Abstract
Purpose
High grade pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas (HGPXAs) are very rare and their management and prognostic outcomes remain unclear. To better understand the disease, we aimed to evaluate the risk factors for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), and propose a treatment protocol based on cases from our institute and cases from the literature.
Methods
The authors reviewed the clinical data of 26 patients with HGPXAs who underwent surgical treatment in Department of Neurosurgery of Beijing Tiantan Hospital between August 2014 and September 2021. We also searched the PubMed database using the keywords “anaplastic” combined with “pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma(s)” between January 1997 and October 2022. Risk factors for PFS and OS were evaluated in the pooled cases.
Results
The authors’ cohort included 11 males and 15 females with a mean age of 36.7 ± 20.3 years (range: 5.5-71 years). Gross-total resection (GTR) and non-GTR were achieved in 17 (65.4%) and 9 (34.6%) patients, respectively. Radiotherapy and chemotherapy were administered to 22 and 20 patients, respectively. After a mean follow-up of 20.5 ± 21.2 months (range: 0.5-78.1 months), 7 patients suffered tumor recurrence and 6 patients died with a mean OS time of 19.4 ± 10.8 months (range: 8-36 months). In the literature between January 1997 and October 2022, 56 cases of HGPXAs were identified in 29 males and 27 females with a mean age of 29.6 ± 19.6 years (range; 4-74 years). Among them, 24 (44.4%) patients achieved GTR. Radiotherapy and chemotherapy was administered to 31 (62%) patients and 23 (46%) patients, respectively. After a median follow-up of 31.4 ± 35.3 months (range: 0.75-144 months), the mortality and recurrence rates were 32.5% (13/40) and 70% (28/40), respectively. Multivariate Cox regression model demonstrated that non-GTR (HR 0.380, 95% CI 0.174-0.831, p=0.015), age≥30 (HR 2.620, 95% CI 1.183-5.804, p=0.018), no RT (HR 0.334,95% CI 0.150-0.744, p=0.007) and no CT (HR 0.422, 95% CI 0.184-0.967, p=0.042) were negative prognostic factors for PFS. Non-GTR (HR 0.126, 95% CI 0.037-0.422, p=0.001), secondary HGPXAs (HR 7.567, 95% CI 2.221-25.781, p=0.001), age≥30 (HR 3.568, 95% CI 1.190-10.694, p=0.023) and no RT (HR 0.223,95% CI 0.073-0.681, p=0.008) were risk factors for OS.
Conclusion:
High grade pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas are very rare brain tumors. Children and younger adults have better clinical outcome than elderly patients. Secondary HGPXAs had worse OS than primary HGPXAs. Complete surgical excision plus RT and CT is recommended for this entity. The frequency of BRAF mutations in HGPXAs is 47.5% (19/40) in this study, however, we do not find the connections between BRAF mutations and clinical outcomes. Future studies with larger cohorts are necessary to verify our findings.
Keywords: high grade, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, gross-total resection, radiotherapy, chemotherapy
Introduction
Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas (PXAs) are rare brain tumors which often occur in children and young adults (1–3). In 1999, Giannini et al. defined ‘PXA with anaplastic features’ as PXA exhibiting increased mitotic activity, >5/10 HPF mitotic figures with or without accompanying necrosis (4). ‘PXA with anaplastic features’ are labelled as anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, according to the 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System (3). In the fifth edition of the WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System, the term “anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma” is no longer listed, however, according to histopathological features of PXA, this entity can still be classified into WHO grade 2 or WHO grade 3 tumors (5). The clinical prognosis of patients with PXAs is usually satisfactory, with a 5-year survival rate of 80% (6). However, patients with HGPXAs have a worse clinical outcome than patients with PXAs (7). Due to the rarity of the tumor, their management and prognostic outcomes remain unclear. In this study, we reported 26 cases with HGPXAs in our institute and performed a pooled analysis of individual data (including cases from our institute and 56 cases from the literature) to propose a treatment protocol.
Methods
We performed a retrospective analysis of 26 cases of high grade pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas (HGPXAs). All the patients accepted surgery in Beijing Tiantan Hospital between August 2014 and September 2021. The following clinical data were included: age, sex, imaging characteristics, extent of tumor resection, histopathological results, treatment protocol and outcomes. Pre- and postoperative MRI images were performed to evaluate the extent of tumor excision, which was defined as gross total resection (GTR) and non-GTR. The follow-up was performed by telephone interview every six months. This research was approved by the Beijing Tiantan Hospital Research Ethics Committee. The pathological diagnosis of HGPXAs was confirmed by the Department of Neuropathology at Beijing Neurosurgical Institute according to the 2021 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System. Histopathological examination showed malignant glial component with numerous mitoses. Eosinophilic granules and ribosome-lamellar complexes can be observed under the light microscope, which are characteristic features of PXA. All cases exhibiting increased mitotic activity, >5/10 HPF mitotic figures with or without accompanying necrosis. The mutation status of BRAF, IDH, and TERT promoter, the methylation status of the MGMT promoter, and the co-deletion status of 1p/19q were also assessed in some of our cases.For the pooled analysis of HGPXAs, we performed a search in the PubMed database between January 1997 and October 2022. The keyword used was “anaplastic” combined with “pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma(s)” and a total of 56 cases were included. All cases were pathologically diagnosed as “anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma”, which were classified into WHO grade 3 PXAs.
Cox regression models were used to evaluate variables and their association with PFS and OS. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to determine the OS and PFS differences with p-values calculated from the log-rank test. Analyses were performed using SPSS Statistical Package software with the significant set at p < 0.05.
Results
Cases from our institute
The author’s cohort included 11 males and 15 females with an average age of 36.7 ± 20.3 years (range: 5.5-71 years). Preoperative seizure was observed in 8 (30.8%) patients. 22 patients experienced primary HGPXAs, 4 patients suffered malignant transformation of previous PXAs. The lesion locations included temporal lobe (n=13), frontal lobe (n=3), occipital lobe (n=2), parietal lobe (n=2), frontal-parietal lobe (n=2), parietal-occipital (n=1), lateral ventricle (n=1), brainstem (n=1), cerebellopontine angle area (n=1). The morphology was classified as solid (n=16) and cystic-solid (n=10). MRI scans showed that peritumoral edema was significant in 21 (80.8%) patients and enhancement was observed in 25 (96.2%) patients. All patients accepted surgical treatment in our hospital. Gross-total resection (GTR) and non-GTR were achieved in 17 (65.4%) and 9 (34.6%) patients, respectively. Combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy was administered to 19 (73.1%) patients, radiotherapy alone was administered to 3 (11.5%) patients, chemotherapy alone was administered to 1 (3.9%) patient and 3 (11.5%) patients did not undergo any adjuvant therapy. After a median follow-up of 20.5 ± 21.2 months (range: 0.5-78.1 months), 7 patients suffered tumor recurrence and 6 patients died with a mean OS time of 19.4 ± 10.8 months (range: 8-36 months). Immunohistochemistry of this series showed a more or less consistent positivity for GFAP, S100, Olig-2 and CD34 with a significant Ki67 expression (ranged from 3.5% to 60%). In our study, 40% (6/15) of the patients exhibited the BRAF V600E mutation, while none of the available patients (13 patients) had IDH mutations. Additionally, we identified TERT promoter mutation in 3 out of the 13 cases examined. Testing the methylation status of the MGMT promoter in 13 patients revealed that 3 patients had MGMT promoter methylation. Furthermore, we examined the co-deletion status of 1p/19q in 15 patients, and none of them exhibited co-deletion of 1p/19q (Table 1).
