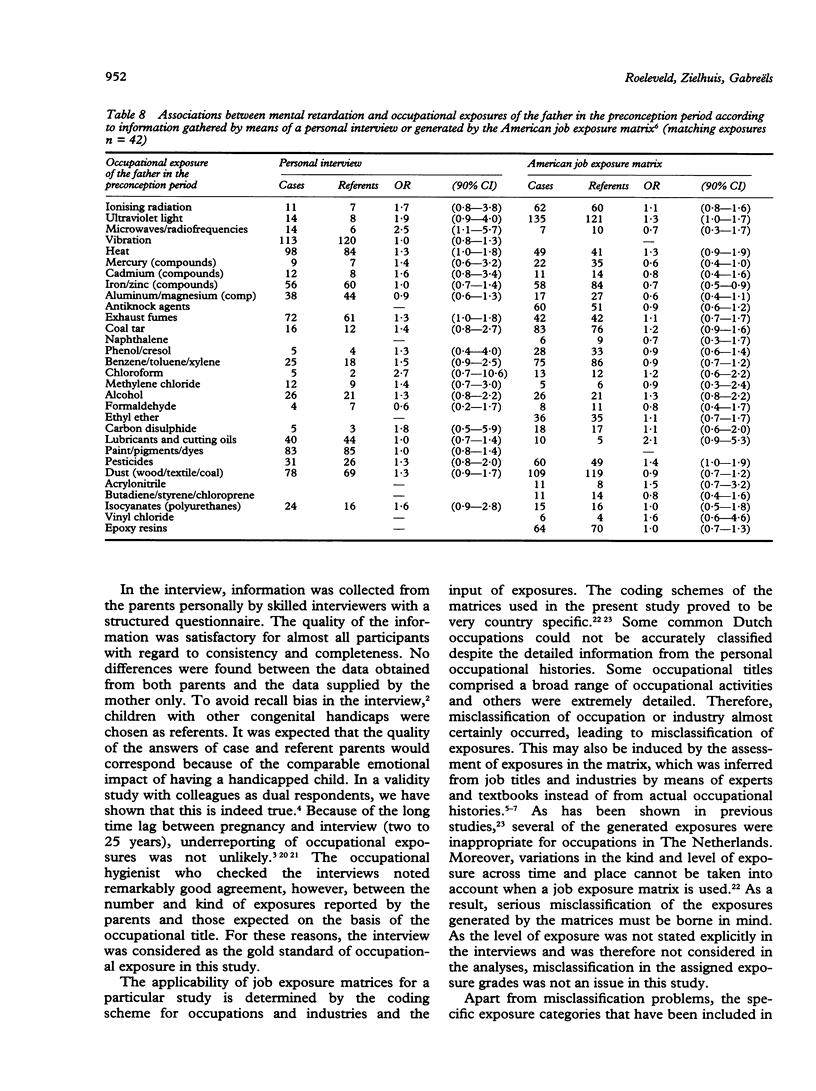
Abstract
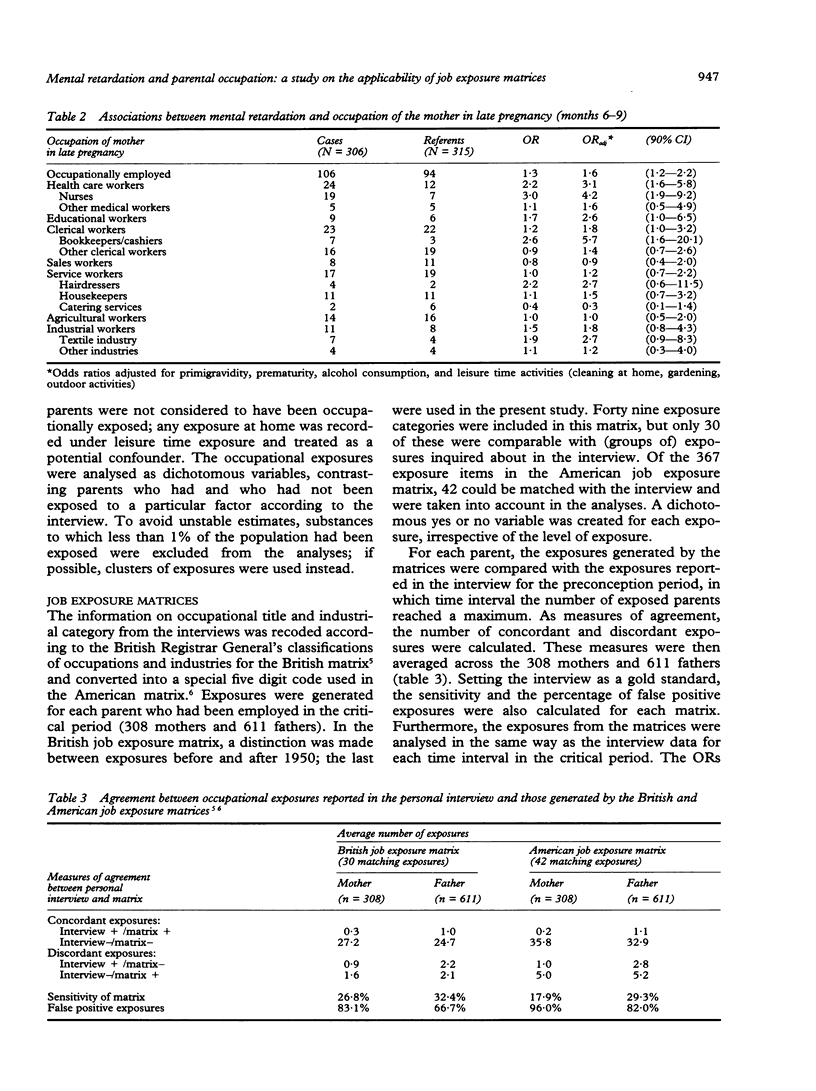
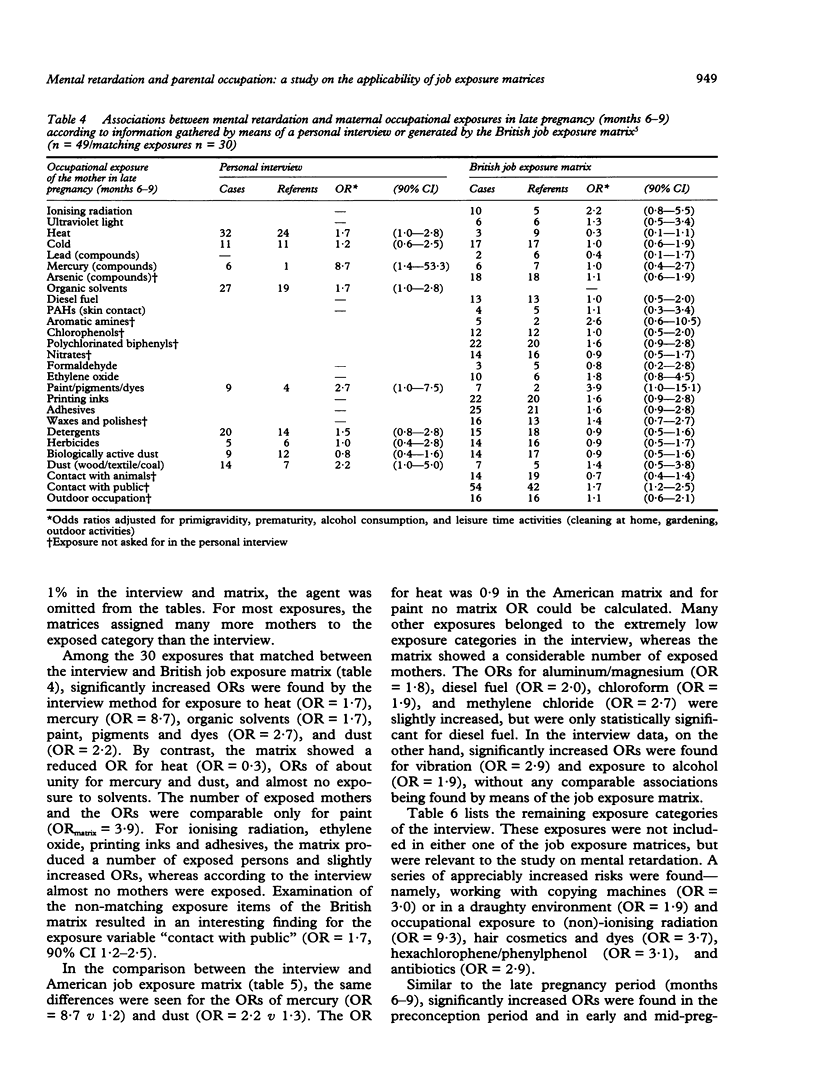
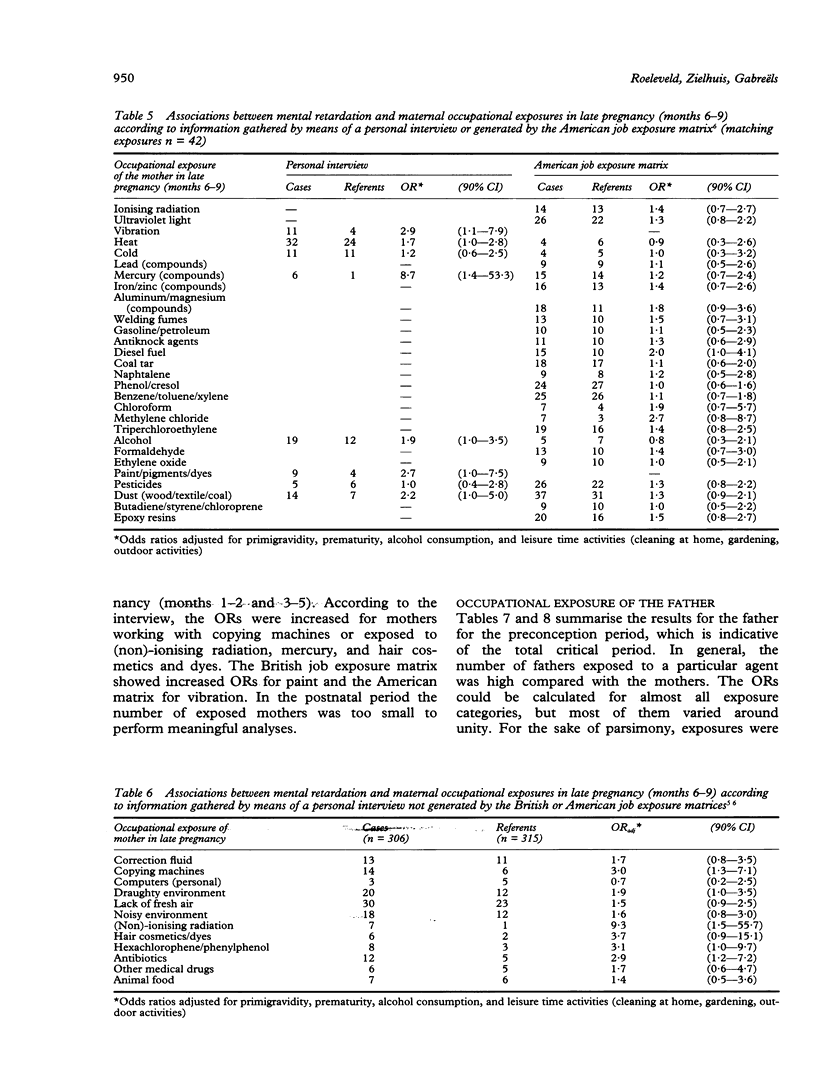
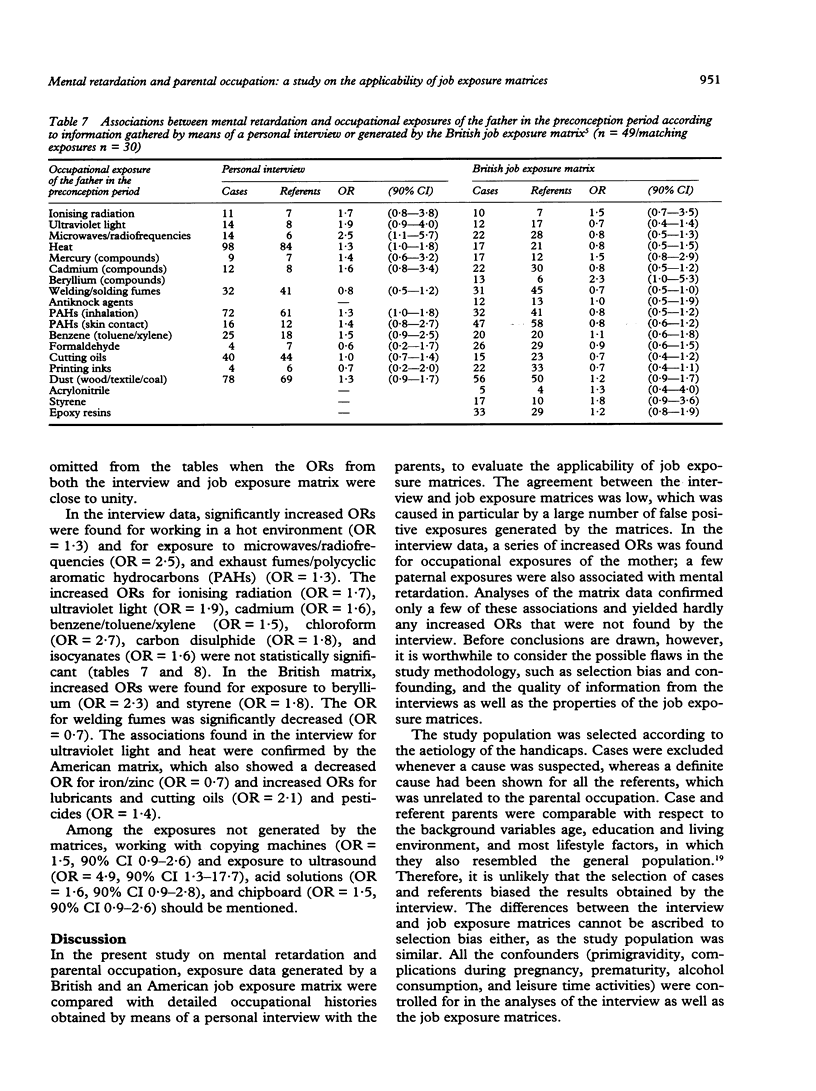
In a case-referent study on mental retardation and parental occupation, the applicability of job exposure matrices for the identification of risk factors was evaluated. The parents of 306 mentally retarded children (cases) and 322 referents were interviewed about their occupational activities in the pregnancy period. Detailed occupational histories were obtained that were compared with exposures generated by two different job exposure matrices. The agreement between interview and matrices was low: the sensitivity ranged from 17.9% to 32.4% and the percentages of false positive exposures from 66.7% to 96.0%. By means of the interview, significantly increased odds ratios (ORs) were found for exposure of the mother in late pregnancy to radiation (OR = 9.3), mercury (OR = 8.7), organic solvents (OR = 1.7), hair cosmetics and dyes (OR = 3.7), paint (OR = 2.7), hexachlorophene/phenylphenol (OR = 3.1), antibiotics (OR = 2.9), and dust (OR = 2.2) and for working with copying machines (OR = 3.0) or in occupations with poor climatological circumstances and permanent contact with people. The last was confirmed by the British matrix (OR = 