Abstract
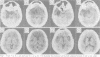
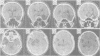
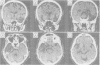
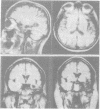
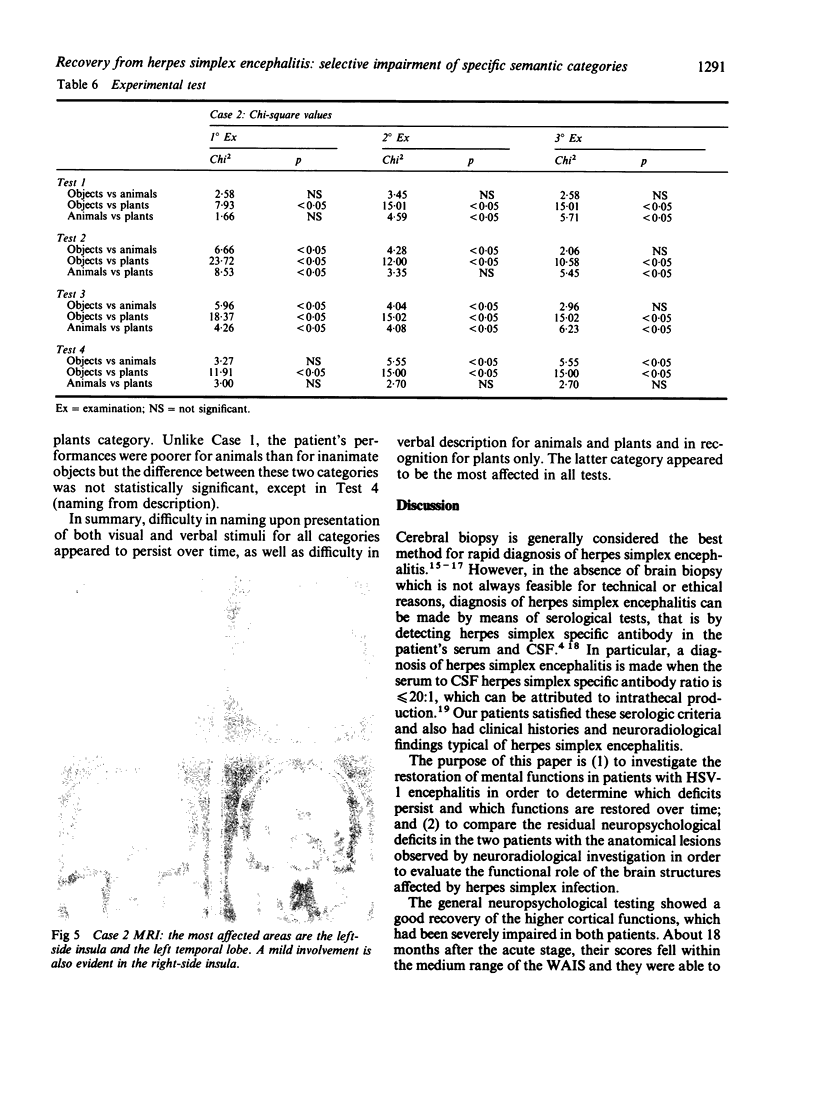
The clinical, neuropsychological and neuroradiological features of two patients affected by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) encephalitis are described. An experimental study for the assessment of naming, recognition and description displayed in one patient a persistent significant impairment in naming living things. The other patient showed a failing "semantic memory" for the same categories, although a significant impairment emerged only for plants. In both patients, the late neuroradiological sequelae were localised mainly in the inferior and middle gyri of the left temporal lobe and in the left-side insula. In one patient, the right-side insula was also involved. The selective cerebral damage induced by HSV-1 is stressed and a correlation between the neuroradiological and neuropsychological findings is attempted. The stereotyped anatomical and neuropsychological changes lead to the belief that the virus may recognise, within the limbic system, particular cellular "strains" on the basis of their molecular specificity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Damasio A. R., Van Hoesen G. W. The limbic system and the localisation of herpes simplex encephalitis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1985 Apr;48(4):297–301. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.48.4.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. M., Davis K. R., Kleinman G. M., Kirchner H. S., Taveras J. M. Computed tomography of herpes simplex encephalitis, with clinicopathological correlation. Radiology. 1978 Nov;129(2):409–417. doi: 10.1148/129.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enzmann D. R., Ranson B., Norman D., Talberth E. Computed tomography of herpes simplex encephalitis. Radiology. 1978 Nov;129(2):419–425. doi: 10.1148/129.2.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., Olson L. C., Buescher E. L. Herpes simplex virus infections of the nervous system. Problems in laboratory diagnosis. Arch Neurol. 1968 Mar;18(3):260–264. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470330050004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. M., Zimmerman R. D., Leeds N. E. Computed tomography in Herpes simplex encephalitis. Neurology. 1979 Oct;29(10):1392–1396. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.10.1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper P. E., Laing I., Longson M. Rapid non-invasive diagnosis of herpes encephalitis. Lancet. 1981 Sep 19;2(8247):607–609. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92744-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskiniemi M., Vaheri A., Taskinen E. Cerebrospinal fluid alterations in herpes simplex virus encephalitis. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;6(5):608–618. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.5.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt P. A monoclonal antibody to limbic system neurons. Science. 1984 Jan 20;223(4633):299–301. doi: 10.1126/science.6199842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Whitley R. J., Visintine A. N., Takei Y., Alford C. A., Jr Herpes simplex virus encephalitis: laboratory evaluations and their diagnostic significance. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):829–836. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbling G., Link H., Ohman S. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. I. Establishment of reference values. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):385–390. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington E. K., McCarthy R. Category specific access dysphasia. Brain. 1983 Dec;106(Pt 4):859–878. doi: 10.1093/brain/106.4.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington E. K., Shallice T. Category specific semantic impairments. Brain. 1984 Sep;107(Pt 3):829–854. doi: 10.1093/brain/107.3.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington E. K., Shallice T. Semantic access dyslexia. Brain. 1979 Mar;102(1):43–63. doi: 10.1093/brain/102.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington E. K. The selective impairment of semantic memory. Q J Exp Psychol. 1975 Nov;27(4):635–657. doi: 10.1080/14640747508400525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R. J., Soong S. J., Dolin R., Galasso G. J., Ch'ien L. T., Alford C. A. Adenine arabinoside therapy of biopsy-proved herpes simplex encephalitis. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases collaborative antiviral study. N Engl J Med. 1977 Aug 11;297(6):289–294. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197708112970601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R. J., Soong S. J., Hirsch M. S., Karchmer A. W., Dolin R., Galasso G., Dunnick J. K., Alford C. A. Herpes simplex encephalitis: vidarabine therapy and diagnostic problems. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 5;304(6):313–318. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102053040602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]