Table 1.
General characteristics of 26 cases in our institute.
| Case | Sex | Age (years) | Seizure | Site | Primary & Secondary | Peritumoral edema | Solid/cystic-solid | Enhancement | Treatment | BRAF | Ki-67 (%) | IDH1 | MGMT promoter | 1p/19q codeletion | TERT promoter mutation | PFS (months) | Follow-up time (months) | Outcome | Recurrence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 65 | No | Frontal-parietal | Primary | Yes | cystic-solid | Yes | Non-GTR | NA | 3.5 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11.0 | 18.0 | Dead | Yes |
| 2 | F | 33 | Yes | Temporal | Secondary | Yes | cystic-solid | Yes | GTR+RT | NA | 60 | - | unmethylated | - | NA | 12.0 | 20.0 | Dead | Yes |
| 3 | F | 8 | Yes | Temporal | Primary | Yes | solid | Yes | GTR+RT | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 78.1 | 78.1 | Alive | No |
| 4 | F | 5.5 | Yes | Temporal | Primary | No | solid | Yes | GTR+RT | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 69.5 | 69.5 | Alive | No |
| 5 | F | 9 | No | Parietal-occipital | Primary | Yes | cystic-solid | Yes | GTR | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 68.3 | 68.3 | Alive | No |
| 6 | M | 24 | No | Lateral ventricle | Primary | Yes | solid | Yes | Non-GTR+RT+CT | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 26.0 | 36.0 | Dead | Yes |
| 7 | F | 45 | No | Temporal | Primary | Yes | solid | Yes | Non-GTR+CT | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 6.0 | 8.0 | Dead | Yes |
| 8 | F | 37 | Yes | occipital | Primary | Yes | cystic-solid | Yes | GTR+RT+CT | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 33.9 | 33.9 | Alive | No |
| 9 | M | 50 | No | Parietal | Primary | Yes | cystic-solid | Yes | Non-GTR+RT+CT | - | 11.5 | - | unmethylated | - | - | 20.0 | 26.5 | Dead | Yes |
| 10 | F | 29 | No | Parietal-temporal | Secondary | Yes | solid | Yes | GTR+RT+CT | + | 20 | - | NA | - | NA | 25.2 | 25.2 | Alive | No |
| 11 | M | 56 | No | Temporal | Secondary | Yes | solid | Yes | GTR | NA | NA | NA | unmethylated | - | - | 6.0 | 8.1 | Dead | Yes |
| 12 | F | 56 | No | Frontal | Primary | Yes | solid | Yes | GTR+RT+CT | NA | 10 | NA | unmethylated | - | - | 21.3 | 21.3 | Alive | No |
| 13 | F | 56 | No | Temporal | Primary | Yes | solid | Yes | GTR+RT+CT | - | 25 | - | methylated | - | - | 19.0 | 21.0 | Alive | Yes |
| 14 | M | 46 | No | Temporal-occipital | Primary | Yes | solid | Yes | GTR+RT+CT | + | 5 | - | methylated | - | - | 15.0 | 15.0 | Alive | No |
| 15 | F | 35 | No | Frontal | Primary | Yes | solid | Yes | GTR+RT+CT | - | 40 | - | NA | NA | NA | 14.3 | 14.3 | Alive | No |
| 16 | M | 20 | Yes | Temporal | Primary | No | solid | No | GTR+RT+CT | + | 30 | - | unmethylated | - | - | 12.9 | 12.9 | Alive | No |
| 17 | M | 6 | No | Brainstem | Primary | No | Solid | Yes | Non-GTR+RT+CT | + | 15 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11.1 | 11.1 | Alive | No |
| 18 | F | 43 | No | Frontal-parietal | Primary | Yes | cystic-solid | Yes | Non-GTR+RT+CT | - | 15 | - | unmethylated | - | - | 9.4 | 9.4 | Alive | No |
| 19 | F | 13 | Yes | Temporal | Primary | No | solid | Yes | GTR+RT+CT | NA | NA | NA | unmethylated | - | - | 7.5 | 7.5 | Alive | No |
| 20 | M | 8 | No | Temporal | Secondary | Yes | cystic-solid | Yes | GTR+RT+CT | - | 15 | - | unmethylated | - | - | 7.4 | 7.4 | Alive | No |
| 21 | M | 52 | No | Temporal | Primary | Yes | cystic-solid | Yes | Non-GTR+RT+CT | - | 40 | - | NA | - | + | 6.9 | 6.9 | Alive | No |
| 22 | M | 53 | Yes | Frontal | Primary | No | cystic-solid | Yes | GTR+RT+CT | - | 10 | - | unmethylated | - | + | 6.7 | 6.7 | Alive | No |
| 23 | F | 42 | No | CPA | Primary | Yes | solid | Yes | Non-GTR+RT+CT | + | 20 | - | NA | NA | NA | 4.5 | 4.5 | Alive | No |
| 24 | F | 65 | No | Temporal-parietal | Primary | Yes | cystic-solid | Yes | GTR+RT+CT | - | 50 | NA | methylated | - | + | 1.5 | 1.5 | Alive | No |
| 25 | F | 71 | Yes | Parietal | Primary | Yes | solid | Yes | GTR+RT+CT | - | 50 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.9 | 0.9 | Alive | No |
| 26 | M | 27 | No | occipital | Primary | Yes | solid | Yes | Non-GTR+RT+CT | + | 30 | - | unmethylated | - | - | 0.5 | 0.5 | Alive | No |
M, male; F:female; GTR, gross total resection; Non-GTR, non- gross total resection; RT, radiotherapy; CT, chemotherapy; NA, not available; PFS, Progression-Free-Survival.
