Kim C. H., Chitnis A. B., Campos-Ortega J. A., et al. (2001). Notch signaling is required for arterial-venous differentiation during embryonic vascular development. Development 128, 3675–3683. 10.1242/dev.128.19.3675 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim C. J., Kain K. H., Tkachenko E., Goldfinger L. E., Gutierrez E., Allen M. D., et al. (2008). Integrin-mediated protein kinase A activation at the leading edge of migrating cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 19, 4930–4941. 10.1091/mbc.e08-06-0564 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Zeng L., Kennedy R. M., Gruenig N. M., Childs S. J. (2012). βPix plays a dual role in cerebral vascular stability and angiogenesis, and interacts with integrin αvβ8. Dev. Biol. 363, 95–105. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.12.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma X. R., Prudencio M., Koike Y., Vatsavayai S. C., Kim G., Harbinski F., et al. (2022). TDP-43 represses cryptic exon inclusion in the FTD-ALS gene UNC13A. Nature 603, 124–130. 10.1038/s41586-022-04424-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamed Z., Lopez-Erauskin J., Baughn M. W., Zhang O., Drenner K., Sun Y., et al. (2019). Premature polyadenylation-mediated loss of stathmin-2 is a hallmark of TDP-43-dependent neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 180–190. 10.1038/s41593-018-0293-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montañez E., Casaroli-Marano R. P., Vilaró S., Pagan R. (2002). Comparative study of tube assembly in three-dimensional collagen matrix and on Matrigel coats. Angiogenesis 5, 167–172. 10.1023/a:1023837821062 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann M., Sampathu D. M., Kwong L. K., Truax A. C., Micsenyi M. C., Chou T. T., et al. (2006). Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314, 130–133. 10.1126/science.1134108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiya N., Kiosses W. B., Han J., Ginsberg M. H. (2005). An alpha4 integrin-paxillin-Arf-GAP complex restricts Rac activation to the leading edge of migrating cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 7, 343–352. 10.1038/ncb1234 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrie R. J., Doyle A. D., Yamada K. M. (2009). Random versus directionally persistent cell migration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 538–549. 10.1038/nrm2729 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymenidou M., Lagier-Tourenne C., Hutt K. R., Huelga S. C., Moran J., Liang T. Y., et al. (2011). Long pre-mRNA depletion and RNA missplicing contribute to neuronal vulnerability from loss of TDP-43. Nat. Neurosci. 14, 459–468. 10.1038/nn.2779 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prudencio M., Belzil V. V., Batra R., Ross C. A., Gendron T. F., Pregent L. J., et al. (2015). Distinct brain transcriptome profiles in C9orf72-associated and sporadic ALS. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 1175–1182. 10.1038/nn.4065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prudencio M., Humphrey J., Pickles S., Brown A. L., Hill S. E., Kachergus J. M., et al. (2020). Truncated stathmin-2 is a marker of TDP-43 pathology in frontotemporal dementia. J. Clin. Invest. 130, 6080–6092. 10.1172/JCI139741 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaegebeur A., Lange C., Carmeliet P. (2011). The neurovascular link in health and disease: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neuron 71, 406–424. 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.07.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin S. J., Kim J. M., Baughn M., Libby R. T., Kim Y. J., Fan Y., et al. (2010). Sporadic ALS has compartment-specific aberrant exon splicing and altered cell-matrix adhesion biology. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19, 313–328. 10.1093/hmg/ddp498 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman B. L., Pham V. N., Lawson N. D., Kulik M., Childs S., Lekven A. C., et al. (2002). Disruption of acvrl1 increases endothelial cell number in zebrafish cranial vessels. Development 129, 3009–3019. 10.1242/dev.129.12.3009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S. (2015). Alterations of the blood-spinal cord barrier in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuropathology 35, 518–528. 10.1111/neup.12221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid B., Hruscha A., Hogl S., Banzhaf-Strathmann J., Strecker K., Van der Zee J., et al. (2013). Loss of ALS-associated TDP-43 in zebrafish causes muscle degeneration, vascular dysfunction, and reduced motor neuron axon outgrowth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110, 4986–4991. 10.1073/pnas.1218311110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seddighi S., Qi Y. A., Brown A.-L., Wilkins O. G., Bereda C., Belair C., et al. (2023). Mis-spliced transcripts generate de novo proteins in TDP-43-related ALS/FTD. bioRxiv. 10.1101/2023.01.23.525149 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengbusch J. K., He W., Pinco K. A., Yang J. T. (2002). Dual functions of [alpha]4[beta]1 integrin in epicardial development: Initial migration and long-term attachment. J. Cell Biol. 157, 873–882. 10.1083/jcb.200203075 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sephton C. F., Good S. K., Atkin S., Dewey C. M., Mayer P., 3R. D., Herz J., et al. (2010). TDP-43 is a developmentally regulated protein essential for early embryonic development. