Abstract
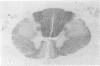
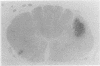
The spinal cords of 10 cases of motor neuron disease were compared with those of six age-matched controls using myelin and silver impregnation methods, and the Marchi reaction for myelin degradation products. These studies revealed striking asymmetry in involvement of the lateral and anterior corticospinal tracts, without concordance in the pattern of involvement of these crossed and uncrossed corticospinal pathways. In addition there was prominent involvement of the posterior and anterior spinocerebellar tracts, but less marked abnormality was seen in the reticulospinal pathways. These findings highlight the asymmetrical involvement of the upper and lower motor neuron components of the motor system that is a characteristic feature of the disease, and demonstrate that involvement of the spinocerebellar system is a frequent finding.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Averback P., Crocker P. Regular involvement of Clarke's nucleus in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1982 Mar;39(3):155–156. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510150025006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell B., Oppenheimer D. R., Hughes J. T. The central nervous system in motor neurone disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Jun;33(3):338–357. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.3.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck P. J., Stevens J. C., Mulder D. W., Espinosa R. E. Frequency of nerve fiber degeneration of peripheral motor and sensory neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Morphometry of deep and superficial peroneal nerves. Neurology. 1975 Aug;25(8):781–785. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.8.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Kurland L. T., Sayre G. P. Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. A subgroup characterized by posterior and spinocerebellar tract involvement and hyaline inclusions in the anterior horn cells. Arch Neurol. 1967 Mar;16(3):232–243. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470210008002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. T. Pathology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Adv Neurol. 1982;36:61–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWYER T., Jr, NETSKY M. G. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1953 Feb;69(2):171–192. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1953.02320260029002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li T. M., Day S. J., Alberman E., Swash M. Differential diagnosis of motoneurone disease from other neurological conditions. Lancet. 1986 Sep 27;2(8509):731–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder D. W., Bushek W., Spring E., Karnes J., Dyck P. J. Motor neuron disease (ALS): evaluation of detection thresholds of cutaneous sensation. Neurology. 1983 Dec;33(12):1625–1627. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.12.1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH M. C. Observations on the extended use of the Marchi method. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1956 May;19(2):67–73. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.19.2.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. S., Stålberg E., Swash M. Pattern of segmental motor involvement in syringomyelia: a single fibre EMG study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 Feb;43(2):150–155. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swash M., Leader M., Brown A., Swettenham K. W. Focal loss of anterior horn cells in the cervical cord in motor neuron disease. Brain. 1986 Oct;109(Pt 5):939–952. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.5.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandan R., Bradley W. G. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Part 1. Clinical features, pathology, and ethical issues in management. Ann Neurol. 1985 Sep;18(3):271–280. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandan R., Bradley W. G. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Part 2. Etiopathogenesis. Ann Neurol. 1985 Oct;18(4):419–431. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]