Cases from literature
56 patients (29 males and 27 females) diagnosed of HGPXAs were included from January 1997 and October 2022. The mean age was 29.6 ± 19.6 years (range: 4-74 years). Preoperative seizure was observed in 20 (38.5%) patients. 45 patients experienced primary HGPXAs, 9 patients suffered malignant transformation of previous PXAs. The lesion locations include temporal lobe (n=27), frontal lobe (n=9), frontal-parietal lobe (n=5), parietal lobe (n=3), parietal-occipital lobe (n=2), cerebellum (n=2), lateral ventricle (n=2), tectal region (n=2), occipital lobe (n=1), occipital-parietal lobe (n=1), posterior fossa (n=1), brainstem (n=1). The morphology was classified as solid (n=19) and cystic-solid (n=16). MRI scans showed that peritumoral edema was significant in 23 (67.6%) patients and enhancement was observed in 32 (97%) patients. GTR and non-GTR were performed in 24 (44.4%) and 30 (55.6%) patients, respectively. Combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy was administered to 19 (38%) patients, radiotherapy alone was administrated to 12 (24%) patients, chemotherapy alone was administrated to 4 (8%) and 15 patients (30%) accepted no adjuvant therapy. 14 (53.8%, n=26) patients harbored BRAF V600E mutation and no patients (9 patients were available) harbored IDH mutations. BRAF inhibitors, such as dabrafenib, trametinib, were used for 7 patients who suffered tumor recurrence and showed clinical stability and radiographic improvement. It is worth noting that 10 (20.4%) patients experienced spinal metastasis. After a median follow-up of 31.4 ± 35.3 months (range: 0.75-144 months), the mortality and recurrence rates were 32.5% (13/40) and 70% (28/40), respectively (Table 2). A summary of the clinical characteristics of HGPXAs from both literature and our institute can be found in Table 3.
Table 2.
Clinical and outcome review of reported 56 cases of APXAs from 1997 to 2022.
| Author&Year | Age, Sex | Seizure | Site | Primary & Secondary | Peritumoral edema | Enhancement | Solid/cystic-solid | Treatment | BRAF | IDH | Ki-67/MIB-1 (%) | Treatment after Recurrence | PFS (months) | Follow-up (months) | Recurrence/metastasis | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bayindir et al, 1997 (8) | 9, F | Yes | Temporal | Secondary | No | Yes | cystic-solid | GTR+RT | NA | NA | 31 | S | 6 | 10 | Yes/Yes | Dead |
| Nasuha et al, 2003 (9) | 10, M | Yes | Temporal | Primary | Yes | Yes | cystic-solid | Non-GTR+RT | NA | NA | NA | - | 24 | 24 | No | Alive |
| Lubansu et al, 2004 (10) | 7, F | No | Temporal | Primary | Yes | Yes | cystic-solid | GTR+CT | NA | NA | <1 | CT | 1 | 26 | Yes/Yes | Alive |
| Gelpi et al, 2005 (11) | 43, F | No | Occipital | Primary | NA | NA | solid | GTR+RT | NA | NA | 11.6 | S | 36 | 43 | Yes | Alive |
| Asano et al, 2006 (12) | 59, F | No | Temporal | Primary | Yes | Yes | solid | GTR | NA | NA | 9.8 | S | 5 | 33 | Yes | Dead |
| Baehring et al, 2006 (13) | 23, F | No | Frontal | Primary | Yes | Yes | cystic-solid | GTR | NA | NA | NA | - | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Chang et al, 2006 (14) | 4, F | No | Cerebellum | Primary | No | Yes | cystic-solid | GTR+RT+CT | NA | NA | 7.5 | - | 144 | 144 | No | Alive |
| Koga et al, 2009 (1) | 47, F | Yes | Frontal | Primary | Yes | Yes | solid | GTR | NA | NA | 4 | SRS, CT | 16 | 66 | Yes/Yes | Dead |
| Okazaki et al, 2009 (15) | 5, M | No | Temporal | Primary | No | Yes | solid | Biopsy+CT | NA | NA | 7.5 | No | 18 | 18 | Yes/Yes | Alive |
| Fu et al, 2010 (16) | 52, M | No | Lateral ventricle | Primary | Yes | Yes | cystic-solid | Non-GTR+RT+CT | NA | NA | 8.7 | - | 6 | 6 | No | Alive |
| Tsutsumi et al, 2010 (17) | 16, F | No | Temporal | Primary | No | Yes | solid | Non-GTR+RT | NA | NA | 6 | S, RT | 13 | 20 | Yes | Alive |
| Rodríguez-Mena et al, 2012 (18) | 54, M | No | Parietal-occipital | Secondary | Yes | Yes | cystic-solid | Biopsy | - | NA | 10 | No | 0.75 | 0.75 | Yes | Dead |
| Nern et al, 2012 (19) | 57, M | No | Temporal | Primary | Yes | Yes | cystic-solid | GTR+RT | - | - | NA | S, RT, CT | 10 | 28 | Yes | Dead |
| Katayama et al, 2013 (20) | 61, M | No | Tectal region | Primary | No | Yes | solid | Non-GTR+RT+CT | NA | - | 32.7 | - | 10 | 10 | No | Alive |
| Montano et al, 2013 (21) | 22, M | Yes | Temporal | Primary | Yes | No | solid | GTR+RT+CT | NA | NA | 4.5 | - | 12 | 12 | No | Alive |
| Martinez et al, 2014 (22) | 59, M | NA | Parietal | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | - | - | 12.5 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 22, M | NA | Temporal | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | - | - | 5 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
| Niamathullah et al, 2014 (23) | 9, F | Yes | Frontal-parietal | Primary | Yes | Yes | cystic-solid | Non-GTR+RT | NA | NA | 8 | - | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Benjamin et al, 2015 (24) | 65, M | No | Temporal | Primary | No | Yes | cystic-solid | Non-GTR | - | NA | 10 | S, RT | 0.5 | 4 | Yes/Yes | Dead |
| Usubalieva et al, 2015 (25) | 56, F | No | Brainstem | Primary | Yes | Yes | solid | GTR | - | NA | 11 | SRS | 4 | 37 | Yes | Alive |