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 6826–6834. 10.1074/jbc.M109.061846 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekmann A. F., Lawson N. D. (2007). Notch signalling limits angiogenic cell behaviour in developing zebrafish arteries. Nature 445, 781–784. 10.1038/nature05577 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons M., Gordon E., Claesson-Welsh L. (2016). Mechanisms and regulation of endothelial VEGF receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 17, 611–625. 10.1038/nrm.2016.87 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel D., Lundkvist A., Sauvaget D., Busse M., Graupera M., Van der Flier A., et al. (2011). Integrin-dependent and -independent functions of astrocytic fibronectin in retinal angiogenesis. Development 138, 4451–4463. 10.1242/dev.071381 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollervey J. R., Curk T., Rogelj B., Briese M., Cereda M., Kayikci M., et al. (2011). Characterizing the RNA targets and position-dependent splicing regulation by TDP-43. Nat. Neurosci. 14, 452–458. 10.1038/nn.2778 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Vazquez J., Gitler A. D., Fraser S. D., Berk J. D., Van N. P., Fishman M. C., et al. (2004). Semaphorin-plexin signaling guides patterning of the developing vasculature. Dev. Cell 7, 117–123. 10.1016/j.devcel.2004.06.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinh L. A., Stainier D. Y. R. (2004). Fibronectin regulates epithelial organization during myocardial migration in zebrafish. Dev. Cell 6, 371–382. 10.1016/s1534-5807(04)00063-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rooijen E., Voest E. E., Logister I., Bussmann J., Korving J., Van Eeden F. J., et al. (2010). von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor mutants faithfully model pathological hypoxia-driven angiogenesis and vascular retinopathies in zebrafish. Dis. Model Mech. 3, 343–353. 10.1242/dmm.004036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E. S., Muro A. F. (2011). Fibronectin splice variants: Understanding their multiple roles in health and disease using engineered mouse models. IUBMB Life 63, 538–546. 10.1002/iub.493 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. S., Cheng W. C., Hou S. C., Yan Y. T., Jiang S. T., Shen C. K. (2010). TDP-43, a neuro-pathosignature factor, is essential for early mouse embryogenesis. Genesis 48, 56–62. 10.1002/dvg.20584 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L.-S., Cheng W.-C., Shen C.-K. J. (2012). Targeted depletion of TDP-43 expression in the spinal cord motor neurons leads to the development of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-like phenotypes in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 27335–27344. 10.1074/jbc.M112.359000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z. S. (2012). Does a loss of TDP-43 function cause neurodegeneration? Mol. Neurodegener. 7, 27. 10.1186/1750-1326-7-27 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Hynes R. O. (1996). Fibronectin receptor functions in embryonic cells deficient in alpha 5 beta 1 integrin can be replaced by alpha V integrins. Mol. Biol. Cell 7, 1737–1748. 10.1091/mbc.7.11.1737 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee C. S., Chandrasekhar A., Halloran M. C., Shoji W., Warren J. T., Kuwada J. Y. (1999). Molecular cloning, expression, and activity of zebrafish semaphorin Z1a. Brain Res. Bull. 48, 581–593. 10.1016/s0361-9230(99)00038-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacchigna S., Lambrechts D., Carmeliet P. (2008). Neurovascular signalling defects in neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 169–181. 10.1038/nrn2336 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlokovic B. V. (2008). The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron 57, 178–201. 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygmunt T., Gay C. M., Blondelle J., Singh M. K., Flaherty K. M., Means P. C., et al. (2011). Semaphorin-PlexinD1 signaling limits angiogenic potential via the VEGF decoy receptor sFlt1. Dev. Cell 21, 301–314. 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.06.033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Tardbpl Morpholino KD in tardbp −/− mutants fully phenocopies the tardbp/tardbpl KO. (A) Western blot indicating successful KD of Tardbpl_tv1protein levels in the wild type and in tardbp −/− mutant background in single embryos (note the high levels of Tardbpl_tv1 in tardbp -/- mutants in lane c compared to wild type in lane a compensating for the loss of Tardbp). Lane e are double homozygous tardbp −/− ; tardbp −/− mutants and in lane f are the corresponding pooled siblings with the genotype tardbp +/- and tardbp +/+; tardbpl −/− loaded. Tubulin serves as a loading control. (B) Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 highlights the vasculature shown in black. KD of Tardbpl in the tardbp-/- is phenotypically indistinguishable from the tardbp-/-; tardbpl-/- mutants (compare d with e). Scale bar 50 μm, anterior to the left. (C) There is no statistically significant difference between tardbp-/-; tardbpl-/- and tardbp-/- Tardbpl KD embryos in the average SA sprout number per somite and the ectopic sprout number per somite. Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’s multiple comparison post test, n ≥ 9, sprouts between boundaries of six somites dorsal to the end of the yolk sack extension were quantified.
