Abstract
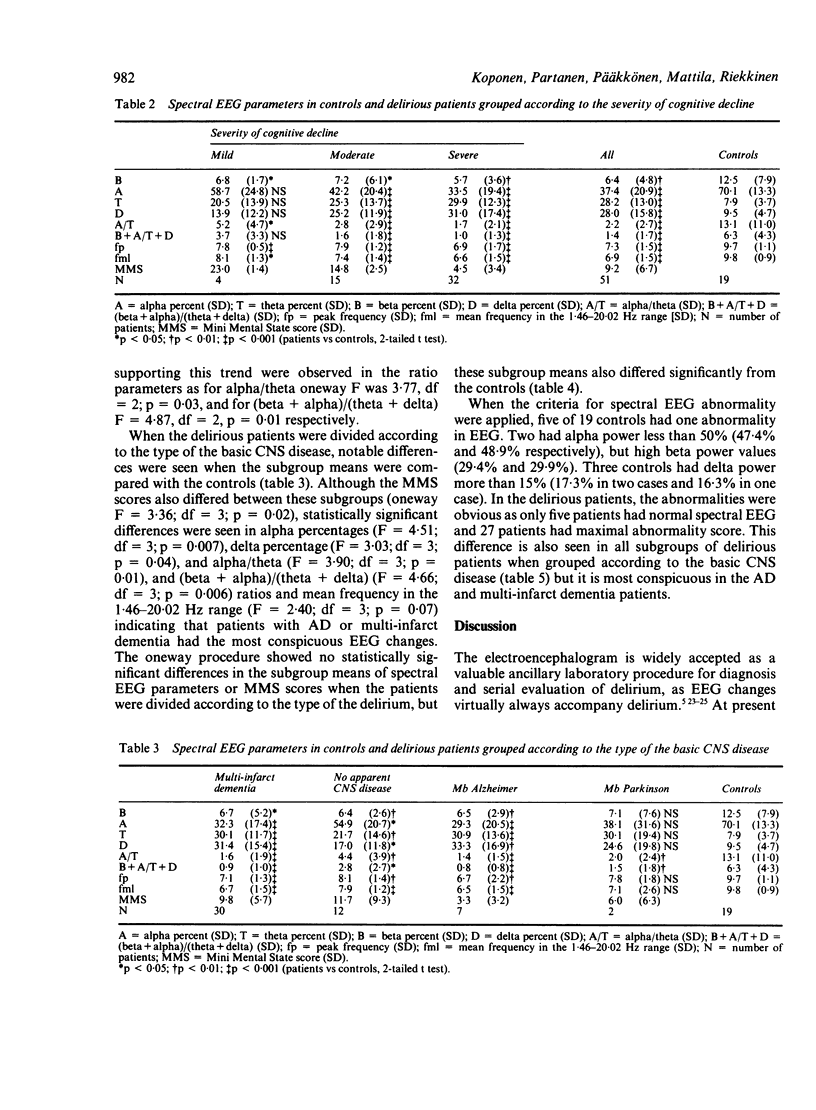
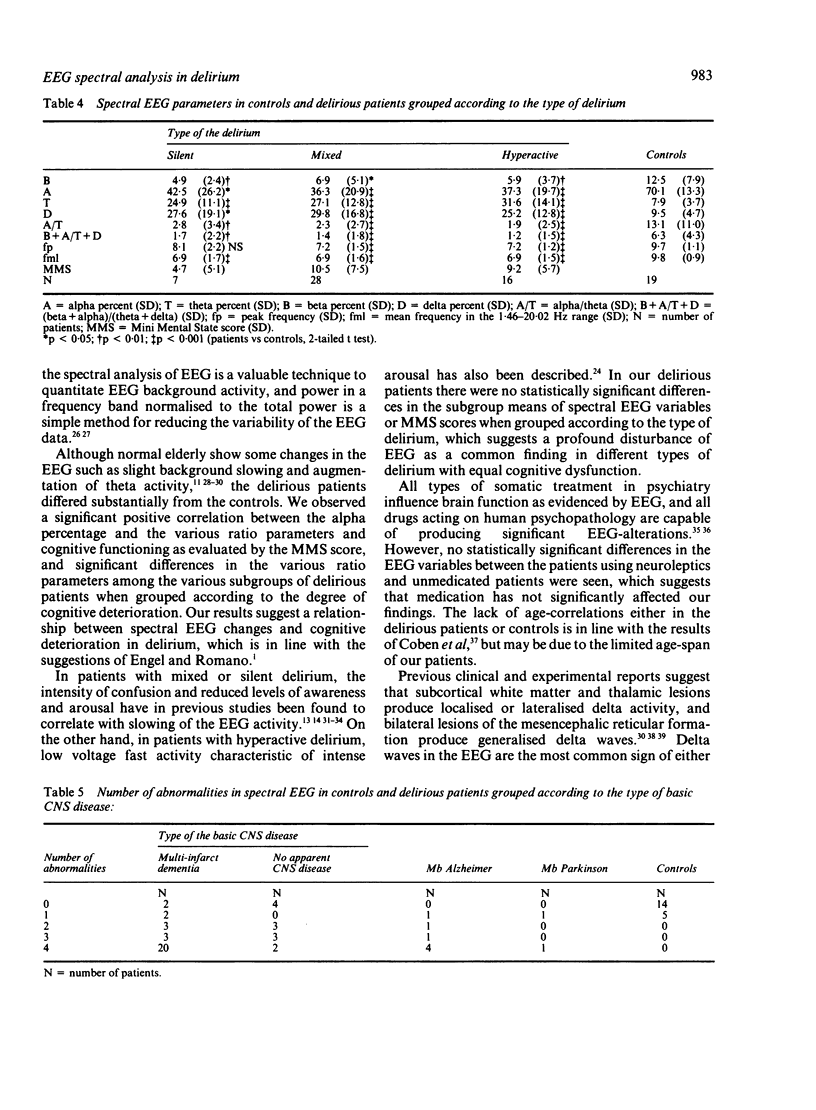
Spectral analysis of EEG was conducted for 51 elderly delirious patients meeting the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders III (DSM-III) criteria and for 19 controls. As a whole group, and also when subdivided according to the type of delirium, severity of cognitive decline or the type of central nervous system disease, delirious patients showed significant reductions of alpha percentage, increased theta and delta activity and slowing of the peak and mean frequencies and these changes were also obvious in individual recordings. The alpha percentage and various ratio parameters correlated significantly with Mini Mental State score, and delta percentage and mean frequency with the lengths of delirium and hospitalisation. The results indicate an association between spectral EEG changes and severity of cognitive deterioration in delirium.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andriola M. R. Role of the EEG in evaluating central nervous system dysfunction. Geriatrics. 1978 Feb;33(2):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse E. W., Wang H. S. The value of electroencephalography in geriatrics. Geriatrics. 1965 Nov;20(11):906–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coben L. A., Danziger W., Storandt M. A longitudinal EEG study of mild senile dementia of Alzheimer type: changes at 1 year and at 2.5 years. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1985 Aug;61(2):101–112. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(85)91048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy F. H., Albert M. S., McAnulty G. Brain electrical activity in patients with presenile and senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Ann Neurol. 1984 Oct;16(4):439–448. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGEL G. L., ROMANO J. Delirium, a syndrome of cerebral insufficiency. J Chronic Dis. 1959 Mar;9(3):260–277. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(59)90165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erkinjuntti T., Larsen T., Sulkava R., Ketonen L., Laaksonen R., Palo J. EEG in the differential diagnosis between Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. Acta Neurol Scand. 1988 Jan;77(1):36–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1988.tb06971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaquinto S., Nolfe G. The EEG in the normal elderly: a contribution to the interpretation of aging and dementia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1986 Jun;63(6):540–546. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(86)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloor P., Ball G., Schaul N. Brain lesions that produce delta waves in the EEG. Neurology. 