| 35, F | No | Temporal | Primary | No | Yes | solid | Non-GTR +RT | + | NA | 15.5 | S, SRS, Dabrafenib | 5 | 26 | Yes | Dead | |
| Choudry et al, 2016 (26) | 55, M | Yes | Temporal | Primary | Yes | Yes | cystic-solid | GTR+RT | NA | NA | 9 | RT | 2.25 | 4 | Yes | Dead |
| Lee et al, 2016 (27) | 41, M | NA | Temporal | Secondary | NA | NA | NA | Non-GTR+RT+CT | + | NA | 20 | Vemurafenib | 6 | 15 | Yes | Alive |
| Patibandla et al, 2016 (28) | 35, M | No | Frontal | Primary | Yes | Yes | solid | Non-GTR +SR | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Rutkowski et al, 2016 (29) | 26, M | Yes | Temporal | Primary | NA | NA | NA | Non-GTR +RT+CT | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Yes | Dead |
| 17, M | No | Frontal | Primary | NA | NA | NA | Non-GTR +RT+CT | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Yes | Dead | |
| 4, F | Yes | Temporal | Primary | NA | NA | NA | Non-GTR +CT | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Yes/Yes | Alive | |
| 4, F | No | Frontal | Secondary | NA | NA | NA | Non-GTR | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Yes/Yes | Dead | |
| 9, F | Yes | Temporal | Secondary | NA | NA | NA | Non-GTR | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Yes | Alive | |
| 38, F | Yes | Frontal | Secondary | NA | NA | NA | GTR | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Yes | Alive | |
| 74, F | No | Posterior fossa | Primary | NA | NA | NA | GTR | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | No | Alive | |
| 54, M | No | Temporal | Primary | NA | NA | NA | Non-GTR+RT+CT | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Yes | Alive | |
| Suzuki et al, 2016 (30) | 17, M | No | Tectal region | Primary | No | Yes | solid | GTR+RT+CT | - | NA | 10 | - | 24 | 24 | No | Alive |
| Yamada et al, 2016 (31) | 42, M | No | Temporal | Primary | Yes | Yes | cystic-solid | Non-GTR+RT+CT | NA | NA | 20 | No | 5.6 | 5.8 | Yes | Dead |
| Brown et al, 2017 (32) | 21, F | No | Temporal | Primary | Yes | Yes | cystic-solid | GTR+RT | + | NA | NA | S, Dabrafenib, Vemurafenib | 3 | 19 | Yes | Alive |
| Migliorini et al, 2017 (33) | 32, F | NA | Parietal | Secondary | No | Yes | solid | Non-GTR+RT+CT | + | NA | NA | Dabrafenib, Trametinib | 6 | 11 | No | Alive |
| Thara et al, 2017 (34) | 42, M | Yes | Temporal | Primary | Yes | NA | solid | Non-GTR | + | NA | 8.5 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Amayiri et al, 2018 (35) | 16, F | Yes | Parietal | Primary | Yes | Yes | cystic-solid | Non-GTR+RT+CT | + | NA | NA | S, CT, Dabrafenib | 36 | 66 | Yes | Alive |
| Hussain et al, 2018 (36) | 43, M | No | Frontal | Primary | NA | NA | NA | GTR+RT | + | NA | NA | Vemurafenib, Trametinib | 24 | 34 | Yes | Alive |
| Oladiran et al, 2018 (37) | 28, M | No | Temporal | Primary | Yes | Yes | solid | Non-GTR | + | NA | NA | - | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Pradhan et al, 2018 (38) | 11, M | No | Occipital-parietal | Primary | NA | NA | NA | Non-GTR+NA | NA | NA | 6 | - | 12 | 12 | No | Alive |
| 40, F | No | Temporal | Primary | NA | NA | NA | GTR+NA | NA | NA | 12.5 | - | 12 | 12 | No | Alive | |
| 19, M | Yes | Frontal-parietal | Primary | NA | NA | NA | Non-GTR+NA | NA | NA | 20 | - | 12 | 12 | No | Alive | |
| 18, F | No | Frontal-parietal | Primary | NA | NA | NA | Non-GTR+NA | NA | NA | 18 | Biopsy | 12 | 36 | Yes/Yes | Alive | |
| Roberti et al, 2018 (39) | 65, F | No | Lateral ventricle | Primary | No | Yes | solid | GTR | NA | NA | 2 | No | 3 | 3 | Yes | Alive |
| Saraf et al, 2018 (40) | 5, M | Yes | Temporal | Primary | Yes | Yes | solid | Non-GTR+GN+CT | - | NA | 25 | CT, Everolimus | NA | 60 | Yes | Alive |
| Fukushima et al, 2019 (41) | 15, F | Yes | Temporal | Secondary | Yes | Yes | solid | GTR | + | NA | 14.4 | Multimodal therapies | 9 | 20 | Yes | Dead |
| Nakamura et al, 2019 (42) | 14, F | No | Cerebellum | Primary | NA | NA | NA | Non-GTR+RT+CT | - | - | NA | CT | NA | 9.4 | Yes | Dead |
| Purkait et al, 2019 (43) | 35, F | No | Parietal-occipital | Primary | Yes | Yes | cystic-solid | GTR+RT | + | - | 12 | No | 18 | 18 | Yes | Alive |
| Sasaki et al, 2019 (44) | 12, M | No | Frontal | Primary | Yes | Yes | cystic-solid | Non-GTR | - | - | NA | S, RT, CT | 2 | 12 | Yes | Alive |
| Thomas et al, 2019 (45) | 16, F | Yes | Frontal | Primary | NA | NA | NA | Non-GTR+RT+CT | + | NA | 15 | Dabrafenib, Trametinib | 6 | 23 | Yes/Yes | Dead |
| Liu et al, 2020 (46) | 28, M | Yes | Frontal-parietal | Primary | Yes | Yes | solid | Non-GTR+CT | - | - | 15 | - | NA | NA | No | Alive |
| Matsumoto et al, 2020 (7) | 32, M | Yes | Temporal | Secondary | No | Yes | solid | GTR+RT+CT | + | - | 12.1 | CT | 24 | 29 | Yes/Yes | Dead |
| Ronsley et al, 2020 (47) | 12, M | No | Temporal | Primary | NA | NA | NA | GTR+ RT+CT | + | NA | NA | GTR+CT | 2 | 144 | Yes | Alive |
| 12, M | Yes | Frontal-parietal | Primary | NA | NA | NA | GTR+RT+CT | - | NA | NA | - | 132 | 132 | No | Alive | |
| 12, F | Yes | Temporal | Primary | NA | NA | NA | GTR+RT+CT | + | NA | NA | - | 48 | 48 | No | Alive |
S, surgery, NA, not available.
Table 3.
Summary of clinical characteristics of Anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma from literature and our institute.