Arterial-venous differentiation and Notch target gene expression patterns are unaffected by TDP-43 KD. WISH with antisense probes specific for the Notch target and the arterial-venous differentiation markers ephrin-B2a and flt4 in tardbp-/- ctr MO injected embryos (Control) and their tardbp-/-; Tardbpl KD siblings at 24 hpf (Magnification: ×10 anterior to the left). Depicted are representative images of embryos from one clutch. Experiment was performed with embryos of three independent clutches.
TDP-43 KD in HUVEC does not increase proliferation and shows no activation of the VEGFR2 signaling pathway. (A) Protein content as a measure of cellular survival is statistically significantly decreased upon TDP-43 KD with two TDP-43 targeting shRNAs. One-way ANOVA, n = 30 in three independent experiments. Cell death due to apoptosis and necrosis determined by quantification of LDH release is statistically significantly increased upon TDP-43 KD with two TDP-43 targeting shRNAs. One-way ANOVA, n = 30 in three independent experiments. KD of TDP-43 in HUVEC does not alter proliferation as shown by quantification of percentage of Ki67 positive cells. Unpaired t test, n = 9 in three independent experiments, p-value 0,5519. (B) Expression as well as phosphorylation levels of VEGFR2 signaling pathway components upon VEGF stimulation is not altered upon TDP-43 KD in HUVEC. Immunoblot of TDP-43 demonstrates successful KD upon transduction with shTARDBP#1 (KD) compared to shCtr transduced HUVEC (shCtr). VEGFR2, AKT, p38, PLCG, and ERK1/2 levels are not altered upon TDP-43 KD or upon stimulation with VEGF after 5/15/30 min. Also, phosphorylation levels of VEGFR2, AKT, p38, PLCG, and ERK1/2 are not altered upon TDP-43 KD or upon stimulation with VEGF after 5/15/30 min (pVEGFR2, pp38, pPLCG, pERK1/2). Time point 0 represents baseline levels after deprivation of growth factors before cells were stimulated with VEGF. Calnexin served as a loading control. Depicted is one representative experiment out of three independent experiments.
Full Western blots. (A) Full Western blots for Fig. 4D. (B) Full Western blot for Fig. S3. Boxes contain corresponding membranes used as loading control and for quantification.
Pathways analysis of NGS hits using Webgestalt.
Individual-nucleotide resolution cross-linking immunoprecipitation (iCPLIP), sequence preference of TDP-43 binding in HUVEC and binding sites of TDP-43 to FN1. (A) Autoradiograph of 32P-labelled RNAs in the presence or absence of UV crosslinking and anti-TDP-43 antibody. High and low concentrations of RNase were used to confirm the presence of RNA bound to TDP-43. The asterisk marks the position in the gel corresponding to the size of a TDP-43 monomer. (B) Z-scores of pentamer occurrences surrounding (−30 nt to +30 nt) all TDP-43 cross-linked sites in HUVEC as determined by iCLIP. The sequences of the two most enriched pentamers are depicted. (C) Pie chart depicting the regional distribution of TDP-43 binding sites identified by TDP-43 iCLIP in HUVEC. TDP-43 cross-linked sites in the FN1 transcript as indicated by the TDP-43 iCLIP experiment in HUVEC cells (n = 2).
itgα4 and vcam1KD strategy and MO validation. (A) Scheme illustrating the first three exons and two introns of zebrafish itgα4. Binding of the itgα4 MO (indicated in red) leads to skipping of exon2, as verified by sequence analysis of the resulting lower band at about 100 bp shown in (B). Primers used for amplification are indicated by black arrows. B) PCR products of cDNA from ctr MO injected (-) or itgα4 MO injected (+) siblings of the embryos used in the rescue experiment shown in Figure 6. Injection of itgα4 MO leads to appearance of a second, lower migrating band representing itgα4 RNA lacking exon2. The upper band represents the normally spliced itgα4 RNA with exon1, 2, and 3. Bands were sequencing confirmed, revealing a frame shift resulting from exon skipping leading to a premature stop codon. (C) Scheme illustrating the first two exons and first intron of vcam1. Binding of the vcam1 MO (indicated in red) leads to partial inclusion of intron1 resulting in two RNAs with different length (see D). This was verified by sequence analysis. Primers used for amplification are indicated by black arrows. (D) PCR products of cDNA from ctr MO injected (-) or vcam1 MO injected (+) siblings of the embryos used in the rescue experiment shown in Figure 6. Injection of vcam1 MO leads to appearance of a second and third, higher migrating band representing vcam1 RNA with partial intron1 inclusion. The lowest band represents the normally spliced vcam1 RNA with exon1 and 2. Bands were sequence confirmed, revealing a frame shift resulting from partial exon inclusion leading to a premature stop codon.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found as follows: The analysis as presented in Supplementary Figure S6 was processed by the iCount software (https://github.com/tomazc/iCount). Original iCLIP data is deposited at: https://imaps.goodwright.com/collections/993546811444/, https://imaps.goodwright.com/collections/285935488641/. The RNA sequencing data is deposited at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE233588.