Abstract
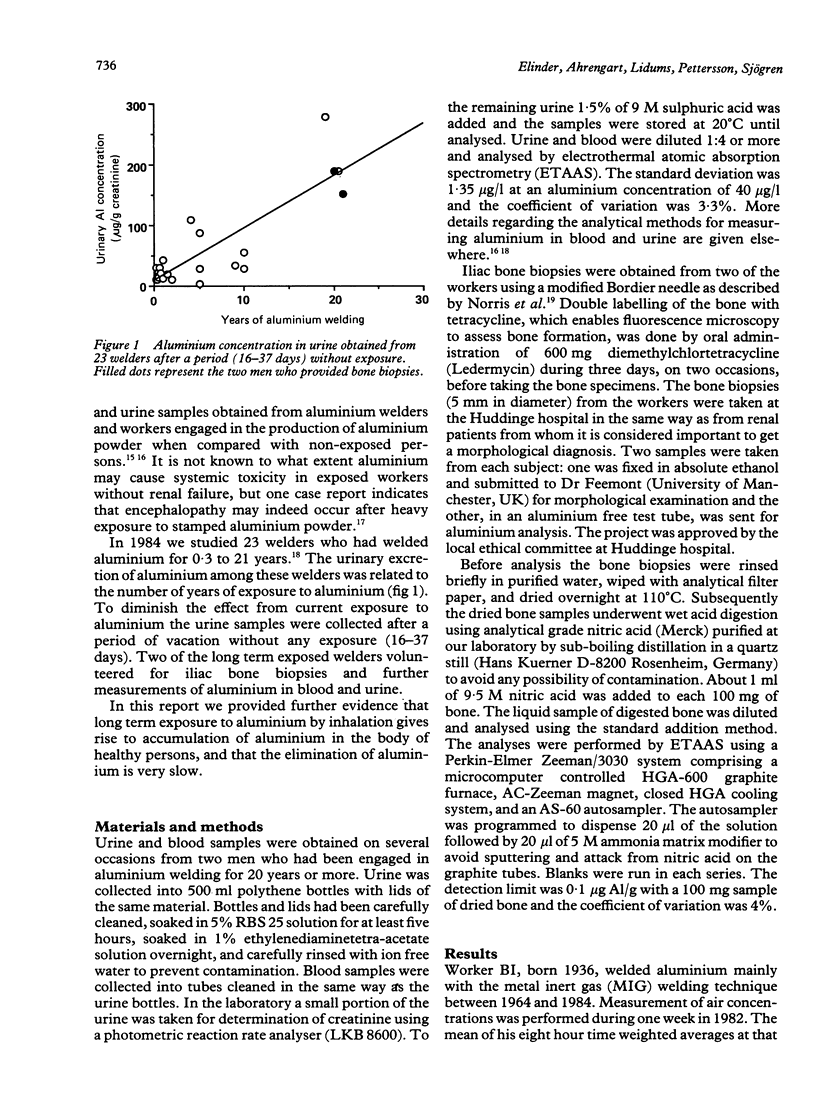
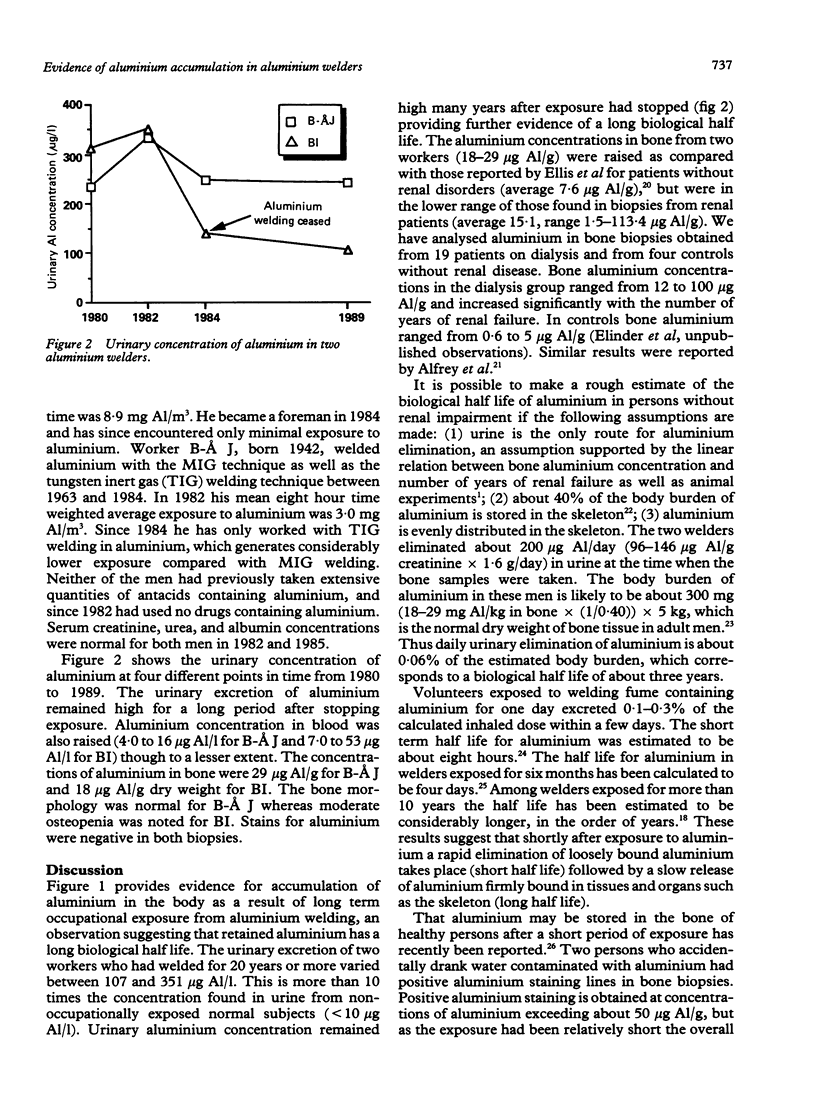
Using atomic absorption spectrometry the aluminium concentrations in blood and urine and in two iliac bone biopsies obtained from welders with long term exposure to fumes containing aluminium were measured. The urinary excretion of two workers who had welded for 20 and 21 years varied between 107 and 351 micrograms Al/l, more than 10 times the concentration found in persons without occupational exposure. Urinary aluminium excretion remained high many years after stopping exposure. Blood and bone aluminium concentrations (4-53 micrograms Al/l and 18-29 micrograms Al/g respectively) were also raised but not to the same extent as urine excretion. It is concluded that long term exposure to aluminium by inhalation gives rise to accumulation of aluminium in the body and skeleton of health persons, and that the elimination of retained aluminium is very slow, in the order of several years.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackrill P., Ralston A. J., Day J. P., Hodge K. C. Successful removal of aluminium from patient with dialysis encephalopathy. Lancet. 1980 Sep 27;2(8196):692–693. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92728-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfrey A. C., Hegg A., Craswell P. Metabolism and toxicity of aluminum in renal failure. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Jul;33(7):1509–1516. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.7.1509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfrey A. C., LeGendre G. R., Kaehny W. D. The dialysis encephalopathy syndrome. Possible aluminum intoxication. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jan 22;294(4):184–188. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197601222940402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmann P., Dhanesha U., Hamon C., Cunningham J., Blair J., Marsh F. Disturbance of cerebral function by aluminium in haemodialysis patients without overt aluminium toxicity. Lancet. 1989 Jul 1;2(8653):7–12. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dementia--the quiet epidemic. Br Med J. 1978 Jan 7;1(6104):1–2. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drüeke T. Dialysis osteomalacia and aluminum intoxication. Nephron. 1980;26(5):207–210. doi: 10.1159/000181985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastwood J. B., Levin G. E., Pazianas M., Taylor A. P., Denton J., Freemont A. J. Aluminium deposition in bone after contamination of drinking water supply. Lancet. 1990 Aug 25;336(8713):462–464. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilleyman J. S. Gerard Slavin: editor, Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978-1988. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Jan;41(1):1–2. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLAUGHLIN A. I., KAZANTZIS G., KING E., TEARED, PORTER R. J., OWEN R. Pulmonary fibrosis and encephalopathy associated with the inhalation of aluminium dust. Br J Ind Med. 1962 Oct;19:253–263. doi: 10.1136/oem.19.4.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mussi I., Calzaferri G., Buratti M., Alessio L. Behaviour of plasma and urinary aluminium levels in occupationally exposed subjects. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1984;54(2):155–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00378518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris K. C., Goodman W. G., Howard N., Nugent M. E., Coburn J. W. Iliac crest bone biopsy for diagnosis of aluminum toxicity and a guide to the use of deferoxamine. Semin Nephrol. 1986 Dec;6(4 Suppl 1):27–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson I. S., Ward M. K., Feest T. G., Fawcett R. W., Kerr D. N. Fracturing dialysis osteodystrophy and dialysis encephalopathy. An epidemiological survey. Lancet. 1979 Feb 24;1(8113):406–409. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90883-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren B., Elinder C. G., Lidums V., Chang G. Uptake and urinary excretion of aluminum among welders. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1988;60(2):77–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00381484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren B., Gustavsson P., Hogstedt C. Neuropsychiatric symptoms among welders exposed to neurotoxic metals. Br J Ind Med. 1990 Oct;47(10):704–707. doi: 10.1136/oem.47.10.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren B., Lidums V., Håkansson M., Hedström L. Exposure and urinary excretion of aluminum during welding. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1985 Feb;11(1):39–43. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren B., Lundberg I., Lidums V. Aluminium in the blood and urine of industrially exposed workers. Br J Ind Med. 1983 Aug;40(3):301–304. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.3.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills M. R., Savory J. Aluminium poisoning: dialysis encephalopathy, osteomalacia, and anaemia. Lancet. 1983 Jul 2;2(8340):29–34. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xamoterol in severe heart failure. The Xamoterol in Severe Heart Failure Study Group. Lancet. 1990 Jul 7;336(8706):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