| Variable | Prior studies (n=56) | Our series | Overall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of available cases | Value | |||
| Mean age, years | 56 | 29.6 ± 19.6 | 36.7 ± 20.3 | 31.9 ± 20.0 |
| Sex (M/F) | 56 | 29/27 | 11/15 | 40/42 |
| Seizure | 52 | 20 (38.5) | 8 (30.8) | 28 (35.9) |
| Temporal | 56 | 27 (48.2) | 13 (50) | 40 (48.8) |
| Primary/Secondary | 54 | 45/9 | 22/4 | 67/13 |
| Peritumoral edema | 34 | 23 (67.6) | 21 (80.8) | 44 (73.3) |
| Solid/cystic-solid | 35 | 19/16 | 16/10 | 35/26 |
| Enhancement | 33 | 32 (97.0) | 25 (96.2) | 57 (96.6) |
| BRAF | 26 | 14 (53.8) | 6 (40) | 20 (48.8) |
| GTR | 54 | 24 (44.4) | 17 (65.4) | 41 (51.3) |
| RT | 50 | 31 (62) | 22 (84.6) | 53 (69.7) |
| CT | 50 | 23 (46) | 20 (76.9) | 43 (56.6) |
| BRAF inhibitor | 56 | 7 (12.5) | 0 | 7 (8.5) |
| Recurrence | 49 | 35 (71.4) | 7 (26.9) | 42 (46) |
| Death | 49 | 16 (32.7) | 6 (23.1) | 22 (29.3) |
| Mean PFS, months | 34 | 19.5 ± 32.2 | 19.0 ± 21.2 | 19.3 ± 27.8 |
| Mean FU, months | 40 | 31.4 ± 35.3 | 20.5 ± 21.2 | 27.1± 30.8 |
Pooled analysis
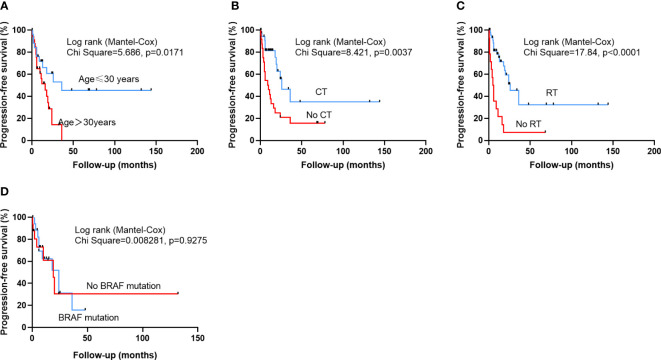
The mean PFS time was 19.3 ± 27.8 months, and the 1-, 2-year and 5-year recurrence rates were 61.1%, 38.7%, 26.1%, respectively. The mean OS time was 27.1 ± 30.8 months, and the 1-, 2-year and 5-year OS rates were 85.3%, 74.2% and 51.5%, respectively. The univariate cox regression analysis revealed that no RT (HR 4.105, 95% CI 1.998-8.432, p<0.001), no CT (HR 2.724, 95% CI 1.329-5.585, p=0.006), age>30 years (HR 2.436, 95% CI 1.135-5.226, p=0.022) years predicted a poor PFS. Multivariate cox regression analysis confirmed that non-GTR (HR 2.633,9 5% CI 1.203-5.762, p=0.015), age>30 years (HR 2.620, 95% CI 1.183-5.804, p=0.018), no CT (HR 2.371, 95% CI, 1.034-5.437, p=0.042) and no RT (HR 2.995, 95% CI 1.344-6.673, p=0.007) were significantly associated with poorer PFS (Table 4). The univariate cox regression analysis revealed that age>30 years (HR 3.946, 95% CI 1.378-11.306, p=0.011), non-GTR (HR 2.876, 95% CI 1.142-7.254, p=0.025), secondary HGPXAs (HR 4.494, 95% CI 1.589-12.708, p=0.005) and no RT (HR 2.593, 95% CI 1.042-6.453, p=0.041) predicted a poor OS. Multivariate cox regression analysis confirmed that non-GTR (HR 7.963, 95% CI 2.368-26.776, p=0.001), secondary HGPXAs (HR 7.567, 95% CI 2.221-25.781, p=0.001), age≥30 (HR 3.568, 95% CI 1.190-10.694, p=0.023) and no RT (HR 4.490,95% CI 1.469-13.726, p=0.008) predicted a poor OS (Table 5). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that age>30 years (p=0.0171), no CT (p=0.0037) and no RT (p<0.0001) predicted a poor PFS (Figures 1A-C). Age>30 years (p=0.0061), non-GTR (p=0.0192), secondary HGPXAs (p=0.0019) and no RT (p=0.0331) predicted a poor OS (Figures 2A-D). There is no significant statistical difference between BRAF mutation group and no BRAF mutation for PFS (Figure 1D) and OS (Figure 2E).
Table 4.
Cox regression model for risk factors predicting PFS.
| Variable | Number of patients | Recurrence | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | |||
| Overall | 60 | 32 (53.3) | ||||
| Age | ||||||
| Age ≤ 30 | 26 | 11 (34.4) | Reference | Reference | ||
| Age>30 | 34 | 21 (65.6) | 2.436 (1.135-5.226) | 0.022* | 2.620 (1.183-5.804) | 0.018* |
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | 32 | 17 (53.1) | Reference | |||
| Male | 28 | 15 (53.6) | 1.259 (0.620-2.556) | 0.524 | ||
| Primary | ||||||
| Yes | 50 | 25 (50) | Reference | |||
| No | 10 | 7 (70) | 1.769 (0.750-4.173) | 0.193 | ||
| Location | ||||||
| Others | 29 | 13 (44.8) | Reference | |||
| Temporal | 31 | 19 (61.3) | 1.724 (0.846-3.511) | 0.134 | ||
| GTR | ||||||
| Yes | 23 | 14 (60.9) | Reference | Reference | ||
| No | 37 | 18 (48.6) | 1.829 (0.897-3.729) | 0.097 | 2.633 (1.203-5.762) | 0.015* |
| RT | ||||||
| Yes | 46 | 19 (41.3) | Reference | Reference | ||
| No | 14 | 13 (92.9) | 4.105 (1.998-8.432) | <0.001* | 2.995 (1.344-6.673) | 0.007* |
| CT | ||||||
| Yes | 36 | 12 (33.3) | Reference | Reference | ||
| No | 24 | 20 (83.3) | 2.724 (1.329-5.585) | 0.006* | 2.371 (1.034-5.437) | 0.042* |
*: p< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Table 5.
Cox regression model for risk factors predicting OS.
| Variable | Number of patients | Death | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | |||
| Overall | 62 | 19 (30.6) | ||||
| Age | ||||||
| Age ≤ 30 | 28 | 5 (17.9) | Reference | Reference | ||
| Age>30 | 34 | 14 (41.2) | 3.946 (1.378-11.306) | 0.011* | 3.568 (1.190-10.694) | 0.023* |
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | 33 | 9 (27.3) | Reference | |||
| Male | 29 | 10 (34.5) | 1.762 (0.710-4.370) | 0.222 | ||
| Primary | ||||||
| Yes | 52 | 13 (25) | Reference | Reference | ||
| No | 10 | 6 (60) | 4.494 (1.589-12.708) | 0.005* | 7.567 (2.221-25.781) | 0.001* |
| Location | ||||||
| Others | 30 | 7 (23.3) | Reference | |||
| Temporal | 32 | 12 (37.5) | 1.855 (0.725-4.472) | 0.197 | ||
| GTR | ||||||
| Yes | 25 | 10 (40) | Reference | Reference | ||
| No | 37 | 9 (24.3) | 2.876 (1.142-7.254) | 0.025* | 7.963 (2.368-26.776) | 0.001* |
| RT | ||||||
| Yes | 14 | 8 (57.1) | Reference | Reference | ||
| No | 48 | 11 (22.9) | 2.593 (1.042-6.453) | 0.041* | 4.490 (1.469-13.726) | 0.008* |
| CT | ||||||
| Yes | 24 | 12 (50) | Reference | |||
| No | 38 | 7 (18.4) | 2.139 (0.839-5.451) | 0.111 | ||
*: p< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Figure 1.
