Abstract
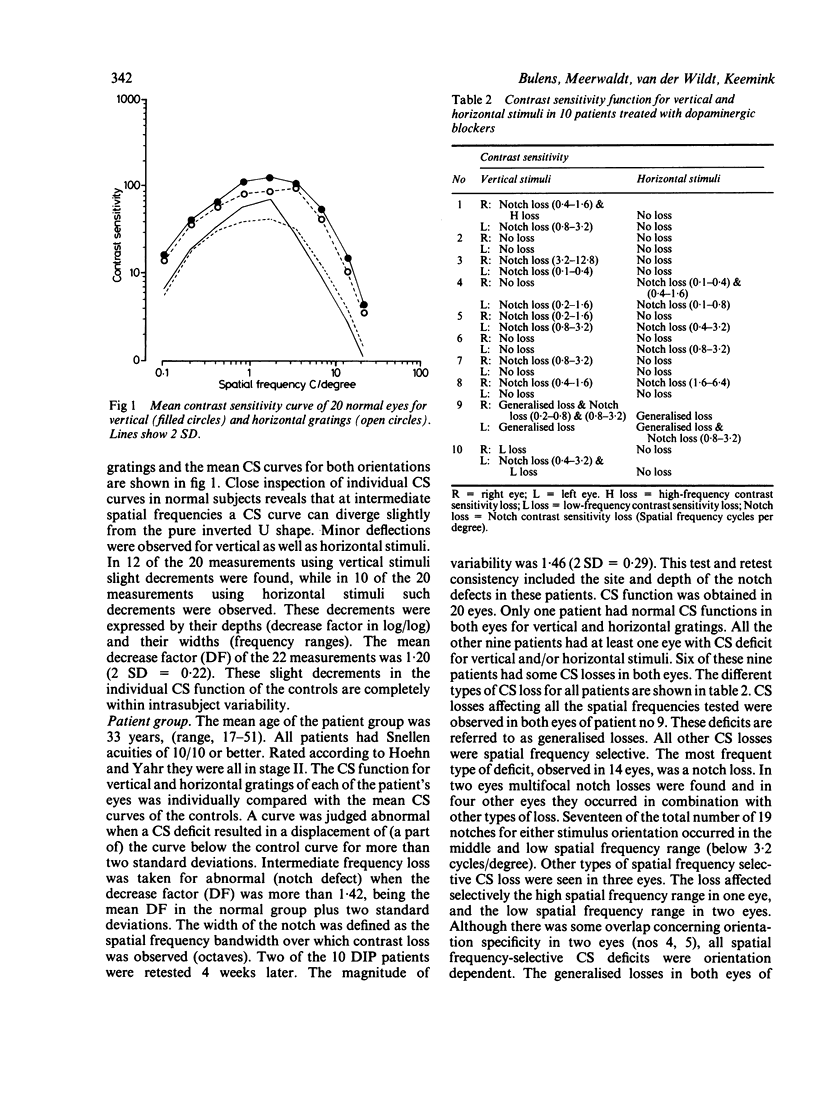
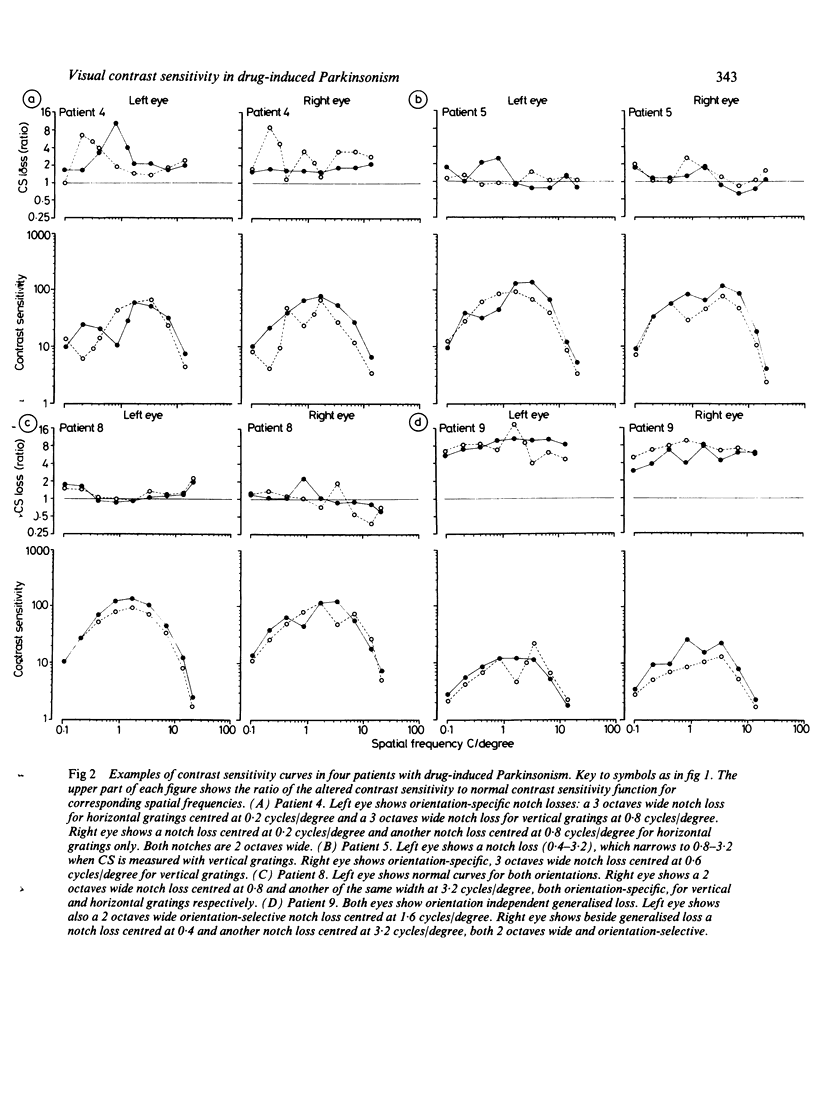
The influence of stimulus orientation on contrast sensitivity function was studied in 10 patients with drug-induced Parkinsonism. Nine of the 10 patients had at least one eye with contrast sensitivity deficit for vertical and/or horizontal stimuli. Only generalised contrast sensitivity loss, observed in two eyes, was stimulus orientation independent. All spatial frequency-selective contrast deficits in 15 eyes were orientation dependent. The striking similarity between the pattern of contrast sensitivity loss in drug-induced Parkinsonism and that in idiopathic Parkinson's disease, suggests that generalised dopaminergic deficiency, from whatever cause, affects visual function in an analogous way.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbeau A., Campanella G., Butterworth R. F., Yamada K. Uptake and efflux of 14-C-dopamine in platelets: evidence for a generalized defect in Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1975 Jan;25(1):1–9. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodis-Wollner I., Yahr M. D. Measurements of visual evoked potentials in Parkinson's disease. Brain. 1978 Dec;101(4):661–671. doi: 10.1093/brain/101.4.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodis-Wollner I., Yahr M. D., Mylin L., Thornton J. Dopaminergic deficiency and delayed visual evoked potentials in humans. Ann Neurol. 1982 May;11(5):478–483. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulens C., Meerwaldt J. D., Van der Wildt G. J. Effect of stimulus orientation on contrast sensitivity in Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1988 Jan;38(1):76–81. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulens C., Meerwaldt J. D., Van der Wildt G. J., Van Deursen J. B. Effect of levodopa treatment on contrast sensitivity in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol. 1987 Sep;22(3):365–369. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulens C., Meerwaldt J. D., van der Wildt G. J., Keemink C. J. Contrast sensitivity in Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1986 Aug;36(8):1121–1125. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.8.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase T. N., Schnur J. A., Gordon E. K. Cerebrospinal fluid monoamine catabolites in drug-induced extrapyramidal disorders. Neuropharmacology. 1970 May;9(3):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(70)90075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederick J. M., Rayborn M. E., Laties A. M., Lam D. M., Hollyfield J. G. Dopaminergic neurons in the human retina. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Sep 1;210(1):65–79. doi: 10.1002/cne.902100108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn M. M., Yahr M. D. Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology. 1967 May;17(5):427–442. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.5.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy H., Martin K. A., Orban G. A., Whitteridge D. Receptive field properties of neurones in visual area 1 and visual area 2 in the baboon. Neuroscience. 1985 Feb;14(2):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan D., Maxner C. Orientation-selective visual loss in patients with Parkinson's disease. Brain. 1987 Apr;110(Pt 2):415–432. doi: 10.1093/brain/110.2.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