1.7). Otherwise, most of the mentioned associations were missed by the job exposure matrices. Therefore, these matrices were not considered to be applicable in this particular study, nor in most other reproductive epidemiological studies in view of their general properties and limitations.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumgarten M., Siemiatycki J., Gibbs G. W. Validity of work histories obtained by interview for epidemiologic purposes. Am J Epidemiol. 1983 Oct;118(4):583–591. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beattie A. D., Moore M. R., Goldberg, Finlayson M. J., Graham J. F., Mackie E. M., Main J. C., McLaren D. A., Murdoch K. M., Steward G. T. Role of chronic low-level lead exposure in the aetiology of mental retardation. Lancet. 1975 Mar 15;1(7907):589–592. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91879-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beattie A. D., Moore M. R., Goldberg, Finlayson M. J., Graham J. F., Mackie E. M., Main J. C., McLaren D. A., Murdoch K. M., Steward G. T. Role of chronic low-level lead exposure in the aetiology of mental retardation. Lancet. 1975 Mar 15;1(7907):589–592. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91879-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson T. W., Nordberg G. F., Sager P. R. Reproductive and developmental toxicity of metals. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1985 Jun;11(3 Spec No):145–154. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. S. Recall bias in epidemiologic studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 1990;43(1):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(90)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada M. Congenital Minamata disease: intrauterine methylmercury poisoning. Teratology. 1978 Oct;18(2):285–288. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420180216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heederik D., Pouwels H., Kromhout H., Kromhout D. Chronic non-specific lung disease and occupational exposures estimated by means of a job exposure matrix: the Zutphen Study. Int J Epidemiol. 1989 Jun;18(2):382–389. doi: 10.1093/ije/18.2.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds M. W., Kolonel L. N., Lee J. Application of a job-exposure matrix to a case-control study of lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 Aug;75(2):193–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoar S. K., Morrison A. S., Cole P., Silverman D. T. An occupation and exposure linkage system for the study of occupational carcinogenesis. J Occup Med. 1980 Nov;22(11):722–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoar S. Job exposure matrix methodology. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1983;21(1-2):9–26. doi: 10.3109/15563658308990408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalter H., Warkany J. Medical progress. Congenital malformations: etiologic factors and their role in prevention (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 24;308(8):424–431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302243080804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalter H., Warkany J. Medical progress. Congenital malformations: etiologic factors and their role in prevention (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 24;308(8):424–431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302243080804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskela R. S., Kolari P. J., Järvinen E., Korhonen H. Completeness of occupational history and occurrences of work-related diseases. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1984 Dec;10(6 Spec No):455–459. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mole R. H. Consequences of pre-natal radiation exposure for post-natal development. A review. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1982 Jul;42(1):1–12. doi: 10.1080/09553008214550861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otake M., Schull W. J. In utero exposure to A-bomb radiation and mental retardation; a reassessment. Br J Radiol. 1984 May;57(677):409–414. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-57-677-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannett B., Coggon D., Acheson E. D. A job-exposure matrix for use in population based studies in England and Wales. Br J Ind Med. 1985 Nov;42(11):777–783. doi: 10.1136/oem.42.11.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pershagen G., Axelson O. A validation of questionnaire information on occupational exposure and smoking. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1982 Mar;8(1):24–28. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeleveld N., Kiemeney L., Schattenberg G., Peer P. Information bias in a case-referent study on mental retardation and parental occupation: colleagues as dual respondents. Epidemiology. 1990 Jul;1(4):292–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeleveld N., Zielhuis G. A., Gabreëls F. Occupational exposure and defects of the central nervous system in offspring: review. Br J Ind Med. 1990 Sep;47(9):580–588. doi: 10.1136/oem.47.9.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeleveld N., Zielhuis G. A., Gabreëls F. Occupational exposure and defects of the central nervous system in offspring: review. Br J Ind Med. 1990 Sep;47(9):580–588. doi: 10.1136/oem.47.9.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