Kaplan-Meier survival curves illustrating the difference PFS. Patients older than 30 years (A), who did not undergo CT (B), or had no RT (C) had a significantly worse PFS. There is no significantly statistical difference between BRAF mutation group and no BRAF mutation group in PFS (D).
Figure 2.
Kaplan-Meier survival curves illustrating the difference OS. Patients older than 30 years (A), who did not undergo GTR (B), secondary HGPXAs, or had no RT (C) had a significantly worse OS. There is no significantly statistical difference between BRAF mutation group and no BRAF mutation group in OS (E).
Discussion
Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA) is a rare brain tumor, which was first reported in 1979 (48, 49). ‘PXA with anaplastic features’ are labelled as anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (APXA), WHO grade III, according to the 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System (3). According recent World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System, PXA was classified into WHO grade 2 or WHO grade 3 tumors (5). Most of the information available about APXA comes from isolated case reports. In our institute, 200 cases with PXAs were pathologically confirmed from August 2014 and September 2021. Among them 26 cases were grade 3 PXAs and 174 cases were grade 2 PXAs, HGPXAs are estimated to comprise 13% of all PXAs in our single center.
Mallick et al. reported the median age of grade 2 PXA patients was 20 years via analyzing 167 cases and Rodrigues et al. reported the median age of grade 2 PXA patients was 21 years via analyzing 346 cases (49, 50). In our pooled cohort, HGPXAs tended to affect middle-aged patients with a median age of 30.5 years, compared to their grade 2 PXA patients. We also found that age>33 years was a risk factor for PFS (p=0.018) and OS (p=0.023) via multivariate cox regression analysis. There is no gender predominance in HGPXAs in this study, which is consistent with previous studies (50). Most intracranial HGPXAs were located in supratentorial area and temporal lobe was the first commonest region, only 5 cases located in infratentorial area. Preoperative seizure is common with the occurrence of 35.9%. 8 cases from our institute presented with preoperative seizure were free of seizure after GTR. HGPXAs can be divided into primary tumors or secondary tumors. Of the pooled analysis, 67 cases were primary tumors and 13 cases were secondary tumors, and secondary tumors had a poorer OS than primary tumors (p=0.001). Radiologically, HGPXAs often appear T1 isointense and T2 hyperintense and the cystic component is often hypodense On Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). PXA usually contains solid and cystic components and the solid component often enhances (8, 51). She et al. reviewed MR imaging features of 9 patients with APXA and 10 patients with PXA. The presence of heterogeneous enhancement of solid mass was observed more frequently in patients with APXA than in those with PXA (52). In our study, enhancement was observed in almost all HGPXAs patients (96.6%) and solid tumors are more common than cystic-solid tumors (35 VS 26 cases). 73.3% patients with HGPXAs had obvious peritumoral edema. However, through cox regression analysis, no peritumoral edema could not predict a better PFS or OS.
Due to the rarity of HGPXAs, there is limited research to identify risk factors for OS or PFS. Patibandla et al. pointed that a complete surgical excision is required for a prolonged disease-free interval (28). Rodrigues et al. analyzed 62 cases of APXA from SEER database and concluded that complete surgical resection could not bring improved outcomes. In our study, we found non-GTR group was associated with a poor PFS (p=0.015) and OS (p=0.001) than GTR group. Maximum safe resection, if feasible, should be the first goal of the neurosurgeon. The role of postoperative radiotherapy and chemotherapy for APXAs is still uncertain (1). Marton et al. reviewed 9 cases with APXA underwent conventional fractionated radiotherapy, but the effect of treatment is not significant (53). Koga et al. reported a case of APXA treated with postoperative stereotactic irradiation (STI) that resulted in long-term control of the tumor (1). Postoperative chemotherapy has been commonly considered ineffective for the treatment of PXAs (54). In our pooled analysis, we found that no postoperative radiotherapy group was associated with a poor PFS (p=0.007) and OS (p=0.008) than postoperative radiotherapy group and no postoperative chemotherapy can predict a better PFS (p=0.042). Based on these, we recommended that postoperative radiotherapy and chemotherapy should be added to conventional treatment protocols. Molecular markers are increasingly used to help doctors to diagnose or subclassify gliomas. BRAF mutations were found in 70% PXAs, but involved less common in HGPXAs (55). Phillips et al (56) performed comprehensive genomic profiling on 15 cases with APXA and found 5 cases with TERT promoter hotspot mutation. In our study, BRAF p.V600E mutations were detected in 48.8% of patients (20/41), and TERT promoter mutations were found in 23.1% of patients (3/13). It is reported that compared to the BRAF wild-type PXA, BRAF-mutated PXA revealed prolonged survival (6). However, we did not find any relationship between BRAF mutation and PFS (p=0.9275) or OS (p=0.4755) for HGPXAs. In previous reports, small molecule drugs, such as BRAF, MEK inhibitors were used for some patients. Brown et al. reported a 21-year-old female suffered occurrence of APXA with a BRAFV600 mutation following 2 operations and radiotherapy. Then she was orally administered with BRAF inhibitors. She was well up to the last follow-up (32). Hussain et al. reported a 43-year-old male underwent GTR plus radiotherapy of an APXA, but, unfortunately, the tumor progression happened 2 years later. Because the tumor harbored a BRAFV600 mutation, combination of vemurafenib (BRAF inhibitor) and trametinib (MEK inhibitor) was added to treatment strategy. Clinical stability and radiographic improvement were achieved for 6 months after the targeted therapy (36). Targeted therapy may bring hope to HGPXAs patients, but more data is needed to prove its effectiveness.
According to previous studies, OS of PXA is favorable with 5-year survival rates of >75% and PFS rates at 5 years are >60% (4, 57). Patibandla et al (28) reviewed 17 cases of APXA reported in the literature till 2010 and found that among 13 patients whose follow-up information was available, 8 patients died with the mean overall survival was 26.1 months (ranges from 1 to 66 months). Compared to PXA, we found that HGPXAs have a relatively poor clinical outcomes with 5-year OS of 51.5% and 5-year PFS of 26.1% and 19 patients died with a mean overall survival was 19.8 months (ranges from 0.75 to 66 months). Although no tumor metastasis was found in our institute, 13.3% (10/75) patients experienced spinal metastasis were founded in reported cases. Spinal MRI should be taken into account during postoperative follow-up for early treatment of the metastatic tumor.
