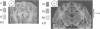Abstract
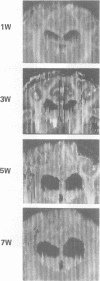
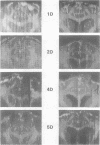
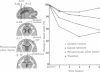
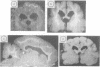
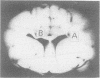
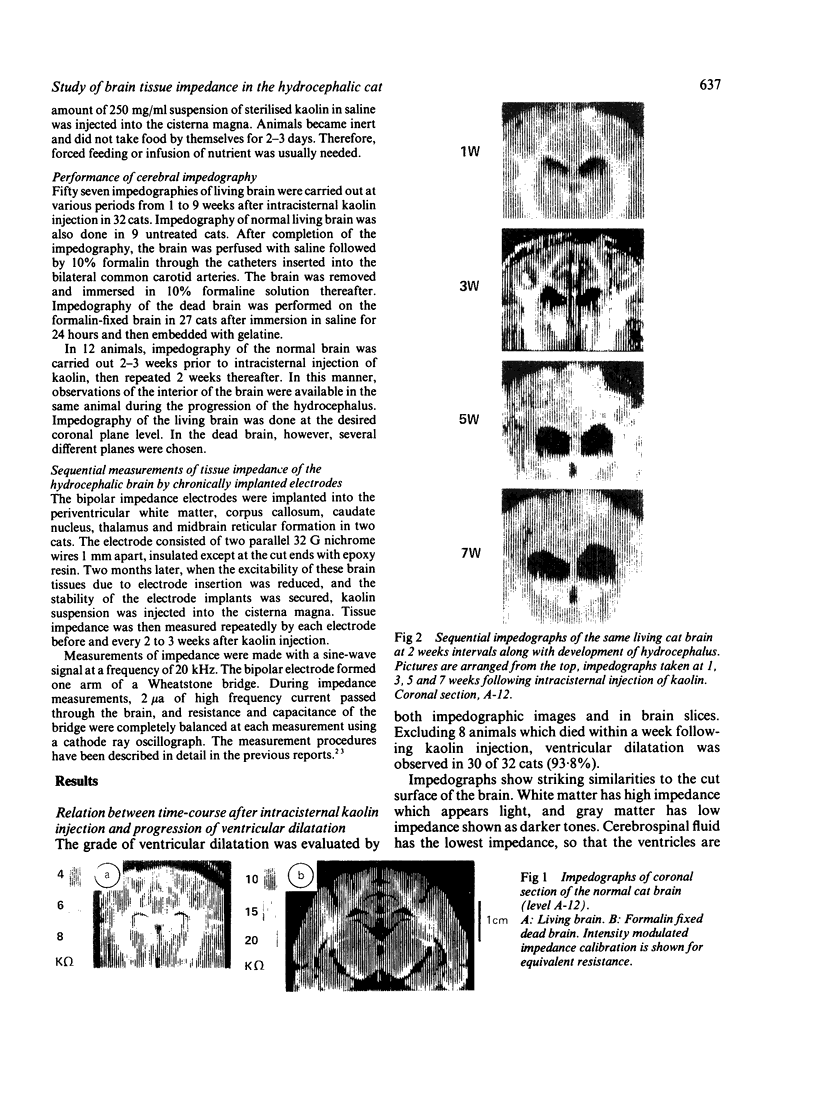
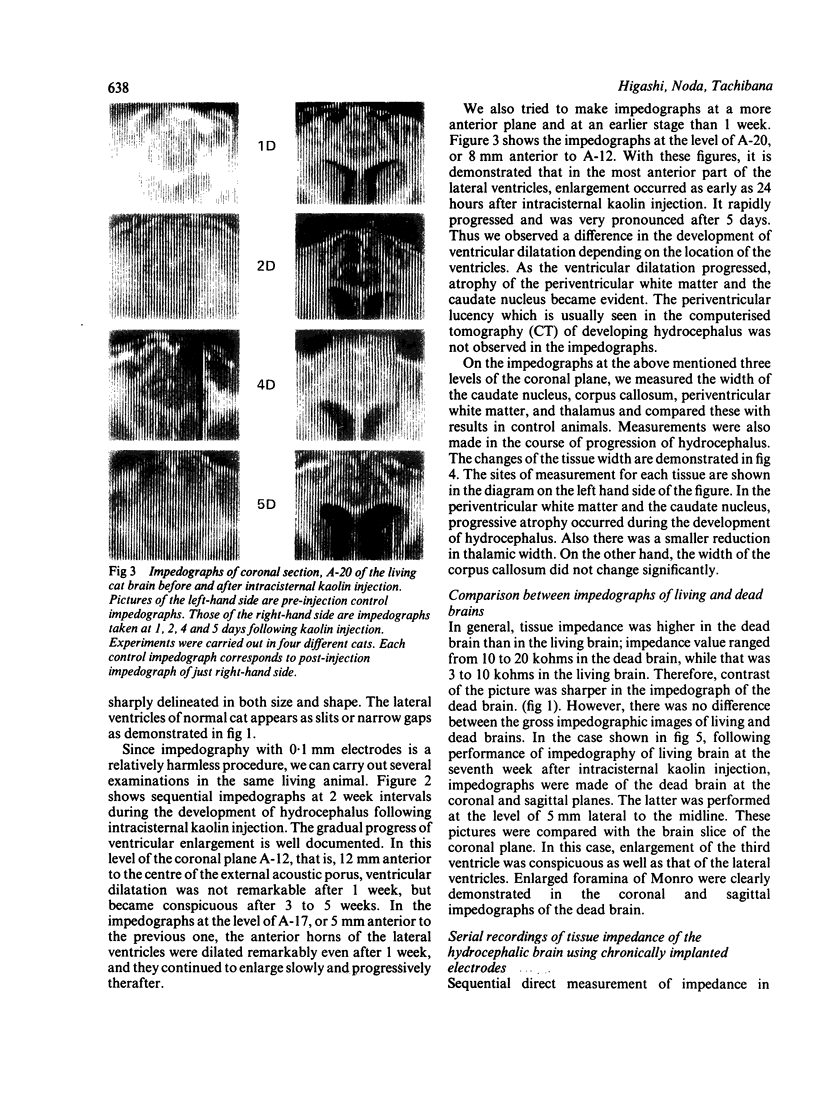
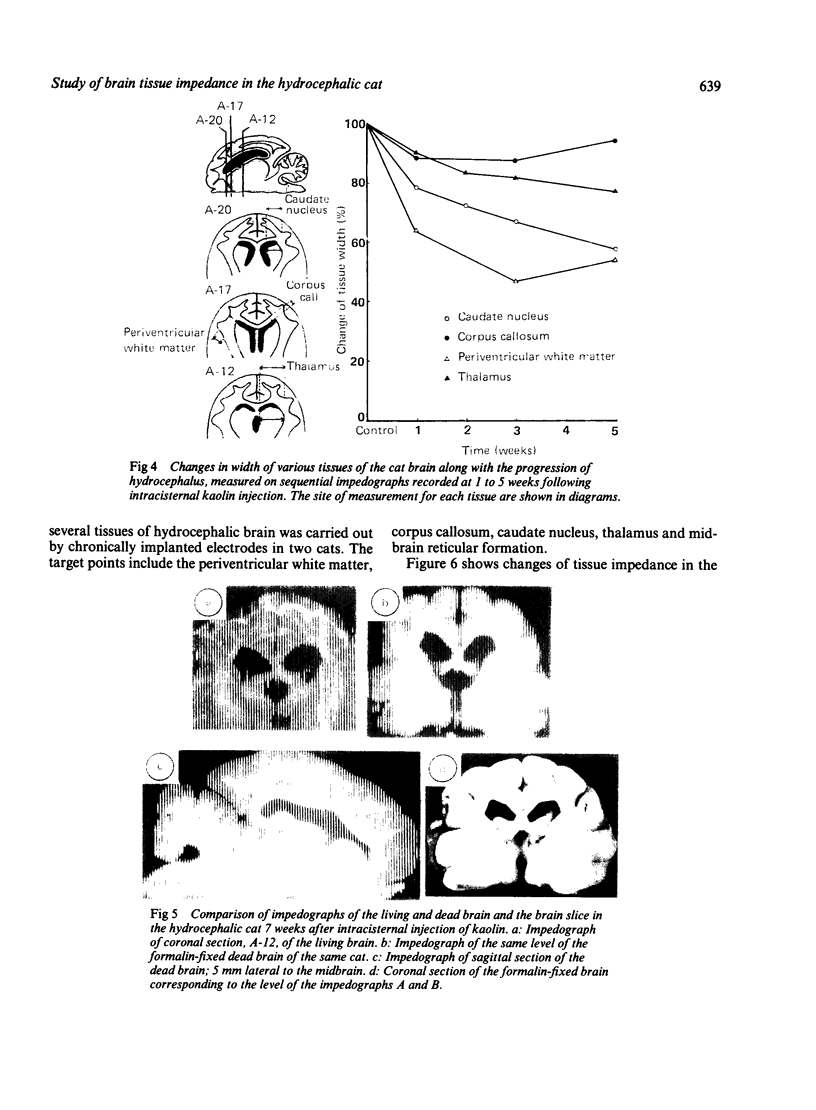
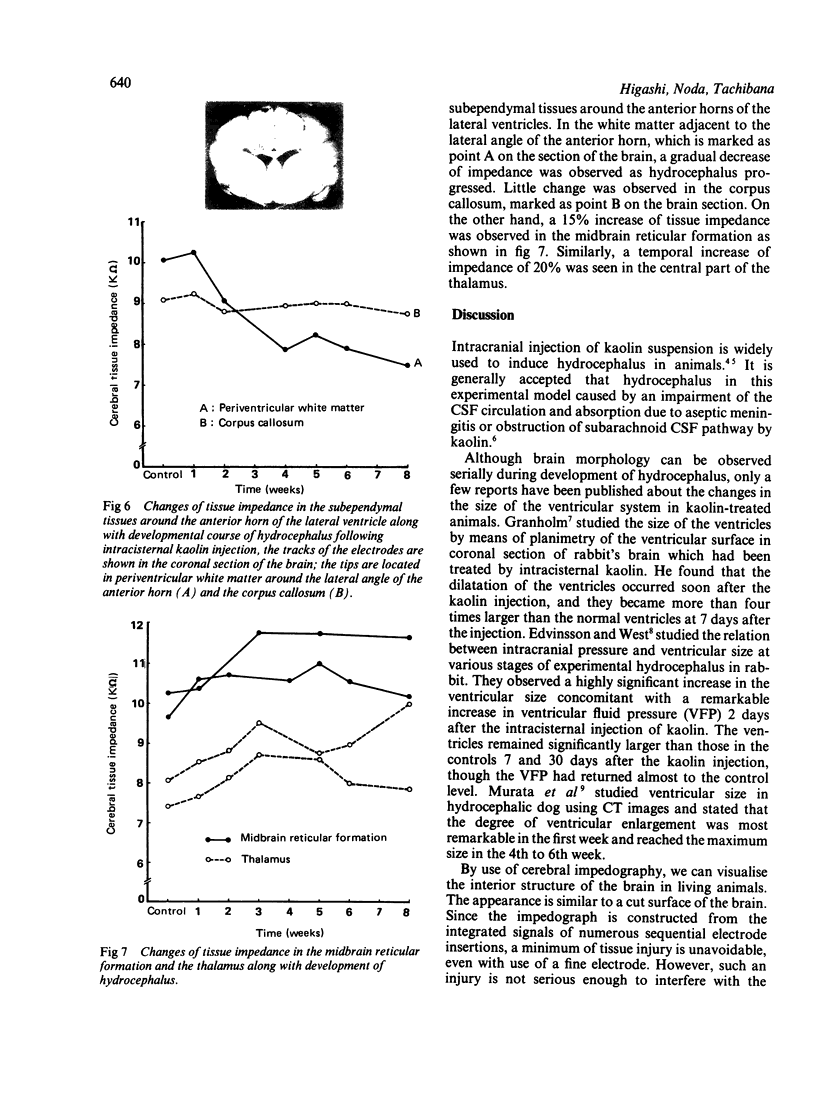
Impedographic studies were made in cats made hydrocephalic by intracisternal kaolin. Enlargement of the anterior horns preceded that of the body of the lateral ventricles, and there was a selectivity to pressure atrophy among different tissues within the brain. Furthermore, sequential measurement of impedance using chronically implanted electrodes demonstrated a gradual decrease of impedance in the periventricular white matter during the development of hydrocephalus, suggesting an expansion of the extracellular space in the tissue around the ventricular wall.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERING E. A., Jr, SATO O. HYDROCEPHALUS: CHANGES IN FORMATION AND ABSORPTION OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID WITHIN THE CEREBRAL VENTRICLES. J Neurosurg. 1963 Dec;20:1050–1063. doi: 10.3171/jns.1963.20.12.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRZIS L., TACHIBANA S. Measurement of local cerebral blood flow by impedance changes. Life Sci. 1962 Nov;1:587–598. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(62)90090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birzis L. Impedance of a measure of flow velocity in salt solutions. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Jan;21(1):329–333. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.1.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., West K. A. Relation between intracranial pressure and ventricular size at various stages of experimental hydrocephalus. Acta Neurol Scand. 1971;47(4):451–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1971.tb07499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazendam J., Go K. G., Van der Meer J. J., Zuiderveen F. Changes of electrical impedance in edematous cat brain during hypoxia and after intracerebral ouabain injection. Exp Neurol. 1979 Oct;66(1):78–87. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(79)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granholm L. Induced reversibility of ventricular dilatation in experimental hydrocephalus. Acta Neurol Scand. 1966;42(5):581–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1966.tb01209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochwald G. M., Sahar A., Sadik A. R., Ransohoff J. Cerebrospinal fluid production and histological observations in animals with experimental obstructive hydrocephalus. Exp Neurol. 1969 Oct;25(2):190–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laatikainen T. Excretion of neutral steroid hormones in human bile. Ann Clin Res. 1970;2(Suppl):1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen L., Johansson G. G., Sipponen P. Impedance and phase angle as a locating method in human stereotaxic surgery. J Neurosurg. 1966 Dec;25(6):628–633. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.25.6.0628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. L., Bak A. F., Parker L. O. Specific resistivity of the cerebral cortex and white matter. Exp Neurol. 1968 Apr;20(4):544–557. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Murata T., Nakano Y., Handa H. Periventricular lucency in hydrocephalus on computerized tomography. Surg Neurol. 1977 Nov;8(5):337–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata T., Mori K., Handa H., Nakano Y. [Computed tomography on experimental canine hydrocephalus. Part I. Observations on changes of ventricular size and periventricular lucency (author's transl)]. No To Shinkei. 1978 Jun;30(6):677–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCHS S., VAN HARREVELD A. Cerebral impedance changes after circulatory arrest. Am J Physiol. 1956 Sep;187(1):180–192. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.1.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Organ L., Tasker R. R., Moody N. F. Brain tumor localization using an electrical impedance technique. J Neurosurg. 1968 Jan;28(1):35–44. doi: 10.3171/jns.1968.28.1.0035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANCK J. B., Jr Specific impedance of rabbit cerebral cortex. Exp Neurol. 1963 Feb;7:144–152. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4886(63)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHURR P. H., MCLAURIN R. L., INGRAHAM F. D. Experimental studies on the circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid and methods of producing communicating hydrocephalus in the dog. J Neurosurg. 1953 Sep;10(5):515–525. doi: 10.3171/jns.1953.10.5.0515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana S., Aguilar J. A., Birzis L. Scanning the interior of living brain by impedography. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Apr;28(4):534–539. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.4.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana S. Homeostatic mechanisms in the hypothalamus. Brain Res. 1969 May;13(3):522–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana S. Impedance study of brain tissue changes after penetrating injury. Exp Neurol. 1971 Aug;32(2):206–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(71)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANHARREVELD A., CROWELL J., MALHOTRA S. K. A STUDY OF EXTRACELLULAR SPACE IN CENTRAL NERVOUS TISSUE BY FREEZE-SUBSTITUTION. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:117–137. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen P. H., Zuiderveen G. G., Buiter D., van der Meer J. Electrical impedance of cat brain with cold-induced edema. Exp Neurol. 1973 Sep;40(3):675–682. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(73)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]