1977 Apr;27(4):326–333. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.4.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon E. B., Sim M. The E.E.G. in presenile dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1967 Jun;30(3):285–291. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.30.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itil T., Fink M. Anticholinergic drug-induced delirium: experimental modification, quantitative EEG and behavioral correlations. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1966 Dec;143(6):492–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johannesson G., Hagberg B., Gustafson L., Ingvar D. H. EEG and cognitive impairment in presenile dementia. Acta Neurol Scand. 1979 May;59(5):225–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1979.tb02933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaszniak A. W., Garron D. C., Fox J. H., Bergen D., Huckman M. Cerebral atrophy, EEG slowing age, education, and cognitive functioning in suspected dementia. Neurology. 1979 Sep;29(9 Pt 1):1273–1279. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.9_part_1.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klass D. W., Westmoreland B. F. Nonepileptogenic epileptiform electroencephalographic activity. Ann Neurol. 1985 Dec;18(6):627–635. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipowski Z. J. Delirium (acute confusional states). JAMA. 1987 Oct 2;258(13):1789–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipowski Z. J. Organic brain syndromes: a reformulation. Compr Psychiatry. 1978 Jul-Aug;19(4):309–322. doi: 10.1016/0010-440x(78)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipowski Z. J. Transient cognitive disorders (delirium, acute confusional states) in the elderly. Am J Psychiatry. 1983 Nov;140(11):1426–1436. doi: 10.1176/ajp.140.11.1426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millaud F. Electroencéphalographie et syndrome confusionnel dans un centre hospitalier spécialisé en psychiatrie. Encephale. 1986 Sep-Oct;12(5):273–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. F., Schwartz G. Electroencephalograms and autopsy findings in geropsychiatry. J Gerontol. 1978 Jul;33(4):504–513. doi: 10.1093/geronj/33.4.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuwer M. R. Quantitative EEG: I. Techniques and problems of frequency analysis and topographic mapping. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1988 Jan;5(1):1–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuwer M. R. Quantitative EEG: II. Frequency analysis and topographic mapping in clinical settings. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1988 Jan;5(1):45–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OBRIST W. D. The electroencephalogram of normal aged adults. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1954 May;6(2):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(54)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrecht R., Okhomina F. O., Scott D. F. Value of EEG in acute confusional states. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1979 Jan;42(1):75–77. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.42.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttilä M., Partanen J. V., Soininen H., Riekkinen P. J. Quantitative analysis of occipital EEG in different stages of Alzheimer's disease. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1985 Jan;60(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(85)90942-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pro J. D., Wells C. E. The use of the electroencephalogram in the diagnosis of delirium. Dis Nerv Syst. 1977 Oct;38(10):804–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabins P. V., Folstein M. F. Delirium and dementia: diagnostic criteria and fatality rates. Br J Psychiatry. 1982 Feb;140:149–153. doi: 10.1192/bjp.140.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaul N., Green L., Peyster R., Gotman J. Structural determinants of electroencephalographic findings in acute hemispheric lesions. Ann Neurol. 1986 Dec;20(6):703–711. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soininen H., Partanen J., Laulumaa V., Helkala E. L., Laakso M., Riekkinen P. J. Longitudinal EEG spectral analysis in early stage of Alzheimer's disease. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1989 Apr;72(4):290–297. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(89)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soininen H., Partanen V. J., Helkala E. L., Riekkinen P. J. EEG findings in senile dementia and normal aging. Acta Neurol Scand. 1982 Jan;65(1):59–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1982.tb03062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J., MacFabe D. F., Vanderwolf C. H. Cholinergic activation of the electrocorticogram: role of the substantia innominata and effects of atropine and quinuclidinyl benzilate. Brain Res. 1984 Nov 26;322(2):219–232. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderwolf C. H., Gutman M., Baker G. B. Hypothalamic self-stimulation: the role of dopamine and possible relations to neocortical slow wave activity. Behav Brain Res. 1984 Apr;12(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(84)90198-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Sweden B. Neuroleptic neurotoxicity; electro-clinical aspects. Acta Neurol Scand. 1984 Mar;69(3):137–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1984.tb07792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