Conclusion
High grade pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas are very rare brain tumors. Children and younger adults have better clinical outcome than elderly patients. Secondary HGPXAs had worse OS than primary HGPXAs. Complete surgical excision plus RT and CT is recommended for this entity. The frequency of BRAF mutations in HGPXAs is 47.5% (19/40) in this study, however, we do not find the connections between BRAF mutations and clinical outcomes. Future studies with larger cohorts are necessary to verify our findings.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by human research ethics committee of Beijing Tiantan Hospital. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
Writing, original draft, Conceptualization: PZ; Statistical analysis: TS, WW; Literature review: TL, YW; Follow up: MZ; Methodology, Resources: ZW, JZ; Review, editing, Supervision: LZ. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding Statement
This study was funded by Multicenter clinical big data study and multi-path tumorigenesis mechanisms and precision treatment research on brainstem glioma (JINGYIYAN2018-7).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
- 1. Koga T, Morita A, Maruyama K, Tanaka M, Ino Y, Shibahara J, et al. Long-term control of disseminated pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features by means of stereotactic irradiation. Neuro-oncology (2009) 11(4):446–51. doi: 10.1215/15228517-2008-112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Kahramancetin N, Tihan T. Aggressive behavior and anaplasia in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: a plea for a revision of the current WHO classification. CNS Oncol (2013) 2(6):523–30. doi: 10.2217/cns.13.56 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, et al. The 2016 world health organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta neuropathologica (2016) 131(6):803–20. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Giannini C, Scheithauer BW, Burger PC, Brat DJ, Wollan PC, Lach B, et al. Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: what do we really know about it? Cancer (1999) 85(9):2033–45. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19990501)85:9<2033::AID-CNCR22>3.0.CO;2-Z [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Louis DN, Perry A, Wesseling P, Brat DJ, Cree IA, Figarella-Branger D, et al. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Neuro-oncology (2021) 23(8):1231–51. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noab106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Ida CM, Rodriguez FJ, Burger PC, Caron AA, Jenkins SM, Spears GM, et al. Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: natural history and long-term follow-up. Brain Pathol (Zurich Switzerland) (2015) 25(5):575–86. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Matsumoto Y, Kobayashi M, Shingu K, Tateishi A, Ohya M, Sano K, et al. An anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with periventricular extension: an autopsy case report and review of the literature. Neuropathology (2020) 40(5):507–14. doi: 10.1111/neup.12666 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Bayindir C, Balak N, Karasu A, Kasaroglu D. Anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. Child’s nervous system (1997) 13(1):50–6. doi: 10.1007/s003810050040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Nasuha NA, Daud AH, Ghazali MM, Yusoff AA, Zainuddin N, Abdullah JM, et al. Molecular genetic analysis of anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. Asian J surgery (2003) 26(2):120–5. doi: 10.1016/s1015-9584(09)60233-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Lubansu A, Rorive S, David P, Sariban E, Seligmann R, Brotchi J, et al. Cerebral anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with meningeal dissemination at first presentation. Child’s nervous system (2004) 20(2):119–22. doi: 10.1007/s00381-003-0854-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Gelpi E, Popovic M, Preusser M, Budka H, Hainfellner J. Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features presenting without GFAP immunoreactivity: implications for differential diagnosis. Neuropathology (2005) 25(3):241–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2005.00612.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Asano K, Miyamoto S, Kubo O, Kikkukawa T, Yagihashi A, Ohkuma H. A case of anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma presenting with tumor bleeding and cerebrospinal fluid dissemination. Brain tumor pathology (2006) 23(1):55–63. doi: 10.1007/s10014-006-0197-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Baehring JM, Vives KP, Bannykh S. Images in neuro-oncology: anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. J Neurooncol (2006) 79(2):151–2. doi: 10.1007/s11060-006-9203-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Chang HT, Latorre JG, Hahn S, Dubowy R, Schelper RL. Pediatric cerebellar pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features: a case of long-term survival after multimodality therapy. Child’s nervous system (2006) 22(6):609–13. doi: 10.1007/s00381-005-0005-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Okazaki T, Kageji T, Matsuzaki K, Horiguchi H, Hirose T, Watanabe H, et al. Primary anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with widespread neuroaxis dissemination at diagnosis–a pediatric case report and review of the literature. J Neurooncol (2009) 94(3):431–7. doi: 10.1007/s11060-009-9876-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Fu YJ, Miyahara H, Uzuka T, Natsumeda M, Okamoto K, Hirose T, et al. Intraventricular pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features. Neuropathology (2010) 30(4):443–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2009.01080.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Tsutsumi S, Abe Y, Yasumoto Y, Ito M. Anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with a component of anaplastic astrocytoma presenting as skull base tumor followed by downward extracranial extension. Case Rep Neurologia medico-chirurgica (2010) 50(12):1108–12. doi: 10.2176/nmc.50.1108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Rodríguez-Mena R, Joanes-Alepuz V, Barbella-Aponte R, Pérez-Valles A. Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with intraventricular extension and anaplastic transformation in an adult patient: case report. Neurocirugia (Asturias Spain) (2012) 23(5):203–10. doi: 10.1016/j.neucir.2011.08.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Nern C, Hench J, Fischmann A. Spinal imaging in intracranial primary pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features. J Clin Neurosci (2012) 19(9):1299–301. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2011.12.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Katayama K, Asano K, Shimamura N, Ogasawara Y, Naraoka M, Ohkuma H, et al. Case of pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features in the pineal gland. Brain tumor pathology (2013) 30(4):242–6. doi: 10.1007/s10014-013-0137-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Montano N, Papacci F, Cioni B, Gaudino S, Della Pepa GM, Conforti G, et al. Primary multicentric anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with atypical features. J Clin Neurosci (2013) 20(11):1605–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2012.09.046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Martinez R, Carmona FJ, Vizoso M, Rohde V, Kirsch M, Schackert G, et al. DNA Methylation alterations in grade II- and anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. BMC cancer (2014) 14:213. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-213 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Niamathullah S, Sivaselvam S, Ghosh M, Ghosh S. Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features: a case report. Indian J Pathol Microbiol (2014) 57(1):101–4. doi: 10.4103/0377-4929.130913 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Benjamin C, Faustin A, Snuderl M, Pacione D. Anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with spinal leptomeningeal spread at the time of diagnosis in an adult. J Clin Neurosci (2015) 22(8):1370–3. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2015.02.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Usubalieva A, Pierson CR, Kavran CA, Huntoon K, Kryvenko ON, Mayer TG, et al. Primary meningeal pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features: a report of 2 cases, one with BRAF(V600E) mutation and clinical response to the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib. J neuropathology Exp neurology (2015) 74(10):960–9. doi: 10.1097/nen.0000000000000240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Choudry UK, Khan SA, Qureshi A, Bari E. Primary anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma in adults. Case Rep Rev literature Int J Surg Case Rep (2016) 27:183–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2016.08.022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Lee EQ, Ruland S, LeBoeuf NR, Wen PY, Santagata S. Successful treatment of a progressive BRAF V600E-mutated anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with vemurafenib monotherapy. J Clin Oncol (2016) 34(10):e87–9. doi: 10.1200/jco.2013.51.1766 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Patibandla MR, Nayak M, Purohit AK, Thotakura AK, Uppin M, Challa S. Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features: a rare case report and review of literature with reference to current management. Asian J neurosurgery (2016) 11(3):319. doi: 10.4103/1793-5482.144161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Rutkowski MJ, Oh T, Niflioglu GG, Safaee M, Tihan T, Parsa AT. Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features: retrospective case series. World Neurosurg (2016) 95:368–74. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.07.068 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Suzuki Y, Akiyama Y, Kimura Y, Sugita S, Hasegawa T, Mikuni N. Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features in the tectal region in a young adult patient: a case report. World Neurosurg (2016) 94:580.e11–580.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.07.110 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Yamada SM, Murakami H, Tomita Y, Nakane M, Shibui S, Takahashi M, et al. Glioblastoma multiforme versus pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with anaplastic features in the pathological diagnosis: a case report. Diagn pathology (2016) 11(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13000-016-0514-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Brown NF, Carter T, Mulholland P. Dabrafenib in BRAFV600-mutated anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. CNS Oncol (2017) 6(1):5–9. doi: 10.2217/cns-2016-0031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Migliorini D, Aguiar D, Vargas MI, Lobrinus A, Dietrich PY. BRAF/MEK double blockade in refractory anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. Neurology (2017) 88(13):1291–3. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0000000000003767 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Thara K, Sharma R, Thiagarajan G, Ramdas A, Varghese RG. Anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma in a case of neurofibromatosis type 1: a case report. J Clin Diagn Res (2017) 11(4):Ed23–ed24. doi: 10.7860/jcdr/2017/26685.9713 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Amayiri N, Swaidan M, Al-Hussaini M, Halalsheh H, Al-Nassan A, Musharbash A, et al. Sustained response to targeted therapy in a patient with disseminated anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. J Pediatr hematology/oncology (2018) 40(6):478–82. doi: 10.1097/mph.0000000000001032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Hussain F, Horbinski CM, Chmura SJ, Yamini B, Lukas RV. Response to BRAF/MEK inhibition after progression with BRAF inhibition in a patient with anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. neurologist (2018) 23(5):163–6. doi: 10.1097/nrl.0000000000000194 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Oladiran O, Nwosu I, Obanor S, Ogbonna-Nwosu C, Le B. Anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma presenting with musical hallucination. Case Rep neurological Med (2018) 2018:6428492. doi: 10.1155/2018/6428492 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Pradhan P, Dey B, Srinivas BH, Jacob SE, Rathakrishnan RKV. Clinico-histomorphological and immunohistochemical profile of anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: report of five cases and review of literature. Int J hematology-oncology Stem Cell Res (2018) 12(4):265–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Roberti F, Baggenstos M. Intraventricular anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: very rare localization and early recurrence of a rare tumor. Cureus (2018) 10(5):e2665. doi: 10.7759/cureus.2665 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Saraf AJ, Elhawary G, Finlay JL, Scott S, Olshefski R, Halverson M, et al. Complete remission of an extracranially disseminated anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with everolimus: a case report and literature review. Pediatr neurology (2018) 88:65–70. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2018.09.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Fukushima H, Nakano Y, Ishii N, Nozuchi N, Okuno T, Yamasaki K, et al. Histological and genetic analysis of anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma suspected of malignant progression over a 12-year clinical course. Pathol Int (2019) 69(10):608–13. doi: 10.1111/pin.12840 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Nakamura T, Fukuoka K, Nakano Y, Yamasaki K, Matsushita Y, Yamashita S, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling shows molecular heterogeneity of anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. Cancer science (2019) 110(2):828–32. doi: 10.1111/cas.13903 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Purkait S, Bansal S, Malgulwar PB. BRAF V600E-mutated central nervous system tumor with divergent morphological feature - anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma-like and astroblastoma-like. Neuropathology (2019) 39(1):64–7. doi: 10.1111/neup.12527 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Sasaki S, Tomomasa R, Nobusawa S, Hirato J, Uchiyama T, Boku E, et al. Anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma associated with an H3G34 mutation: a case report with review of literature. Brain tumor Pathol (2019) 36(4):169–73. doi: 10.1007/s10014-019-00349-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Thomas AA, Tucker SM, Nelson CJ, Nickerson JP, Durham SR, Homans AC. Anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma with leptomeningeal dissemination responsive to BRAF inhibition and bevacizumab. Pediatr Blood cancer (2019) 66(1):e27465. doi: 10.1002/pbc.27465 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Liu J, Sun Y, Liu X. Anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: a case report and literature review. Int J Gen Med (2020) 13:1581–7. doi: 10.2147/ijgm.S285989 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Ronsley R, Dunham C, Yip S, Brown L, Zuccato JA, Karimi S, et al. A case series of pediatric survivors of anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. Neuro-oncology Adv (2021) 3(1):vdaa176. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdaa176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Kepes JJ, Rubinstein LJ, Eng LF. Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: a distinctive meningocerebral glioma of young subjects with relatively favorable prognosis. A study 12 cases Cancer (1979) 44(5):1839–52. doi: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Mallick S, Benson R, Melgandi W, Giridhar P, Rath GK. Grade II pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma; a meta-analysis of data from previously reported 167 cases. J Clin Neurosci (2018) 54:57–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2018.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Rodrigues A, Bhambhvani H, Medress ZA, Malhotra S, Hayden-Gephart M. Differences in treatment patterns and overall survival between grade II and anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas. J Neurooncol (2021) 153(2):321–30. doi: 10.1007/s11060-021-03772-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Shaikh N, Brahmbhatt N, Kruser TJ, Kam KL, Appin CL, Wadhwani N, et al. Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: a brief review. CNS Oncol (2019) 8(3):Cns39. doi: 10.2217/cns-2019-0009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. She D, Liu J, Xing Z, Zhang Y, Cao D, Zhang Z. MR imaging features of anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma mimicking high-grade astrocytoma. AJNR Am J neuroradiology (2018) 39(8):1446–52. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A5701 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Marton E, Feletti A, Orvieto E, Longatti P. Malignant progression in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: personal experience and review of the literature. J neurological Sci (2007) 252(2):144–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2006.11.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Kepes JJ, Rubinstein LJ, Ansbacher L, Schreiber DJ. Histopathological features of recurrent pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas: further corroboration of the glial nature of this neoplasm. A study 3 cases Acta neuropathologica (1989) 78(6):585–93. doi: 10.1007/bf00691285 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Dias-Santagata D, Lam Q, Vernovsky K, Vena N, Lennerz JK, Borger DR, et al. BRAF V600E mutations are common in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. PloS One (2011) 6(3):e17948. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017948 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Phillips JJ, Gong H, Chen K, Joseph NM, van Ziffle J, Bastian BC, et al. The genetic landscape of anaplastic pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. Brain Pathol (2019) 29(1):85–96. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12639 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Lim S, Kim JH, Kim SA, Park ES, Ra YS, Kim CJ. Prognostic factors and therapeutic outcomes in 22 patients with pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. J Korean Neurosurgical Society (2013) 53(5):281–7. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2013.53.5.281 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.